Android 蓝牙连接
一、概述
蓝牙是一种无线技术标准,可实现固定设备、移动设备和楼宇个人域网之间的短距离数据交换。最多可以同时和7个其它蓝牙设备建立连接,进行通信。蓝牙可分为两大类:传统蓝牙(蓝牙3.0规范之前),低功耗蓝牙(蓝牙4.0规范之后)。
Android 从4.3版本(API Level 18)开始支持低功耗蓝牙Bluetooth Low Energy(BLE)通信。Android提供了相应的 API, 应用程序通过这些 API 可以实现 蓝牙设备扫描、配对、连接、传输数据等功能。
二、Android BLE API几个重要类
1、BluetoothAdapter
本地的蓝牙适配器。是所有蓝牙交互操作的入口点。通过这个类可以发现其他蓝牙设备,查询已配对的设备列表,使用一个已知的MAC地址来实例化一个BluetoothDevice,以及创建一个BluetoothServerSocket来为监听与其他设备的通信。
2、BluetoothDevice
远程蓝牙设备。使用这个类来请求一个与远程设备的BluetoothSocket连接,或者查询关于设备名称、地址、类和连接状态等设备信息。
3、BluetoothSocket
代表一个蓝牙socket的接口(和TCP Socket类似)。这是一个连接点,它允许一个应用与其他蓝牙设备通过InputStream和OutputStream交换数据。
4、BluetoothServerSocket
代表一个开放的服务器socket,它监听接受的请求(与TCP ServerSocket类似)。为了连接两台Android设备,一个设备必须使用这个类开启一个服务器socket。当一个远程蓝牙设备开始一个和该设备的连接请求,BluetoothServerSocket将会返回一个已连接的BluetoothSocket,接受该连接。
三、蓝牙开发
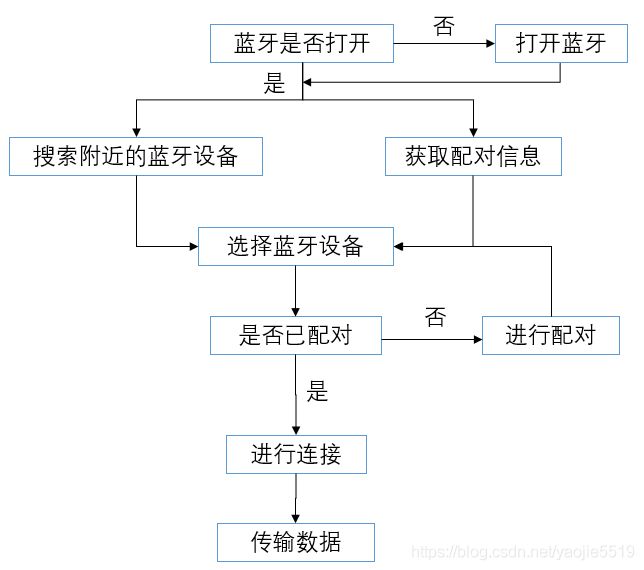
1、流程
2、开启权限
3、开启蓝牙
public void isBluetoothEnable() {
//获取蓝牙适配器
mBluetoothAdapter = BluetoothAdapter.getDefaultAdapter();
if (mBluetoothAdapter != null){
// 蓝牙已打开
if (mBluetoothAdapter.isEnabled()){
}else{//未打开则开启,此处可以通过弹框提示来提示用户开启
mBluetoothAdapter.enable()
}
}
}4、搜索附近蓝牙设备
/**
* 注册搜索蓝牙设备的广播
*/
private void startDiscovery() {
IntentFilter filter = new IntentFilter(BluetoothDevice.ACTION_FOUND);
registerReceiver(receiver, filter);
IntentFilter filter1 = new IntentFilter(BluetoothAdapter.ACTION_DISCOVERY_FINISHED);
registerReceiver(receiver, filter1);
startScanBluetooth();
}
private void startScanBluetooth() {
// 判断是否在搜索,如果在搜索,就取消搜索
if (bluetoothAdapter.isDiscovering()) {
bluetoothAdapter.cancelDiscovery();
}
// 开始搜索
bluetoothAdapter.startDiscovery();
}
/**
* 蓝牙广播接收
*/
private final BroadcastReceiver receiver = new BroadcastReceiver() {
@Override
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
String action = intent.getAction();
if (BluetoothDevice.ACTION_FOUND.equals(action)) {
BluetoothDevice device = intent.getParcelableExtra(BluetoothDevice.EXTRA_DEVICE);
//蓝牙rssi参数,代表蓝牙强度
short rssi = intent.getExtras().getShort(BluetoothDevice.EXTRA_RSSI);
//蓝牙设备名称
String name = device.getName();
//蓝牙设备连接状态
int status = device.getBondState();
...
} else if (action.equals(BluetoothDevice.ACTION_BOND_STATE_CHANGED)) {
...
} else if (BluetoothAdapter.ACTION_DISCOVERY_FINISHED.equals(action)) {
Toast.makeText(context, "蓝牙设备搜索完成", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
}
};关于蓝牙连接状态:
BluetoothDevice.BOND_BONDED:已配对
BluetoothDevice.BOND_BONDING:配对中
BluetoothDevice.BOND_NONE:未配对或取消配对
关于蓝牙强度rssi:
单位是dbm,蓝牙信号的强度RSSI = 10*log P,P代表接收到的信号功率。蓝牙会发送广播,距离大小会影响信号功率强弱。假设发射功率取最大值为1mw,那么RSSI的值为0,也就是说你的距离离蓝牙最近时在理想状态下所获取的RSSI的值为0,但在实际中基本不会存在这个理想状态,因此RSSI的值基本都为负数。
一般说来,在BLE中,假设信号强度按强、中、弱、差4个等级划分,rssi范围依次是:-60 ~ 0 、-70 ~ -60、-80 ~ -70、<-80。
5、配对
//获取已配对设备信息
public List getPairedBluetoothDevices() {
List deviceList = new ArrayList<>();
Set pairedDevices = mBluetoothAdapter.getBondedDevices();
if (pairedDevices.size() > 0) {
for (BluetoothDevice device : pairedDevices) {
deviceList.add(device);
}
}
return deviceList;
} //若已配对设备数为0,跳转到手机系统蓝牙设置界面
Intent enableBtIntent = new Intent(Settings.ACTION_BLUETOOTH_SETTINGS);
mContext.startActivity(enableBtIntent);//手动配对,完成配对后重新扫描即可
Method method = BluetoothDevice.class.getMethod("createBond");
method.invoke(itemlist.get(position).getDevice());
6、连接
蓝牙连接需要在子线程中完成
public class BluetoothConnectThread extends Thread {
private static final UUID BluetoothUUID = UUID.fromString("00001101-0000-1000-8000-00805F9B34FB");
BluetoothSocket bluetoothSocket;
BluetoothDevice bluetoothDevice;
private boolean connected = false;
private Object lock = new Object();
//蓝牙连接回调接口
private BluetoothConnectCallback connectCallback;
public BluetoothConnectThread(BluetoothDevice device,
BluetoothConnectCallback callback) {
try {
bluetoothDevice = device;
bluetoothSocket = bluetoothDevice.createInsecureRfcommSocketToServiceRecord(BluetoothUUID);
connectCallback = callback;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void run() {
if (bluetoothSocket != null) {
if (connected) {
cancel2();
connected = false;
}
}
new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
connect();
if (connected) {
if (connectCallback != null){
connectCallback.connectSuccess(bluetoothSocket);
}
}
}
}.start();
}
public void connect() {
try {
synchronized (lock) {
bluetoothSocket.connect();
connected = true;
}
} catch (Exception connectException) {
connectException.printStackTrace();
cancel();
try {
Method m;
m = bluetoothDevice.getClass().getMethod("createRfcommSocket", new Class[]{int.class});
bluetoothSocket = (BluetoothSocket) m.invoke(bluetoothDevice, Integer.valueOf(1));
bluetoothSocket.connect();
connected = true;
} catch (Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
if (connectCallback != null){
connectCallback.connectFailed(ex.getMessage());
}
}
}
}
public void cancel() {
try {
synchronized (lock) {
if (connected) {
bluetoothSocket.close();
connected = false;
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
}
}
public void cancel2() {
try {
synchronized (lock) {
bluetoothSocket.close();
connected = false;
}
} catch (IOException e) {
}
}
}public interface BluetoothConnectCallback {
void connectSuccess(BluetoothSocket socket);
void connectFailed(String errorMsg);
void connectCancel();
}注意以上,BluetoothUUID一般为固定的,connect()放在子线程中可以提高连接成功率(不明所以),注意connect失败需要通过反射createRfcommSocket该方法完成,自验目前连接成功率较高。
7、传输数据
//获取BluetoothSocket输出流
OutputStream outputStream = bluesocket.getOutputStream();
//之后将数据写入输出流完成传输
outputStream.write(data);
outputStream.flush();