SpringBoot整合Swagger
1、什么是Swagger
Swagger 是一款RESTFUL接口的文档在线自动生成+功能测试功能软件。本文简单介绍了在项目中集成swagger的方法和一些常见问题。
Swagger 是一个规范和完整的框架,用于生成、描述、调用和可视化 RESTful 风格的 Web 服务。总体目标是使客户端和文件系统作为服务器以同样的速度来更新。文件的方法,参数和模型紧密集成到服务器端的代码,允许API来始终保持同步。Swagger 让部署管理和使用功能强大的API从未如此简单。
Swagger的目标是为REST APIs 定义一个标准的,与语言无关的接口,使人和计算机在看不到源码或者看不到文档或者不能通过网络流量检测的情况下能发现和理解各种服务的功能。当服务通过Swagger定义,消费者就能与远程的服务互动通过少量的实现逻辑。类似于低级编程接口,Swagger去掉了调用服务时的很多猜测。
2、为什么要使用Swagger
想想我们之前在项目中的接口,通常都要给每个接口写对应的接口文档,如果项目中的接口都是内部使用并且开发团队都在一起,也许可以省掉写接口文档,开发一个新的接口直接口头表述,后面自己去看这些接口都不知道是干什么用,更别说接口给外部团队使用了。之前编写接口文档可能都是用Word文档写或者用javadoc注释生成文档。两种都比较麻烦,手写耗时耗力,生成文档每次都要编译一遍。使用Swagger则可以快速的生成文档。
3、使用Swagger的好处
- 前后端分离开发
- API文档非常明确
- 测试的时候不需要再使用URL输入浏览器的方式来访问Controller
- 传统的输入URL的测试方式对于post请求的传参比较麻烦(当然,可以使用postman这样的浏览器插件)
- Swagger与SpringBoot的集成简单
4、将Swagger与SpringBoot集成
4.1 添加依赖
在项目的pom.xml添加swagger依赖,这里就不介绍SpringBoot依赖添加了。
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfoxgroupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger2artifactId>
<version>2.7.0version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfoxgroupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger-uiartifactId>
<version>2.7.0version>
dependency>4.2 创建Swagger配置类
/**
* Swagger2启动类
* Created by Arvin on 2017/12/7.
*/
@Configuration
@EnableSwagger2
public class Swagger2 {
/**
* 创建用户API文档
* @return
*/
@Bean
public Docket createRestUserApi(){
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.groupName("user")
.apiInfo(createUserApiInfo())
.select()
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("com.tenghu.swa.user"))
.paths(PathSelectors.any())
.build();
}
/**
* 创建客户API文档
* @return
*/
@Bean
public Docket createRestCusApi(){
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.groupName("cus")
.apiInfo(createCusApiInfo())
.select()
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("com.tenghu.swa.cus"))
.paths(PathSelectors.any())
.build();
}
/**
* 创建用户API信息
* @return
*/
private ApiInfo createUserApiInfo(){
return new ApiInfoBuilder()
.title("处理用户信息相关接口")
.description("以下接口只操作用户信息")
.contact(new Contact("Arvin","http://blog.csdn.net/tenghu8888","[email protected]"))
.version("1.0")
.build();
}
/**
* 创建客户API信息
* @return
*/
private ApiInfo createCusApiInfo(){
return new ApiInfoBuilder()
.title("处理客户信息相关接口")
.description("以下接口只操作客户信息")
.contact(new Contact("Arvin","http://blog.csdn.net/tenghu8888","[email protected]"))
.version("1.0")
.build();
}
}
创建Swagger配置类时,类名随意创建,但是类上面必须添加@Configuration、@EnableSwagger2这两个注解,通过@Configuration注解,让Spring来加载该类配置,@EnableSwagger2注解来启用Swagger2。再通过被@Bean注解的函数创建Docket的Bean之后,apiInfo()用来创建该Api的基本信息(这些基本信息会展现在文档页面中)。select()函数返回一个ApiSelectorBuilder实例用来控制哪些接口暴露给Swagger来展现,本例采用指定扫描的包路径来定义,Swagger会扫描该包下所有Controller定义的API,并产生文档内容(除了被@ApiIgnore注解的API)。这里如果函数上面不配置@Bean,那么Swagger只是启动了,没有创建API信息。
从上面配置类中可以创建多个函数并用@Bean注解,这样就可以针对不同的Controller创建出各自的API文档。
需要注意的是:在创建多个API时,需要指定API文档的名称。groupName(),如果不指定在项目启动的时候就会报错。
4.3 编写Controller
在这里编写自己的RESTFull风格的接口,跟正常开发没什么区别,只是要在对应的类、函数、参数上加上Swagger注解就可以了。注解说明:
1. @Api:用在类上,说明该类的作用
2. @ApiOperation:用在方法上,说明方法的作用
3. @ApiImplicitParams:用在方法上包含一组参数说明
4. @ApiImplicitParam:用在@ApiImplicitParams注解中,指定一个请求参数的各个方面
paramType:参数放在哪个地方
header请求参数的获取:@RequestHeader
query请求参数的获取:@RequestParam
path(用于restful接口)–>请求参数的获取:@PathVariable
body(不常用)
form(不常用)
name:参数名
dataType:参数类型
required:参数是否必须传
value:参数的意思
defaultValue:参数的默认值
5. @ApiResponses:用于表示一组响应
6. @ApiResponse:用在@ApiResponses中,一般用于表达一个错误的响应信息
code:数字,例如400
message:信息,例如”请求参数没填好”
response:抛出异常的类
7. @ApiModel:描述一个Model的信息(这种一般用在post创建的时候,使用@RequestBody这样的场景,请求参数无法使用@ApiImplicitParam注解进行描述的时候)
8. @ApiModelProperty:描述一个model的属性
9. @ApiIgnore:生成文档时忽略
具体其他注解及详细解释查看:
https://github.com/swagger-api/swagger-core/wiki/Annotations#apimodel
/**
* Created by Arvin on 2017/12/7.
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping(value = "/cus")
@Api(value = "客户服务接口",description = "提供对客户操作服务接口(增、删、改、查)用户信息")
public class CusController {
private static List customerList=new ArrayList();
static {
customerList.add(new Customer("1","G00001","广州视源股份有限公司","CVTE","广州市黄埔区云埔6号"));
customerList.add(new Customer("2","G00002","广州赛意信息科技股份有限公司","SIE","佛山市顺德区北滘镇新城区怡和路怡和中心11楼"));
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/all",method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ApiOperation(value = "获取所有客户信息",notes = "获取当前所有有效客户信息")
public List getAllCustomer(){
return customerList;
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/get/{cusId}",method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ApiOperation(value = "根据客户ID获取客户信息",notes = "根据客户ID获取客户信息")
@ApiImplicitParam(paramType = "path",name = "cusId",required = true,value = "客户ID",dataType = "string")
public Customer getCusById(@PathVariable("cusId") String cusId){
for (Customer customer:customerList){
if(cusId.equals(customer.getCusId())){
return customer;
}
}
return null;
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/save",method = RequestMethod.POST)
@ApiOperation(value = "保存客户信息",notes = "保存客户信息",httpMethod = "POST")
public List saveCus(
@ApiParam(name = "customer",required = true,type = "object",value = "客户信息")
Customer customer){
customerList.add(customer);
return customerList;
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/del/{cusId}",method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ApiOperation(value = "刪除客戶信息",notes = "根据客户ID删除客户信息")
@ApiImplicitParam(value = "客户ID",name = "cusId",paramType = "path",required = true)
public List deleteCus(@PathVariable("cusId") String cusId){
for (Customer customer:customerList){
if (cusId.equals(customer.getCusId())){
customerList.remove(customer);
}
}
return customerList;
}
}
这里只贴出一个Controller代码,其他Controler一样的写法。
4.4 编写SpringBoot启动类
@ComponentScan({"com.tenghu.ws"})
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}完成以上代码,启动SpringBoot后,在浏览器输入http://127.0.0.1:8091/note/swagger-ui.html 就可以看到一下界面。
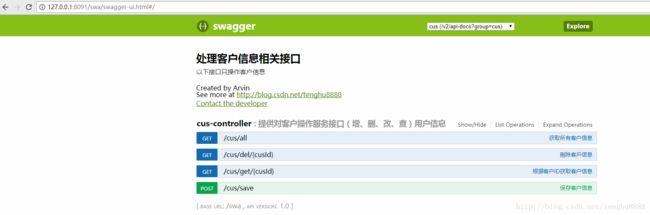

上面有提到过在Swagger里面创建了两个API,在界面就可以看到两个API的选项,如下:

5、源码下载
完整结果实例可查看:SpringBoot-Swagger