APP登陆协议的分析
1、前言
最近暴雨不断,只能宅在家里,闲来无事,写写文章
2、整体分析
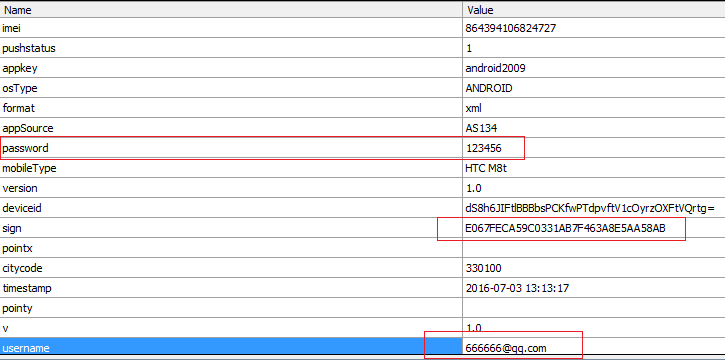
通过抓包工具,简单看看登陆封包内容,如下:
其中密码为123456

居然是明文传输密码和账号,不止如此,传输居然采用http,看到这,这款企业级的app安全性,可以想象,根本毫无安全可言。另外,可以看到封包最后有个签名sign,如果我们把sign算法搞定,那岂不是,可以写自动注册机了。
3、登陆签名算法分析
搜索”注册成功”,来到关键的处理登陆信息的代码,如下:
public static HashMap a(final HashMap hashMap) {
hashMap.put("appkey", "android2009");
hashMap.put("timestamp", ps.a());
hashMap.put("v", "1.0");
hashMap.put("format", "xml");
hashMap.put("appSource", ot.v);
hashMap.put("osType", "ANDROID");
hashMap.put("osVersion", Build$VERSION.RELEASE);
if (!hashMap.containsKey("appVersion")) {
hashMap.put("appVersion", pj.a);
}
if (!hashMap.containsKey("apptype")) {
hashMap.put("apptype", "cinema");
}
if (!hashMap.containsKey("version")) {
hashMap.put("version", "1.0");
}
if (!hashMap.containsKey("memberEncode")) {
final String a = px.a();
if (pq.i(a)) {
hashMap.put("memberEncode", a);
}
}
if (!hashMap.containsKey(ot.p)) {
hashMap.put("deviceId", ot.f);
}
if (!hashMap.containsKey(ot.o)) {
hashMap.put("mobileType", ot.d);
}
if (!hashMap.containsKey(ot.q)) {
hashMap.put("imei", ot.e);
}
if (!hashMap.containsKey(ot.n)) {
hashMap.put("mprovider", ot.h);
}
if (!hashMap.containsKey(ot.m)) {
hashMap.put("mnet", ot.g);
}
if (!hashMap.containsKey(ot.r)) {
hashMap.put("citycode", ot.i);
}
if (!hashMap.containsKey(ot.t)) {
hashMap.put("pointx", ot.k);
}
if (!hashMap.containsKey(ot.u)) {
hashMap.put("pointy", ot.l);
}
final ArrayList list = new ArrayList();
final ArrayList list2 = new ArrayList();
for (final Map.Entry entry : hashMap.entrySet()) {
if (entry.getValue() == null) {
list2.add(entry.getKey());
}
list.add(entry.getKey());
}
for (int size = list2.size(), i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
hashMap.remove(list2.get(i));
list.remove(list2.get(i));
}
Collections.sort(list);
final int size2 = list.size();
final TreeMap treeMap = new TreeMap();
for (int j = 0; j < size2; ++j) {
treeMap.put(list.get(j), hashMap.get(list.get(j)));
}
String a2 = "";
while (true) {
try {
a2 = om.a(treeMap, "prikey-android");
hashMap.put("sign", a2);
hashMap.put("signmethod", "MD5");
return hashMap;
}
catch (Exception ex) {
continue;
}
break;
}
} 可以非常清晰的看到,通过获取一系列的信息放到map中,然后通过 a2 = om.a(treeMap, “prikey-android”) 进行签名。最后,作者居然把签名算法提示出来类,无语。。。。。。
我们再来详细可看,签名算法
public static String a(final Map map, final String s) throws IOException {
final TreeMap treeMap = new TreeMap(map);
final StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (final Map.Entry entry : treeMap.entrySet()) {
sb.append(entry.getKey()).append("=").append((String)entry.getValue()).append("&");
}
final byte[] digest = a().digest((pp.a(sb.toString(), "&") + s).getBytes("UTF-8"));
final StringBuilder sb2 = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < digest.length; ++i) {
final String hexString = Integer.toHexString(digest[i] & 0xFF);
if (hexString.length() == 1) {
sb2.append("0");
}
sb2.append(hexString.toUpperCase());
}
return sb2.toString().toUpperCase();
} 代码比较清晰,获取map中的key 和value,重新组合,调用pp.a(String, String)方法,返回值加上传递进来的参数s转换成byte数组,传递给a().digest。再说明a()之前,首先说下pp.a(String, String)的作用,该函数对传入的字符串进行非空和空白字符判断,并去掉第一个参数末尾的标识,其中标识由第二个参数指定。处理后的字符串如下:
appSource=AS134&appVersion=6.0.1&appkey=android2009&apptype=cinema&citycode=330100&deviceId=68F72842A46E&deviceid=dS8h6JIFtlBBBbsPCKfwPTdpvftV1cOyrzOXFtVQrtg=&format=xml&imei=864394106824727&method=xxxxxx.login&mnet=WIFI&mobileType=HTC M8t&mprovider=46000&osType=ANDROID&osVersion=4.4.2&password=123456&pointx=&pointy=&pushstatus=1×tamp=2016-07-03 12:36:41&username=666666@qq.com&v=1.0&version=1.0prikey-android下面,来看下a()方法,比较简单返回MD5数字签名实例,如下:
private static MessageDigest a() throws IOException {
try {
return MessageDigest.getInstance("MD5");
}
catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException ex) {
throw new IOException(ex.getMessage());
}
}继续分析,代码的后半部分,作用就是转换成大写十六进制格式的md5.
最后,附上md5加密算法模板
/*
* MD5加密
*/
public String getMD5Str(String str) {
MessageDigest messageDigest = null;
String result = null;
try {
messageDigest = MessageDigest.getInstance("MD5");
messageDigest.reset();
messageDigest.update(str.getBytes("UTF-8"));
byte[] byteArray = messageDigest.digest();
StringBuffer md5StrBuff = new StringBuffer();
for (int i = 0; i < byteArray.length; i++) {
if (Integer.toHexString(0xFF & byteArray[i]).length() == 1)
md5StrBuff.append("0").append(Integer.toHexString(0xFF & byteArray[i]));
else
md5StrBuff.append(Integer.toHexString(0xFF & byteArray[i]));
}
//16位加密,从第9位到25位
result = md5StrBuff.substring(8, 24).toString().toUpperCase();
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) {
System.out.println("NoSuchAlgorithmException caught!");
result = null;
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
result = null;
}
return result;
}