Java进阶——Java中的克隆
对象的创建
在Android中,对象的创建分为两种形式,一种是使用new操作符创建对象,另一种是调用clone方法复制对象
- 使用new操作符创建对象:对new的对象分配内存,调用其构造方法,并将创建好的对象引用发布到外部
- 调用clone方法复制对象:对clone的对象分配内存,对新分配的内存域使用原对象进行填充
克隆的使用
在对象中可以使用clone(),必须实现Cloneable接口,复写clone方法,外部才可以调用clone()
public class Person implements Cloneable{
public String name;
public int age;
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return super.clone();
}
}拷贝对象和拷贝引用
一、拷贝对象
Person p1 = new Person();
Person p2 = p1;
Log.e("TAG", p1.toString());
Log.e("TAG", p2.toString());通过输出的结果看出,两个对象的地址是相同的,所以这两个对象是同一个对象,这种现象叫做拷贝对象
com.hensen.fashionsource.Person@a6ea782
com.hensen.fashionsource.Person@a6ea782二、拷贝引用
try {
Person p1 = new Person();
Person p2 = (Person) p1.clone();
Log.e("TAG", p1.toString());
Log.e("TAG", p2.toString());
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}通过输出的结果看出,两个对象的地址不相同,所以这两个对象是不同对象,这种现象叫做拷贝引用
com.hensen.fashionsource.Person@38b31e93
com.hensen.fashionsource.Person@3046fed0浅拷贝和深拷贝
在clone()的过程中,clone会遇到浅拷贝和深拷贝的问题。本质上clone()属于浅拷贝,但是也可以将clone()转换成深拷贝来处理。下面是浅拷贝和深拷贝的概念介绍:
- 浅拷贝:将对象中的所有字段复制到新的对象中。其中,基本数据类型的值被复制到对象中后,在对象中的修改不会影响到源对象对应的值。而引用类型的值被复制到对象中还是引用类型,在对象中对引用类型的字段做修改会影响到源对象本身。简单的说,拷贝基本数据类型的值和拷贝引用类型的引用
- 深拷贝:将对象中的所有字段复制到新的对象中。不过,无论是对象的基本数据类型,还是引用类型,都会被重新创建并赋值,对于新对象的修改,不会影响到源对象本身。简单的说,拷贝出完全相同的对象,对新对象的修改和源对象没有任何影响
一、浅拷贝
clone()属于浅拷贝,那么怎么去验证它呢?下面我们通过人->手->手指的嵌套关系来验证
public class Person implements Cloneable{
public String name;
public int age;
public Hand hand;
public Person(String name, Hand hand) {
this.name = name;
this.hand = hand;
}
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return super.clone();
}
}
public class Hand {
public Finger finger;
public String name;
public Hand(Finger finger, String name) {
this.finger = finger;
this.name = name;
}
}
public class Finger {
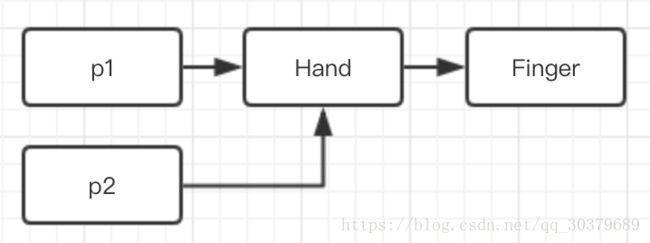
}当前数据结构如图所示
我们通过比较手和手指的引用类型地址是否相同,可以看出clone()的本质是浅拷贝
try {
Person p1 = new Person("张三", new Hand(new Finger(), "A"));
Person p2 = (Person) p1.clone();
Log.e("TAG", "" + p1);
Log.e("TAG", "" + p2);
Log.e("TAG", "" + p1.hand);
Log.e("TAG", "" + p2.hand);
Log.e("TAG", "" + p1.hand.finger);
Log.e("TAG", "" + p2.hand.finger);
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
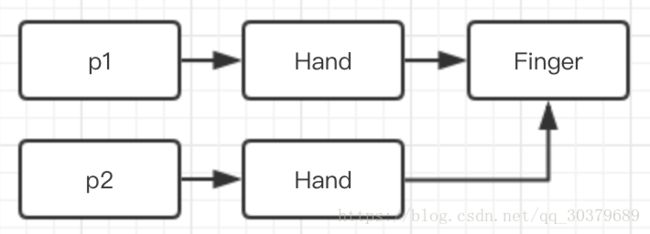
}输出结果可以看出,clone()引用类型的地址是相同的
com.hensen.fashionsource.Person@330bedb4
com.hensen.fashionsource.Person@2503dbd3
com.hensen.fashionsource.Hand@38b31e93
com.hensen.fashionsource.Hand@38b31e93
com.hensen.fashionsource.Finger@3046fed0
com.hensen.fashionsource.Finger@3046fed0当前数据结构如图所示
三、深拷贝
1、如果我们想对Person的Hand对象进行深拷贝该怎么做呢?可以让Person的Hand对象具有拷贝功能,对Hand进行改造
public class Person implements Cloneable{
public String name;
public int age;
public Hand hand;
public Person(String name, Hand hand) {
this.name = name;
this.hand = hand;
}
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
Person newPer = (Person) super.clone();
newPer.hand = (Hand) hand.clone();
return newPer;
}
}
public class Hand implements Cloneable{
public Finger finger;
public String name;
public Hand(Finger finger, String name) {
this.finger = finger;
this.name = name;
}
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return super.clone();
}
}
public class Finger {
}下面我们继续输出拷贝前p1的地址和拷贝后p2的地址,我们可以发现Hand已经完成了深拷贝
com.hensen.fashionsource.Person@330bedb4
com.hensen.fashionsource.Person@2503dbd3
com.hensen.fashionsource.Hand@38b31e93
com.hensen.fashionsource.Hand@3046fed0
com.hensen.fashionsource.Finger@14be0ec9
com.hensen.fashionsource.Finger@14be0ec9当前数据结构如图所示
2、如果我们想对Person的Hand和Finger对象进行深拷贝该怎么做呢?同样重复上面的步骤,对Finder进行改造
public class Person implements Cloneable{
public String name;
public int age;
public Hand hand;
public Person(String name, Hand hand) {
this.name = name;
this.hand = hand;
}
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
Person newPer = (Person) super.clone();
newPer.hand = (Hand) hand.clone();
return newPer;
}
}
public class Hand implements Cloneable{
public Finger finger;
public String name;
public Hand(Finger finger, String name) {
this.finger = finger;
this.name = name;
}
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
Hand newHand = (Hand) super.clone();
newHand.finger = (Finger) finger.clone();
return newHand;
}
}
public class Finger implements Cloneable{
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return super.clone();
}
}下面我们继续输出拷贝前p1的地址和拷贝后p2的地址,我们可以发现Finger已经完成了深拷贝
com.hensen.fashionsource.Person@330bedb4
com.hensen.fashionsource.Person@2503dbd3
com.hensen.fashionsource.Hand@38b31e93
com.hensen.fashionsource.Hand@3046fed0
com.hensen.fashionsource.Finger@14be0ec9
com.hensen.fashionsource.Finger@35e3b9ce当前数据结构如图所示
三、String类型的特殊性
由于String并不是基本数据类型,且String没有实现Cloneable接口,在深拷贝的时候并没有进行新地址的拷贝,仅仅只是拷贝了引用,也就是说违反了深拷贝。按照上面的理论,在深拷贝的时候,只是拷贝引用,那么如果对String类型的值重新赋值,将会影响到源对象的值。事实是不是如此呢?答案是否定,对String类型的深拷贝将不会影响到源对象的值
原因是String类型被final修饰,在内存中是不可以被改变的对象,每次对新的字符串赋值都会分配一块新内存,并指向它。所以在String类型进行深拷贝的时候是属于特殊情况,但String类型在浅拷贝的时候还是属于拷贝引用,下面还是通过刚才的例子进行验证
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
Person p1 = new Person("张三", new Hand(new Finger(), "AAA"));
Person p2 = (Person) p1.clone();
p2.name = "李四";
p2.hand.name = "BBB";
System.out.println(p1.name.toString());
System.out.println(p2.name.toString());
System.out.println(p1.hand.name.toString());
System.out.println(p2.hand.name.toString());
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}1、当Person的Hand对象为浅拷贝时,即在clone()中没有做任何处理
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return super.clone();
}其输出的结果为
张三
李四
BBB
BBB分析:
- 由于Person本身实现了Clonable接口,对于
p1.clone()属于深拷贝,所以Person的name字段是会重新分配内存 - 由于Person的Hand对象并没有在Person的clone()中进行拷贝处理,所以Person的Hand对象的name字段只是拷贝引用
2、当Person的Hand对象为深拷贝时,即在clone()中对Hand对象进行拷贝
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
Person newPer = (Person) super.clone();
newPer.hand = (Hand) hand.clone();
return newPer;
}其输出的结果为
张三
李四
AAA
BBB分析:
- 由于Person本身实现了Clonable接口,对于
p1.clone()属于深拷贝,所以Person的name字段是会重新分配内存 - 由于Person的Hand对象在Person的clone()中进行拷贝处理,所以Person的Hand对象的name字段是会重新分配内存
利用序列化实现深拷贝
在内存中可以直接通过字节流的拷贝完成深拷贝,其具体步骤如下
- 将源对象写入到字节流中
- 读取源对象的字节流
- 生成新的对象
public class CloneUtils {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public static T clone(T obj){
T cloneObj = null;
try {
//写入字节流
ByteArrayOutputStream out = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream obs = new ObjectOutputStream(out);
obs.writeObject(obj);
obs.close();
//读取字节流
ByteArrayInputStream in = new ByteArrayInputStream(out.toByteArray());
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(in);
//生成新对象
cloneObj = (T) ois.readObject();
ois.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return cloneObj;
}
} 总结
- clone的使用必须实现Cloneable的接口
- clone属于浅拷贝,也可以通过处理clone()实现深拷贝
- clone对String类型的深拷贝具有特殊性