android 蓝牙4.0(BLE)开发
最近刚好项目需要手机与蓝牙模块通信,基于蓝牙4.0,网上资料较少也有些小坑,故作一下总结。
关键术语和概念
- 蓝牙有传统蓝牙(3.0以下)和低功耗蓝牙(BLE,又称蓝牙4.0)之分,而蓝牙4.0开发需要android4.3版本(API 18)及以上才支持BLE API。相比传统的蓝牙,BLE更显著的特点是低功耗。这一优点使android App可以与具有低功耗要求的BLE设备通信,如近距离传感器、心脏速率监视器、健身设备等。
- BLE 全称 Bluetooth Low Energy
- Generic Attribute Profile(GATT)—GATT配置文件是一个通用规范,用于在BLE链路上发送和接收被称为“属性”的数据块。目前所有的BLE应用都基于GATT。 蓝牙SIG规定了许多低功耗设备的配置文件。配置文件是设备如何在特定的应用程序中工作的规格说明。注意一个设备可以实现多个配置文件。例如,一个设备可能包括心率监测仪和电量检测。
- Attribute Protocol(ATT)—GATT在ATT协议基础上建立,也被称为GATT/ATT。ATT对在BLE设备上运行进行了优化,为此,它使用了尽可能少的字节。每个属性通过一个唯一的的统一标识符(UUID)来标识,每个String类型UUID使用128 bit标准格式。属性通过ATT被格式化为characteristics和services。
- Characteristic 一个characteristic包括一个单一变量和0-n个用来描述characteristic变量的descriptor,characteristic可以被认为是一个类型,类似于类。
- Descriptor Descriptor用来描述characteristic变量的属性。例如,一个descriptor可以规定一个可读的描述,或者一个characteristic变量可接受的范围,或者一个characteristic变量特定的测量单位。
- Service service是characteristic的集合。例如,你可能有一个叫“Heart Rate Monitor(心率监测仪)”的service,它包括了很多characteristics,如“heart rate measurement(心率测量)”等。你可以在bluetooth.org 找到一个目前支持的基于GATT的配置文件和服务列表。
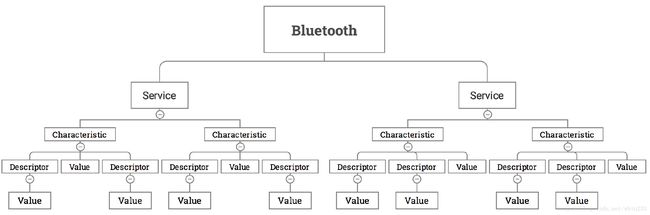
蓝牙4.0的结构
简单的说,就是BLE是基于GATT实现的,BLE分为三个部分Service、Characteristic、Descriptor,每个部分都拥有不同的 UUID来标识。一个BLE设备可以拥有多个Service,一个Service可以包含多个Characteristic, 一个Characteristic包含一个Value和多个Descriptor,一个Descriptor包含一个Value。 通信数据一般存储在Characteristic内,目前一个Characteristic中存储的数据最大为20 byte。 与Characteristic相关的权限字段主要有READ、WRITE、WRITE_NO_RESPONSE、NOTIFY。 Characteristic具有的权限属性可以有一个或者多个。
开发流程
1. 获取相关权限
在AndroidManifest.xml声明相关权限
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.BLUETOOTH" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.BLUETOOTH_ADMIN" />
<uses-permission
android:name="android.permission.WRITE_SETTINGS" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION" />2. 获取BluetoothManager和BluetoothAdapter
BluetoothManager manager = (BluetoothManager) getSystemService(Context.BLUETOOTH_SERVICE);
BluetoothAdapter bleAdapter = manager.getAdapter();
// 也可以通过以下方式获取BluetoothAdapter
BluetoothAdapter bleAdapter = BluetoothAdapter.getDefaultAdapter();3. 检测蓝牙是否打开或可用
public boolean check() {
return (null != bleAdapter && bleAdapter.isEnabled() && !bleAdapter.isDiscovering());
}4. 扫描蓝牙并实现回调接口LeScanCallback
// 开始扫描
public void startScan(long scanDelay) {
if(!check()) return; // 检测蓝牙
BleScanCallback leScanCallback = new BleScanCallback(); // 回调接口
if (bleAdapter.startLeScan(leScanCallback)) {
timer.schedule(new TimerTask() { // 扫描一定时间"scanDelay"就停止。
@Override
public void run() {
stopScan();
}
}, scanDelay);
}
}
// 实现扫描回调接口
private class BleScanCallback implements BluetoothAdapter.LeScanCallback {
// 扫描到新设备时,会回调该接口。可以将新设备显示在ui中,看具体需求
@Override
public void onLeScan(BluetoothDevice device, int rssi, byte[] scanRecord) {
Log.e(TAG, "found device name : " + device.getName() + " address : " + device.getAddress());
}
}有一个地方可以注意下,在API 21及以上,不推荐使用BluetoothAdapter.startLeScan和stopLeScan。而是新引入了BluetoothLeScanner类和ScanCallback回调接口。由于需要兼容API 19,所以这里不作过多的阐述,有需要可以查看官方文档了解。
5. 连接蓝牙设备并实现连接回调接口
// 连接蓝牙设备,device为之前扫描得到的
public void connect(BluetoothDevice device) {
if(!check()) return; // 检测蓝牙
if (null != bleAdapter) {
bleAdapter.stopLeScan(leScanCallback);
}
if (bleGatt.connect()) { // 已经连接了其他设备
// 如果是先前连接的设备,则不做处理
if (TextUtils.equals(device.getAddress(), bleGatt.getDevice().getAddress())) {
return;
} else {
disconnect(); // 否则断开连接
}
}
// 连接设备,第二个参数为是否自动连接,第三个为回调函数
bleGatt = device.connectGatt(context, false, bleGattCallback);
}
// 实现连接回调接口[关键]
private class BleGattCallback extends BluetoothGattCallback {
// 连接状态改变(连接成功或失败)时回调该接口
@Override
public void onConnectionStateChange(BluetoothGatt gatt, int status, int newState) {
if (newState == BluetoothGatt.STATE_CONNECTED) { // 连接成功
Intent intent = new Intent(ActionBle.CONNECTED);
context.sendBroadcast(intent); // 这里是通过广播通知连接成功,依各自的需求决定
gatt.discoverServices(); // 则去搜索设备的服务(Service)和服务对应Characteristic
} else { // 连接失败
Intent intent = new Intent(ActionBle.CONNECT_FAIL);
context.sendBroadcast(intent);
}
}
// 发现设备的服务(Service)回调,需要在这里处理订阅事件。
@Override
public void onServicesDiscovered(BluetoothGatt gatt, int status) {
if (status == BluetoothGatt.GATT_SUCCESS) {
services = gatt.getServices();
characteristics = new ArrayList<>();
descriptors = new ArrayList<>();
for (BluetoothGattService service : services) {
Log.e(TAG, "-- service uuid : " + service.getUuid().toString() + " --");
for (BluetoothGattCharacteristic characteristic : service.getCharacteristics()) {
Log.e(TAG, "---- characteristic uuid : " + characteristic.getUuid() + " ----");
characteristics.add(characteristic);
if (characteristic.getUuid().toString().equals(Command.READ_UUID)) {
// 订阅信息,否则接收不到数据「关键!」
setCharacteristicNotification(characteristic, true);
}
for (BluetoothGattDescriptor descriptor : characteristic.getDescriptors()) {
Log.e(TAG, "-------- descriptor uuid : " + characteristic.getUuid() + " --------");
descriptors.add(descriptor);
}
}
}
Intent intent = new Intent(ActionBle.DISCOVER_SERVICES_SUCCESS);
context.sendBroadcast(intent);
} else {
Intent intent = new Intent(ActionBle.DISCOVER_SERVICES_FAIL);
context.sendBroadcast(intent);
}
}
// 发送消息结果回调
@Override
public void onCharacteristicWrite(BluetoothGatt gatt,
BluetoothGattCharacteristic characteristic,
int status) {
Intent intent;
if (BluetoothGatt.GATT_SUCCESS == status) { // 发送成功
intent = new Intent(ActionBle.WRITE_DATA_SUCCESS);
} else { // 发送失败
intent = new Intent(ActionBle.WRITE_DATA_FAIL);
}
context.sendBroadcast(intent);
}
// 当订阅的Characteristic接收到消息时回调
@Override
public void onCharacteristicChanged(BluetoothGatt gatt,
BluetoothGattCharacteristic characteristic) {
// 数据为 characteristic.getValue())
Log.e(TAG, "onCharacteristicChanged: " + Arrays.toString(characteristic.getValue()));
}
}
// 订阅特征集!「关键,才能接收到数据」
// public static final String DESCRIPTORS_UUID = "00002902-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb";
// 这个uuid一般是固定的,不一样视情况改变
private boolean setCharacteristicNotification(BluetoothGattCharacteristic characteristic, boolean enabled) {
if (bleGatt == null) {
return false;
}
BluetoothGattDescriptor localBluetoothGattDescriptor = characteristic.getDescriptor(UUID.fromString(DESCRIPTORS_UUID));
if (enabled) {
localBluetoothGattDescriptor.setValue(BluetoothGattDescriptor.ENABLE_NOTIFICATION_VALUE);
} else {
localBluetoothGattDescriptor.setValue(BluetoothGattDescriptor.DISABLE_NOTIFICATION_VALUE);
}
bleGatt.writeDescriptor(localBluetoothGattDescriptor);
return bleGatt.setCharacteristicNotification(characteristic, enabled);
}连接设备的回调函数很关键,有几个点需要注意:
1. 当设备连接状态改变(连接成功或失败)时,会回调onConnectionStateChange接口,需要在连接成功的时候调用gatt.discoverServices();去搜索设备的服务Service集合。
2. 当设备搜索服务状态(成功找到服务或失败)时,会回调onServicesDiscovered接口,这里面很关键,需要处理订阅相关特征Characteristic:
bleGatt.setCharacteristicNotification(characteristic, true);
这个需要依据蓝牙模块协议而定,只有在这里订阅了,才能接收到蓝牙模块发送过来的数据。
这里还有个大坑,具体看setCharacteristicNotification。
3. 订阅的特征Characteristic接收到消息,也就是蓝牙模块发送数据过来时,会回调onCharacteristicChanged接口,数据的处理就在该接口处理。
6. 向蓝牙模块发送数据
其实也很简单,根据协议往相关特征写入数据即可。
public boolean writeCharacteristic(String uuid, byte[] bytes) {
if (null == characteristics) {
return false;
}
Log.e(TAG, "writeCharacteristic to " + uuid + " : " + Arrays.toString(bytes));
if (null != bleGatt) {
// characteristics保存了蓝牙模块所有的特征Characteristic
for (BluetoothGattCharacteristic characteristic : characteristics) {
// 判断是否为协议约定的特征Characteristic
if (TextUtils.equals(uuid, characteristic.getUuid().toString())) {
// 找到特征,设置要写入的数据
characteristic.setValue(bytes);
// 写入数据,蓝牙模块就接收到啦
return bleGatt.writeCharacteristic(characteristic);
}
}
}
return false;
}注意这里会回调上面实现的BluetoothGattCallback.onCharacteristicWrite接口
这里我用的蓝牙模块约定发送和接收的特征uuid如下:
String READ_UUID = "6e400003-b5a3-f393-e0a9-e50e24dcca9e"; // 读
String WRITE_UUID = "6e400002-b5a3-f393-e0a9-e50e24dcca9e"; // 写具体蓝牙模块看具体的协议而定。
7. 断开连接
public void disconnect() {
if (null != bleGatt) {
bleGatt.disconnect();
}
Log.e(TAG, "disconnect");
}8. 数据的转换
与蓝牙模块的通信一般都是采用16进制,byte[]传输,因此需提供几个格式转换的方法。
// byte转十六进制字符串
public static String bytes2HexString(byte[] bytes) {
String ret = "";
for (byte item : bytes) {
String hex = Integer.toHexString(item & 0xFF);
if (hex.length() == 1) {
hex = '0' + hex;
}
ret += hex.toUpperCase(Locale.CHINA);
}
return ret;
}
// 将16进制的字符串转换为字节数组
public static byte[] getHexBytes(String message) {
int len = message.length() / 2;
char[] chars = message.toCharArray();
String[] hexStr = new String[len];
byte[] bytes = new byte[len];
for (int i = 0, j = 0; j < len; i += 2, j++) {
hexStr[j] = "" + chars[i] + chars[i + 1];
bytes[j] = (byte) Integer.parseInt(hexStr[j], 16);
}
return bytes;
}以上就是android 蓝牙4.0的基本操作啦,可以实现基本的通信啦,瑟瑟发抖。