1、容器的创建
通过idea快速搭建一个基于spring的web应用,我们就可以从web.xml中spring监听器开始入手
1.1 context的创建
在tomcat启动webapp应用的时候会使用多线程调用StandardContext的start方法,在StandarContext启动的时候会调用实现了ServletContextListener的监听器,spring的容器创建就由此开始
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event) {
//(1)初始化web应用上下文
initWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());
}
//(1) 初始化web应用上下文
public WebApplicationContext org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoader.initWebApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext) {
//如果已经存在就不允许再次加载
if (servletContext.getAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE) != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Cannot initialize context because there is already a root application context present - " +
"check whether you have multiple ContextLoader* definitions in your web.xml!");
}
Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(ContextLoader.class);
servletContext.log("Initializing Spring root WebApplicationContext");
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext: initialization started");
}
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
// Store context in local instance variable, to guarantee that
// it is available on ServletContext shutdown.
if (this.context == null) {
//这个应用上下文的实现可以用contextClass在web.xml指定
//如果没有指定,那么就默认加载配置文件中的应用上下文,这里是
//XmlWebApplicationContext,并且必须是ConfigurableWebApplicationContext
//类型的,因为需要加载配置,这个接口定义了如何加载配置
this.context = createWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
}
if (this.context instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) this.context;
//这个active在refresh的时候会被设置为true,表示容器已经被激活,父容器已经被加载(激活可以作为是否设置父容器,id,甚至以后扩展的其他功能的标识)
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
// The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as
// setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etc
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
// The context instance was injected without an explicit parent ->
// determine parent for root web application context, if any.
//(2)加载父容
ApplicationContext parent = loadParentContext(servletContext);
cwac.setParent(parent);
}
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac, servletContext);
}
}
//将创建的context设置到applicationContext中,我们可以从ServletContext中获取到这个Context
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, this.context);
//...省略部分代码
}
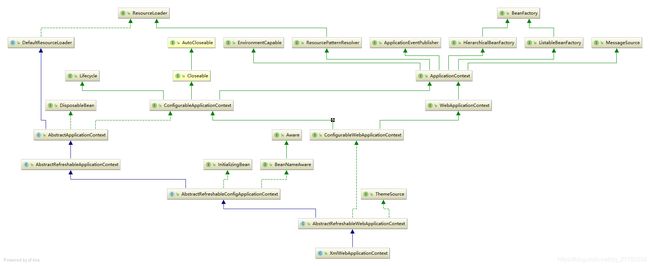
由于我们在web.xml没有指定contextClass,所以上面创建了一个默认的XmlWebApplicationContext,我们以后使用到的context就是这个类的实例,所以我们有必要去了解一下这个类的继承结构,以便对它有更多的认识。
ResourceLoader(接口,用于资源的加载,比如配置文件)
DefaultResourceLoader(实现了基本classpath的加载资源)
DisposableBean(定义了如何去销毁一个bean)
Lifecycle(定义生命周期能力,start,stop,isRuning)
Closeable (定义关闭资源的能力)
EnvironmentCapable(定义获取Environment的能力)
ResourcePatternResolver(通过模式路径获取资源)
ApplicationEventPublisher(定义发布事件的能力)
HierarchicalBeanFactory(定义获取父工厂bean的能力)
ListableBeanFactory(可枚举的能力)
MessageSource(定义获取国际化信息的能力)
WebApplicationContext(定义获取ServletContext的能力,并且定义了一系列scope常量)
Environment(继承自PropertyResolver,提供解析占位符与获取对应属性的值)
ApplicationContext(主要定义获取可配置Bean工厂的能力)
ConfigurableApplicationContext(可配置的,提供可扩展的功能,比如添加BeanFactoryPostProcessor,用于加载配置文件之后可修改BeanDefinition或者添加BeanDefinition)
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext(提供获取和设置配置的能力)
AbstractRefreshableWebApplicationContext(提供可刷新和获取servletContext的能力)
AbstractApplicationContext(模板类,提供了refersh方法)
AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext(定义是否允许BeanDefinition重载,是否允许循环依赖,持有可枚举BeanFactory,实现了相同的ListableBeanFactory,属于装饰器模式,具有刷新容器的能力,也就是重新启动容器)
AbstractRefreshableConfigApplicationContext(具有设置配置文件,获取配置文件的能力,配置可以供其他的继承者使用,用于加载配置文件,比如ClassPathXMLApplicationContext)
BeanFactroy(接口,提供基本的getBean等功能)
ThemeSource(提供获取主题的能力)
Aware(标记接口,用于通知spring容器进行一些回调功能)
BeanNameAware(具有设置BeanName的能力)
InitializingBean(初始化能力,在spring属性注入之后调用,这里主要用于context做为bean注入的时候使用)
XmlWebApplicationContext(提供从xml中获取加载BeanDefinition的能力)
1.2 父context的创建
//(2)如果当前容器没有激活,并且没有设置父容器,那么尝试加载父容器。
protected ApplicationContext org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoader.loadParentContext.loadParentContext(ServletContext servletContext) {
ApplicationContext parentContext = null;
//LOCATOR_FACTORY_SELECTOR_PARAM locatorFactorySelector
//从web.xml配置中获取配置文件地址
String locatorFactorySelector = servletContext.getInitParameter(LOCATOR_FACTORY_SELECTOR_PARAM);
//LOCATOR_FACTORY_KEY_PARAM parentContextKey
//父容器的key,从locatorFactorySelector指定的容器中获取对应key的容器
String parentContextKey = servletContext.getInitParameter(LOCATOR_FACTORY_KEY_PARAM);
if (parentContextKey != null) {
// locatorFactorySelector may be null, indicating the default "classpath*:beanRefContext.xml"
//(3)如果locatorFactorySelector为空,那么就使用默认配置地址classpath*:beanRefContext.xml
BeanFactoryLocator locator = ContextSingletonBeanFactoryLocator.getInstance(locatorFactorySelector);
Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(ContextLoader.class);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Getting parent context definition: using parent context key of '" +
parentContextKey + "' with BeanFactoryLocator");
}
//(4)
this.parentContextRef = locator.useBeanFactory(parentContextKey);
parentContext = (ApplicationContext) this.parentContextRef.getFactory();
}
return parentContext;
}
//(3)
public static BeanFactoryLocator org.springframework.context.access.ContextSingletonBeanFactoryLocator.getInstance(String selector) throws BeansException {
//资源地址
String resourceLocation = selector;
if (resourceLocation == null) {
resourceLocation = DEFAULT_RESOURCE_LOCATION;
}
// For backwards compatibility, we prepend "classpath*:" to the selector name if there
// is no other prefix (i.e. "classpath*:", "classpath:", or some URL prefix).
if (!ResourcePatternUtils.isUrl(resourceLocation)) {
resourceLocation = ResourcePatternResolver.CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX + resourceLocation;
}
synchronized (instances) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("ContextSingletonBeanFactoryLocator.getInstance(): instances.hashCode=" +
instances.hashCode() + ", instances=" + instances);
}
//从缓存中加载Bean工厂定位器
BeanFactoryLocator bfl = instances.get(resourceLocation);
if (bfl == null) {
bfl = new ContextSingletonBeanFactoryLocator(resourceLocation);
instances.put(resourceLocation, bfl);
}
return bfl;
}
}
(4)ContextSingletonBeanFactoryLocator
public BeanFactoryReference useBeanFactory(String factoryKey) throws BeansException {
synchronized (this.bfgInstancesByKey) {
//从缓存中获取beanfactory组,所谓beanfactory组就是保存了一系列BeanFactory的容器
BeanFactoryGroup bfg = this.bfgInstancesByKey.get(this.resourceLocation);
//如果不为空,那么这个bean工程会设置个子容器,那么引用计数加一
if (bfg != null) {
bfg.refCount++;
}
else {
// This group definition doesn't exist, we need to try to load it.
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Factory group with resource name [" + this.resourceLocation +
"] requested. Creating new instance.");
}
// Create the BeanFactory but don't initialize it.
//创建一个ClassPathXmlApplicationContext容器组,但不进行初始化
/**
protected BeanFactory createDefinition(String resourceLocation, String factoryKey) {
return new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(new String[] {resourceLocation}, false);
}
**/
BeanFactory groupContext = createDefinition(this.resourceLocation, factoryKey);
// Record its existence now, before instantiating any singletons.
//将这个上下文context记录到一个 BeanFactoryGroup,并用refCount记录其被应用的次数
bfg = new BeanFactoryGroup();
bfg.definition = groupContext;
bfg.refCount = 1;
//记录到缓存中
this.bfgInstancesByKey.put(this.resourceLocation, bfg);
this.bfgInstancesByObj.put(groupContext, bfg);
//
try {
//由于我们创建的是ClassPathXmlApplicationContext实现了ConfigurableApplicationContext,所以这里直接调用的refresh()进行初始化等操作。
initializeDefinition(groupContext);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
this.bfgInstancesByKey.remove(this.resourceLocation);
this.bfgInstancesByObj.remove(groupContext);
throw new BootstrapException("Unable to initialize group definition. " +
"Group resource name [" + this.resourceLocation + "], factory key [" + factoryKey + "]", ex);
}
}
try {
BeanFactory beanFactory;
//从刚才创建的容器组中获取指定类型的容器
if (factoryKey != null) {
beanFactory = bfg.definition.getBean(factoryKey, BeanFactory.class);
}
else {
beanFactory = bfg.definition.getBean(BeanFactory.class);
}
//创建一个实现了BeanFactoryReference接口类的实例
//这个接口具有获取指定BeanFactory实例的能力,和释放
//BeanFactory的能力,一旦引用计数变成了零,那么这个
//BeanFactoryGroup就可以被销毁。(引用计数法)
return new CountingBeanFactoryReference(beanFactory, bfg.definition);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
throw new BootstrapException("Unable to return specified BeanFactory instance: factory key [" +
factoryKey + "], from group with resource name [" + this.resourceLocation + "]", ex);
}
}
}
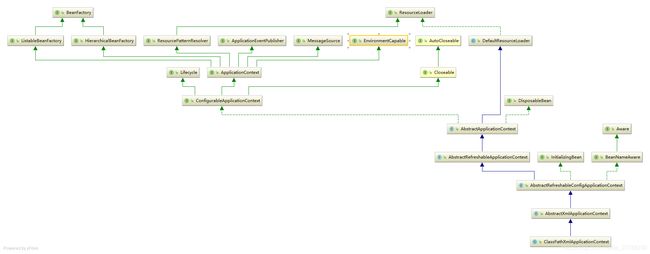
在创建父context的时候,spring使用的是ClasspathXmlApplicationContext,那么这个类与其子context有啥区别呢?我们来看看它的类图
AbstractXmlApplicationContext(提供获取配置文件和加载配置文件的能力)
DisposableBean(提供销毁能力)
从类图来看,ClasspathXmlApplicationContext与XmlWebApplicationContext最大的差别就是没有实现WebApplicationContext,也就是说ClasspathXmlApplicationContext不具有从web上下文获取属性资源以及request,session,globalSession生命周期的能力,除此之外,其他能力都差不多,所以这里我不会去研究ClassPathXmlApplicationContext是怎么初始化的,我们只需要知道XmlWebApplicationContext是怎么初始化的,那么前者的初始化自然就知道了。
接下来,在看下创建父容器所涉及到的一些类的关系类图
BeanFactoryLocator(定义获取BeanFactory引用的能力)
BeanFactoryReference(定义获取BeanFactory和释放BeanFactory,引用计数递减,销毁容器的能力)
SingletonBeanFactoryLocator(实现BeanFactoryLocator,并提供了两个静态属性
bfgInstancesByKey:资源地址–》BeanFactoryGroup
bfgInstancesByObj:具体容器组-》BeanFactoryGroup
)
ContextSingletonBeanFactoryLocator(SingletonBeanFactoryLocator的继承者,并提供了一个静态变量instances,用于维护资源与BeanFactoryLocator的关系
)
CountingBeanFactoryReference(BeanFactoryReference的实现者,持有需要获取的目标BeanFactory和目标BeanFactory所属的容器组,可通过它进行容器的引用计数递减,甚至容器的销毁)
本人水平有限,如有错误,请大佬们指出,文中使用的画图工具为 IDEA与IBM Rational Rose。