【图像识别】MNIST的分类问题(CNN)
本模型构建了3个卷积层和3个池化层,1个全连接层和1个输出层;
采用RMSProp算法的优化器,学习率为0.001,衰减率为0.9。
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
# ---1. 加载数据 ---
# 加载数据
mnist=input_data.read_data_sets("MNIST_data/", one_hot=True)
trX, trY, teX, teY = mnist.train.images, mnist.train.labels, mnist.test.images, mnist.test.labels
trX = trX.reshape(-1, 28, 28, 1)
teX = teX.reshape(-1, 28, 28, 1)
X = tf.placeholder("float", [None, 28, 28, 1])
Y = tf.placeholder("float", [None, 10])
# ---2. 构建模型 ---
# 初始化权重与定义网络结构,构建3个卷积层和3个池化层,1个全连接层和1个输出层
def init_weights(shape):
return tf.Variable(tf.random_normal(shape, stddev=0.01))
# 三层卷积层
w = init_weights([3, 3, 1, 32]) # 卷积核大小为3*3,输入维度为1,输出维度为32(下同)
w2 = init_weights([3, 3, 32, 64])
w3 = init_weights([3, 3, 64, 128])
# 全连接层
w4 = init_weights([128 * 4 * 4, 625]) # 输入维度为128*4*4,输出维度为625
# 输出层
w_o = init_weights([625, 10]) # 输入维度为625,输出维度为10
# 神经网络模型的构建函数
# X: 输入数据 w: 每一层的权重 p_keep_conv, p_keep_hidden: dropout要保留的神经元比例
def model(X, w, w2, w3, w4, w_o, p_keep_conv, p_keep_hidden):
# 第一层卷积层及池化层,最后dropout一些神经元
# relu(): 这个函数的作用是计算激活函数 relu,即 max(features, 0)
# conv2d(X: 输入数据, w: 每一层的权重, strides: 步长<一般是[1, stride,stride, 1]>, padding: 填充类型)
l1a = tf.nn.relu(tf.nn.conv2d(X, w, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME'))
# max_pool 采用最大池化,ksize:池化窗口的大小<一般是[1, height, width, 1]>
l1 = tf.nn.max_pool(l1a, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1],strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME')
# dropout:按照传入的p_keep_conv(保留比例) 对神经元做处理
l1 = tf.nn.dropout(l1, p_keep_conv)
# 第二组卷积层及池化层,最后dropout 一些神经元
l2a = tf.nn.relu(tf.nn.conv2d(l1, w2, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME'))
l2 = tf.nn.max_pool(l2a, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME')
l2 = tf.nn.dropout(l2, p_keep_conv)
# 第三组卷积层及池化层,最后dropout 一些神经元
l3a = tf.nn.relu(tf.nn.conv2d(l2, w3, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME'))
l3 = tf.nn.max_pool(l3a, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME')
l3 = tf.reshape(l3, [-1, w4.get_shape().as_list()[0]]) # reshape to (?, 2048)
l3 = tf.nn.dropout(l3, p_keep_conv)
# 全连接层
l4 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(l3,w4))
l4 = tf.nn.dropout(l4, p_keep_hidden)
# 输出层
pyx = tf.matmul(l4, w_o)
# 返回预测值
return pyx
p_keep_conv = tf.placeholder("float")
p_keep_hidden = tf.placeholder("float")
py_x = model(X, w, w2, w3, w4, w_o, p_keep_conv, p_keep_hidden) #得到预测值
# 定义损失函数,比较预测值和实际值,并做均值处理
cost = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=py_x, labels=Y))
# 采用RMSProp算法的优化器,学习率为0.001,衰减率为0.9
train_op = tf.train.RMSPropOptimizer(0.001, 0.9).minimize(cost)
predict_op = tf.argmax(py_x, 1)
# ---3. 训练模型 ---
# 定义训练时和评估时的批次大小
batch_size = 128
test_size = 256
# 开始训练
with tf.Session() as sess:
tf.global_variables_initializer().run()
for i in range(100):
training_batch = zip(range(0, len(trX), batch_size),
range(batch_size, len(trX)+1, batch_size))
for start, end in training_batch:
sess.run(train_op, feed_dict={X: trX[start:end], Y: trY[start:end],
p_keep_conv: 0.8, p_keep_hidden: 0.5})
test_indices = np.arange(len(teX)) # Get A Test Batch
np.random.shuffle(test_indices)
test_indices = test_indices[0:test_size]
print(i, np.mean(np.argmax(teY[test_indices], axis=1) ==
sess.run(predict_op, feed_dict={X: teX[test_indices],
p_keep_conv: 1.0,
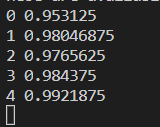
p_keep_hidden: 1.0})))运行结果:
(运行速度有点慢,所以到4我就终止了,但还是可以看出CNN训练后的准确率比普通神经网络高很多)
(附:图像识别——MNIST的分类问题(普通神经网络))