Spring学习(三)AOP
Spring学习(三)AOP
在了解AOP之前首先我们了解一下动态代理
代理设计模式的原理:使用一个代理将对象包装起来,然后用该代理对象取代原始对象。任何对原始对象的调用都要通过代理。代理对象决定是否以及何时将方法调用转到原始对象上。
动态代理小案例 房屋中介帮房东将房屋出租出去
//实现房屋出租的接口
public interface Rent {
//房屋出租 以及房东设置的一些条件
public void renting();
}//房东 将房屋租出去
public class Landlord implements Rent {
public void renting() {
System.out.println("房屋出租 一个月2000");
}
}//代理角色 房屋中介 代理房东将房屋租出去
public class ProxySubject implements InvocationHandler {
//写成Object类 则可以变成通用代理
private Object target;
public void setRent(Object target) {
this.target = target;
}
//生成代理类ProxySubject,第二个参数,获取要代理的抽象角色(全部是通过反射实现)
public Object getProxy(){
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(this.getClass().getClassLoader(),
target.getClass().getInterfaces(),this);
}
// proxy : 代理类 method : 代理类的调用处理程序的方法对象.
// 处理代理实例上的方法调用并返回结果
public Object invoke(Object o, Method method, Object[] objects) throws Throwable {
Object result = method.invoke(target, objects);
return result;
}
}1、AOP的简介
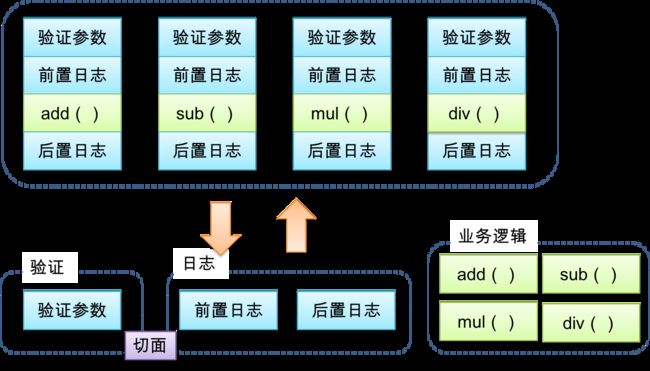
- AOP(Aspect-Oriented Programming, 面向切面编程): 是一种新的方法论, 是对传统 OOP(Object-Oriented Programming, 面向对象编程) 的补充.
- AOP 的主要编程对象是切面(aspect), 而切面模块化横切关注点.
- 在应用 AOP 编程时, 仍然需要定义公共功能, 但可以明确的定义这个功能在哪里, 以什么方式应用, 并且不必修改受影响的类. 这样一来横切关注点就被模块化到特殊的对象(切面)里.
- AOP 的好处:
- 每个事物逻辑位于一个位置, 代码不分散, 便于维护和升级
- 业务模块更简洁, 只包含核心业务代码
2、AOP术语
-
切面(Aspect): 横切关注点(跨越应用程序多个模块的功能)被模块化的特殊对象
-
通知(Advice): 切面必须要完成的工作
-
目标(Target): 被通知的对象
-
代理(Proxy): 向目标对象应用通知之后创建的对象
-
连接点(Joinpoint):横切关注点在程序代码中的具体体现,对应程序执行的某个特定位置。例如:类某个方法调用前、调用后、方法捕获到异常后等
-
切点(pointcut):定位连接点的方式。每个类的方法中都包含多个连接点,所以连接点是类中客观存在的事物。如果把连接点看作数据库中的记录,那么切入点就是查询条件——AOP可以通过切入点定位到特定的连接点。切点通过org.springframework.aop.Pointcut 接口进行描述,它使用类和方法作为连接点的查询条件
3、通知方法
-
@Before: 前置通知, 在方法执行之前执行
-
@After: 后置通知 是在连接点完成之后执行的,即连接点返回结果或者抛出异常的时候
-
@AfterRunning返回通知, 在方法返回结果之后执行
-
@AfterThrowing:异常通知, 在方法抛出异常之后
-
@Around: 环绕通知, 围绕着方法执行
AOP实现案例 我们想要在用户调用方法时进行一些提醒操作 不改变业务核心代码
首先导入依赖的jar包
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectjgroupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaverartifactId>
<version>1.9.4version>
dependency>public interface Calculator {
public int add(int i,int j);
public int sub(int i,int j);
public int mul(int i,int j);
public int div(int i,int j);
}@Service
public class MyMathCalculator implements Calculator {
@Override
public int add(int i, int j) {
return i+j;
}
@Override
public int sub(int i, int j) {
return i-j;
}
@Override
public int mul(int i, int j) {
return i*j;
}
@Override
public int div(int i, int j) {
return i/j;
}
}@Aspect
@Component
public class LogUtils {
@Before("execution(public int com.rg.impl.MyMathCalculator.*(int,int))")
public static void LogBefore(){
System.out.println("快开始呢");
}
@After("execution(public int com.rg.impl.MyMathCalculator.*(int,int))")
public static void LogAfter(){
System.out.println("结束呢");
}
@AfterReturning("execution(public int com.rg.impl.MyMathCalculator.*(int,int))")
public static void LogReturning(){
System.out.println("结果是");
}
@AfterThrowing("execution(public int com.rg.impl.MyMathCalculator.*(int,int))")
public static void LogThrowing(){
System.out.println("哈哈哈错了");
}
}Spring配置
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.rg">context:component-scan>
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>
beans>测试
public class AOPTest {
ApplicationContext aop = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
@Test
public void test(){
Calculator bean = aop.getBean(Calculator.class);
int add = bean.add(1, 2);
System.out.println(add);
}
}切入点表达式的作用
通过表达式的方式定位一个或多个具体的连接点
切入点表达式的语法格式
execution([权限修饰符] [返回值类型] [简单类名/全类名] [方法名]([参数列表]))
使用XML配置
public class LogUtils2 {
public static void LogBefore(){
System.out.println("快开始呢");
}
public static void LogAfter(){
System.out.println("结束呢");
}
public static void LogReturning(){
System.out.println("结果是");
}
public static void LogThrowing(){
System.out.println("哈哈哈错了");
}
}
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.rg">context:component-scan>
<bean id="logUtils2" class="com.rg.util.LogUtils2"/>
<aop:config>
<aop:aspect ref="logUtils2">
<aop:pointcut id="LogPonitcut" expression="execution(* com.rg.impl.MyMathCalculator.*(..))"/>
<aop:before pointcut-ref="LogPonitcut" method="LogBefore"/>
<aop:after pointcut-ref="LogPonitcut" method="LogAfter"/>
<aop:after-returning pointcut-ref="LogPonitcut" method="LogReturning"/>
<aop:after-throwing pointcut-ref="LogPonitcut" method="LogThrowing"/>
aop:aspect>
aop:config>
beans>测试
@Test
public void test01(){
Calculator bean = aop.getBean(Calculator.class);
int sub = bean.sub(10, 2);
System.out.println(sub);
}- 切入点使用aop:pointcut元素声明。
- 切入点必须定义在aop:aspect元素下,或者直接定义在aop:config元素下。
- 定义在aop:aspect元素下:只对当前切面有效
- 定义在aop:config元素下:对所有切面都有效
- 基于XML的AOP配置不允许在切入点表达式中用名称引用其他切入点
若想了解更多的Spring建议查看 Spring官网
Spring下载地址
推荐学习Spring的视频 B站 遇见狂神说 或者 尚硅谷
谢谢大家的阅读! 若上面有写错的 欢迎纠正哦!