【手写MyBatis】(04)- Mapper.xml文件加载过程
文章目录
- 手写MyBatis框架
- Code:解析UserMapper.xml文件
- Configuration对象添加属性
- XMLMapperParser
- XMLStatementParser 与 MappedStatement
- SqlSource 与 ParameterMapping
- XMLScriptParser 与 SqlNode
- NodeHandler 与 IfNodeHandler
- Test:测试UserMapper.xml文件解析
手写MyBatis框架
Code:解析UserMapper.xml文件
解析单个对应的Document
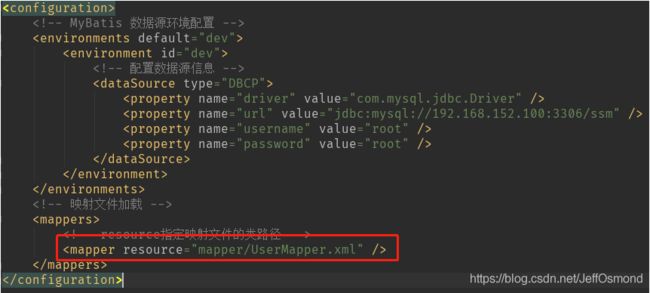
XMLConfigParser 的parseMapper方法中,我们已经得到了每一个标签的resource属性对应的Document对象,所以下一步即可对每一个Document对象进行解析,并把解析内容存入Configuration对象中。
创建XMLMapperParser专门用于解析Mapper.xml文件内容,采用构造函数的方式将Configuration对象从XMLConfigParser传递到XMLMapperParser进行操作。
public class XMLConfigParser {
...
/**
* 解析多个mapper标签
* @param mapperElement
*/
private void parseMapper(Element mapperElement) {
// 获取映射文件的路径
String resource = mapperElement.attributeValue("resource");
// 获取指定路径的IO流
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
// 获取映射文件对应的Document对象
Document document = DocumentUtils.readDocument(inputStream);
// 按照mapper标签语义去解析Document
XMLMapperParser mapperParser = new XMLMapperParser(configuration);
mapperParser.parse(document.getRootElement());
}
}
Configuration对象添加属性
对于Mapper.xml文件对应的Document解析的内容,我们将其封装为MappedStatement对象,因此,在Configuration对象中应添加一个新的属性:Map 这个Map的Key,是Mapper.xml文件的唯一标识,值即为Mapper.xml解析后得来的MappedStatement对象。
由于mappedStatements属性并非常规的Map对象,因此我们为其单独编写get/set方法,使其更容易使用。
public class Configuration {
// 省略DataSource 相关代码
Map<String,MappedStatement> mappedStatements = new HashMap<>();
public MappedStatement getMappedStatementById(String statementId) {
return mappedStatements.get(statementId);
}
public void setMappedStatement(String statementId, MappedStatement mappedStatement) {
mappedStatements.put(statementId, mappedStatement);
}
}
XMLMapperParser
XMLMapperParser类负责解析Mapper.xml的最外层内容,包含select、update、delete、insert 标签、sql片段等,这里我们只实现select标签的解析。解析出来的select标签交由新的类XMLStatementParser来进一步处理
public class XMLMapperParser {
private Configuration configuration;
public XMLMapperParser(Configuration configuration) {
this.configuration = configuration;
}
public void parse(Element rootElement) {
String namespace = rootElement.attributeValue("namespace");
// mapper标签下会包含一些sql片段标签、resultMap标签等,这些标签直接解析处理,而statement相关的标签单独处理
// 此处可以使用XPath语法来进行通配
List<Element> elements = rootElement.elements("select|update|insert|delete");
for (Element selectElement : elements) {
// select update delete insert 都对应一个statement
XMLStatementParser scriptParser = new XMLStatementParser(configuration);
// 将处理的半成品传递给XMLStatementParser
scriptParser.parseStatement(selectElement,namespace);
}
}
}
这里由于使用XPath进行匹配节点,所以要添加一个依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>jaxengroupId>
<artifactId>jaxenartifactId>
<version>1.2.0version>
dependency>
XMLStatementParser 与 MappedStatement
我们将这种statement放在单独的类中进行解析。
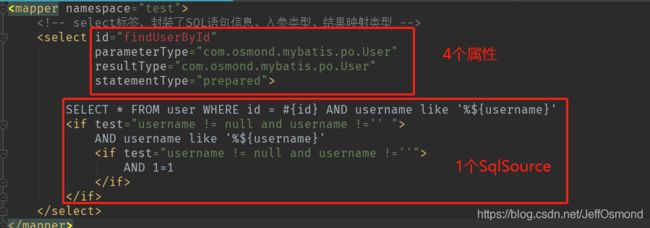
在这里需要对标签进行解析的内容有:
- 4个属性:id、parameterType、resultType、statementType。
- 1个SqlSource对象
其中parameterType和resultType需要使用工具类,将全路径名映射成Class类,留作后续sql填充动态参数和查询后的结果映射。
随后,对以上内容进行封装成一个MappedStatement对象,并存入Configuration对象中的Map里
public class XMLStatementParser {
private Configuration configuration;
public XMLStatementParser(Configuration configuration) {
this.configuration = configuration;
}
public void parseStatement(Element statementElement, String namespace) {
String id = statementElement.attributeValue("id");
String parameterType = statementElement.attributeValue("parameterType");
Class<?> parameterTypeClass = resolveClass(parameterType);
String resultType = statementElement.attributeValue("resultType");
Class<?> resultTypeClass = resolveClass(resultType);
String statementType = statementElement.attributeValue("statementType");
statementType = statementType == null || "".equals(statementType) ? "prepared" : statementType;
// SqlSource就是封装了SQL语句
// 此时封装的SQL语句是没有进行处理的,什么时候处理呢?
// 处理时机,就是在SqlSession执行的时候
SqlSource sqlSource = createSqlSource(statementElement);
String statementId = namespace + "." + id;
// 此处使用构建者模式改造
MappedStatement mappedStatement = MappedStatement.builder()
.statementId(statementId)
.parameterTypeClass(parameterTypeClass)
.resultTypeClass(resultTypeClass)
.statementType(statementType)
.sqlSource(sqlSource)
.build();
configuration.setMappedStatement(statementId, mappedStatement);
}
private Class<?> resolveClass(String clazz) {
try {
return Class.forName(clazz);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
}
在以上的实现代码中:
- 对于Configurationz中的mappedStatements的Key,采用Mapper.xml的namespace属性 拼接上"."以及statement的id,作为MappedStatement的唯一标识。这说明了,在同一个命名空间下,等标签的ID不可重复的原因。
- 在MappedStatement的创建过程中,本可以采用构造函数的方式进行创建,但这并不是一个好的实现方式,对于创建对象的人来说,不需要知道对象创建的细节(对象的字段、构造函数的参数顺序…),因此改造成构建者模式。
MappedStatement (构建者模式)
/**
* Statement 信息存储
* 使用构建者模式实现
* @author JeffOsmond
* @create 2020/6/3 11:13
*/
public class MappedStatement {
private String statementId;
private Class<?> parameterTypeClass;
private Class<?> resultTypeClass;
private String statementType;
private SqlSource sqlSource;
// 省略各属性的get/set方法
public MappedStatement(Builder builder) {
this.statementId = builder.statementId;
this.parameterTypeClass = builder.parameterTypeClass;
this.resultTypeClass = builder.resultTypeClass;
this.statementType = builder.statementType;
this.sqlSource = builder.sqlSource;
}
public static Builder builder() {
return new Builder();
}
public static class Builder {
private String statementId;
private Class<?> parameterTypeClass;
private Class<?> resultTypeClass;
private String statementType;
private SqlSource sqlSource;
public Builder statementId(String statementId){
this.statementId = statementId;
return this;
}
public Builder parameterTypeClass(Class<?> parameterTypeClass){
this.parameterTypeClass = parameterTypeClass;
return this;
}
public Builder resultTypeClass(Class<?> resultTypeClass){
this.resultTypeClass = resultTypeClass;
return this;
}
public Builder statementType(String statementType){
this.statementType = statementType;
return this;
}
public Builder sqlSource(SqlSource sqlSource){
this.sqlSource = sqlSource;
return this;
}
public MappedStatement build(){
return new MappedStatement(this);
}
}
}
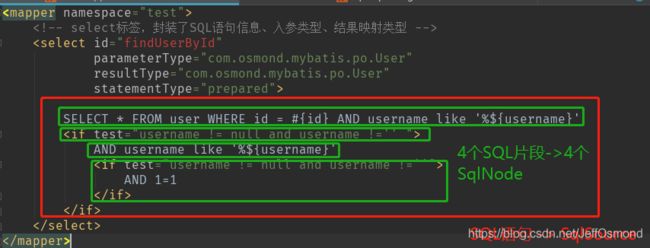
除标签的四个属性以外,我们还需要将SQL语句进行详细解析。一条完整的sql语句,对应一个SqlSource对象,一个SqlSource中包含多个SqlNode,而SqlNode就是对一条完整sql语句中不同的部分的封装。
public class XMLStatementParser {
...
/**
* 创建SqlSource其实就是对select等CRUD标签中的sql脚本进行处理
* @param statementElement
* @return
*/
private SqlSource createSqlSource(Element statementElement) {
XMLScriptParser scriptParser = new XMLScriptParser(configuration);
SqlSource sqlSource = scriptParser.parseScriptNode(statementElement);
return sqlSource;
}
}
SqlSource 与 ParameterMapping
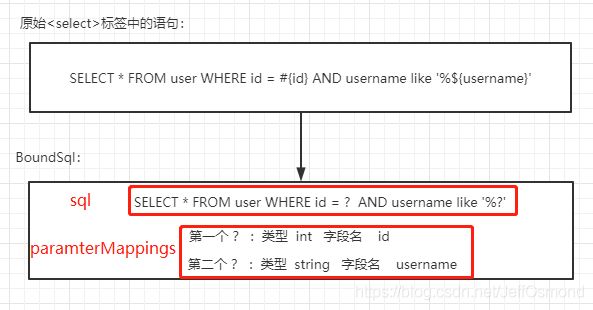
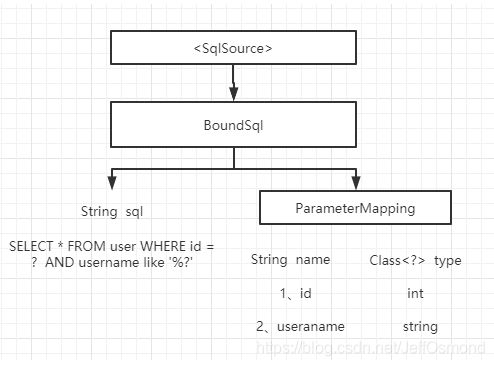
- 该接口用于获取可以被JDBC直接执行的sql语句。这个sql语句我们将其称为BoundSql。BoundSql是什么呢?
- 因此,我们将要建立的SQL解析的类结构为:
- BoundSql中,我们也为parameterMappings这个list单独编写get/add 方法。
public interface SqlSource {
BoundSql getBoundSql(Object param);
}
public class BoundSql {
private String sql;
private List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings = new ArrayList<>();
public String getSql() {
return sql;
}
public void setSql(String sql) {
this.sql = sql;
}
public List<ParameterMapping> getParameterMappings() {
return parameterMappings;
}
public void addParameterMapping(ParameterMapping parameterMapping) {
this.parameterMappings.add(parameterMapping);
}
public BoundSql(String sql) {
super();
this.sql = sql;
}
}
public class ParameterMapping {
private String name;
private Class<?> type;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Class<?> getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(Class<?> type) {
this.type = type;
}
public ParameterMapping(String name) {
super();
this.name = name;
}
}
- getBoundSql() 方法的入参是什么?我们的BoundSql中的ParameterMapping就是该方法的入参param(也就是mapper方法的入参) 与原始sql中的 ${} 、#{} 的映射关系。
XMLScriptParser 与 SqlNode
出于面向对象的考虑,创建XMLScriptParser类,用于专门解析SQL语句为多个SqlNode,随之共同组成一个SqlSource.
分析parseScriptNode方法要做的事情:
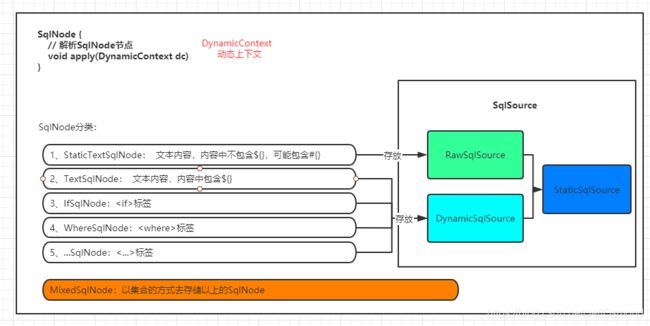
- 首先先将sql脚本按照不同的类型,封装到不同的SqlNode
- 再将SqlNode集合封装到SqlSource中(由于带有#{}和${}、动态标签的sql处理方式不同,所以需要封装到不同的SqlSource中)
SqlNode种类划分:
select标签的内部有很多行sql片段,而每一个sql片段的样式(包含的动态标签)都不一样,所以我们解析出来的应该是一个SqlNode集合,里面包含了不同种类的SqlNode。那么,SqlNode、SqlSouce的种类划分是如何呢?
- DynamicSqlSource的处理逻辑类似于JDBC中Statement传参的处理逻辑,就是字符串的拼接。每次获取的sql语句很可能不相同。所以sql与参数的拼接发生在getBoundSql的时候。
- RawSqlSource的处理逻辑类似于JDBC中PreparedStatement的处理逻辑,是预处理。每次获取的语句是同一个,所以sql与参数的拼接发生在类构造的时候。
准备SqlNode相关类和SqlSource相关类:
SqlSource与SqlNode实现类
/**
* 专门封装和处理带有${}和动态sql标签的sql语句
*/
public class DynamicSqlSource implements SqlSource {
private SqlNode rootSqlNode;
public DynamicSqlSource(MixedSqlNode rootSqlNode) {
this.rootSqlNode = rootSqlNode;
}
/**
* 在sqlsession执行的时候,才调用该方法
*/
@Override
public BoundSql getBoundSql(Object param) {
return null;
}
}
public class RawSqlSource implements SqlSource {
private SqlNode rootSqlNode;
public RawSqlSource(SqlNode rootSqlNode) {
this.rootSqlNode = rootSqlNode;
// 待完善:在这里要先对sql节点进行解析
}
@Override
public BoundSql getBoundSql(Object param) {
return null;
}
}
/**
* 提供对sql脚本的解析
* @author JeffOsmond
* @create 2020/6/5 14:19
*/
public interface SqlNode {
void apply(DynamicContext context);
}
/**
* 动态上下文
* 作用:存储SqlNode解析过程中产生的sql片段,并完成字符串拼接 存储SqlNode解析过程中需要的入参信息
* @author JeffOsmond
* @create 2020/6/5 14:20
*/
public class DynamicContext {
private StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
private Map<String, Object> bindings = new HashMap<String, Object>();
public DynamicContext(Object param) {
bindings.put("_parameter", param);
}
/**
* 添加sql片段
* @param sql
*/
public void appendSql(String sql) {
sb.append(sql);
sb.append(" ");
}
public String getSql() {
return sb.toString();
}
public Map<String, Object> getBindings() {
return bindings;
}
}
public class MixedSqlNode implements SqlNode {
private List<SqlNode> sqlNodes = new ArrayList<SqlNode>();
public MixedSqlNode(List<SqlNode> sqlNodes) {
this.sqlNodes = sqlNodes;
}
@Override
public void apply(DynamicContext context) {
for (SqlNode sqlNode : sqlNodes) {
sqlNode.apply(context);
}
}
}
public class StaticTextSqlNode implements SqlNode {
private String sqlText;
public StaticTextSqlNode(String sqlText) {
super();
this.sqlText = sqlText;
}
@Override
public void apply(DynamicContext context) {
}
}
public class TextSqlNode implements SqlNode {
private String sqlText;
public TextSqlNode(String sqlText) {
this.sqlText = sqlText;
}
@Override
public void apply(DynamicContext context) {
}
}
XMLScriptParser:
public class XMLScriptParser {
private Configuration configuration;
// 是否是动态sql
private boolean isDynamic = false;
public XMLScriptParser(Configuration configuration) {
this.configuration = configuration;
}
public SqlSource parseScriptNode(Element statementElement) {
// 首先先将sql脚本按照不同的类型,封装到不同的SqlNode
MixedSqlNode rootSqlNode = parseDynamicTags(statementElement);
// 再将SqlNode集合封装到SqlSource中
// 由于带有#{}和${}、动态标签的sql处理方式不同,所以需要封装到不同的SqlSource中
SqlSource sqlSource;
if(isDynamic){
// - 只要有${}和动态标签的,不管是否有#{}
sqlSource = new DynamicSqlSource(rootSqlNode);
}else{
// - 只有#{}的
sqlSource = new RawSqlSource(rootSqlNode);
}
return sqlSource;
}
}
- 以上代码中的isDynamic变量用于标记当前的statementElement是否是动态sql。其值取决于后续对sql进行解析时判断是否存在动态标签或者${}
对SqlNode的分类解析
public class XMLScriptParser {
...
public XMLScriptParser(Configuration configuration) {
this.configuration = configuration;
initNodeHandlerMap();
}
private Map<String, NodeHandler> nodeHandlerMap = new HashMap<String, NodeHandler>();
private void initNodeHandlerMap() {
nodeHandlerMap.put("if", new IfNodeHandler());
// nodeHandlerMap.put("where", new WhereNodeHandler());
// nodeHandlerMap.put("foreach", new ForeachNodeHandler());
}
private MixedSqlNode parseDynamicTags(Element statementElement) {
// 创建SqlNode列表
List<SqlNode> nodeList = new ArrayList<>();
// 先得到标签的子节点数量
int nodeCount = statementElement.nodeCount();
for (int i = 0; i < nodeCount; i++) {
Node node = statementElement.node(i);
// 判断Node类型,解析成不同的SqlNode
// - 如果是文本类型则封装到TextSqlNode或者StaticTextSqlNode
if (node instanceof Text) {
String sqlText = node.getText().trim();
if (sqlText == null || sqlText.equals("")) {
continue;
}
TextSqlNode sqlNode = new TextSqlNode(sqlText);
// 判断文本中是否带有${}
if (sqlNode.isDynamic()) {
nodeList.add(sqlNode);
isDynamic = true;
} else {
nodeList.add(new StaticTextSqlNode(sqlText));
}
}
// - 如果是动态标签,例如、,则递归解析
else if (node instanceof Element) {
Element nodeToHandle = (Element) node;
String nodeName = nodeToHandle.getName().toLowerCase();
// 根据标签名称,获取对应的处理类,封装到不同的节点信息
NodeHandler nodeHandler = nodeHandlerMap.get(nodeName);
nodeHandler.handleNode(nodeToHandle, nodeList);
isDynamic = true;
}
}
return new MixedSqlNode(nodeList);
}
}
// TextSqlNode是否为动态的判断:
public class TextSqlNode implements SqlNode {
...
public boolean isDynamic() {
if (sqlText.indexOf("${") > -1) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
这一部分是对SqlNode的详细解析。
- 先判断节点类型是纯文本还是动态标签,如果是动态标签,则单独使用解析器去处理。对于不同的动态标签,需要从预先定义的nodeHandlerMap中获取对应的Handler类进行处理。
- 如果节点类型是纯文本,则继续判断是仅包含#{}的StaticTextSqlNode还是包含${}的TextSqlNode.
无论是包含${}的纯文本还是动态标签,都需要将 isDynamic 变量置为true。
NodeHandler 与 IfNodeHandler
写到此处,我们剩余的解析任务只剩下对动态标签的解析了。使用NodeHandler来处理动态标签。而动态标签有很多类型,所以NodeHanlder是一个接口,对应有很多类型的实现类来处理不同的标签。
/**
* 针对不同子标签进行处理,处理之后,封装到对应的SqlNode对象中
* 比如if标签被处理之后,会封装到IfSqlNode对象中
*/
public interface NodeHandler {
void handleNode(Element nodeToHandle, List<SqlNode> targetContents);
}
我们简化代码,仅关注实现逻辑,所以仅用解析标签举例:
由于在解析动态标签的过程中,依旧会遇到文本类型的node节点,需要递归使用parseDynamicTags方法,所以我们将IfNodeHandler定义为XMLScriptParser的内部类。
当我们确定了node的类型为类型,在IfNodeHandler中,就可以把Node转换为IfSqlNode对象,并放入nodeList中
public class XMLScriptParser{
...
public class IfNodeHandler implements NodeHandler {
@Override
public void handleNode(Element nodeToHandle, List<SqlNode> targetContents) {
// 对if标签进行解析
MixedSqlNode rootSqlNode = parseDynamicTags(nodeToHandle);
String test = nodeToHandle.attributeValue("test");
IfSqlNode ifSqlNode = new IfSqlNode(test, rootSqlNode);
targetContents.add(ifSqlNode);
}
}
}
IfSqlNode
IfSqlNode的主要职责就是根据标签中定义的OGNL表达式:username != null and username !=''判断是否要继续解析内部sql片段,若要解析,则把解析好的内部sql片段放入动态上下文中(apply方法)
public class IfSqlNode implements SqlNode {
/**
* OGNL表达式
*/
private String test;
private SqlNode rootSqlNode ;
public IfSqlNode(String test, SqlNode rootSqlNode) {
this.test = test;
this.rootSqlNode = rootSqlNode;
}
@Override
public void apply(DynamicContext context) {
boolean evaluateBoolean = OgnlUtils.evaluateBoolean(test, context.getBindings().get("_parameter"));
if (evaluateBoolean) {
rootSqlNode.apply(context);
}
}
}
OGNL工具类
public class OgnlUtils {
/**
* 根据Ongl表达式,获取指定对象的参数值
* @param expression
* @param paramObject
* @return
*/
public static Object getValue(String expression, Object paramObject) {
try {
OgnlContext context = new OgnlContext();
context.setRoot(paramObject);
//mybatis中的动态标签使用的是ognl表达式
//mybatis中的${}使用的是ognl表达式
Object ognlExpression = Ognl.parseExpression(expression);// 构建Ognl表达式
Object value = Ognl.getValue(ognlExpression, context, context.getRoot());// 解析表达式
return value;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
/**
* 通过Ognl表达式,去计算boolean类型的结果
* @param expression
* @param parameterObject
* @return
*/
public static boolean evaluateBoolean(String expression, Object parameterObject) {
Object value = OgnlUtils.getValue(expression, parameterObject);
if (value instanceof Boolean) {
return (Boolean) value;
}
if (value instanceof Number) {
return new BigDecimal(String.valueOf(value)).compareTo(BigDecimal.ZERO) != 0;
}
return value != null;
}
}
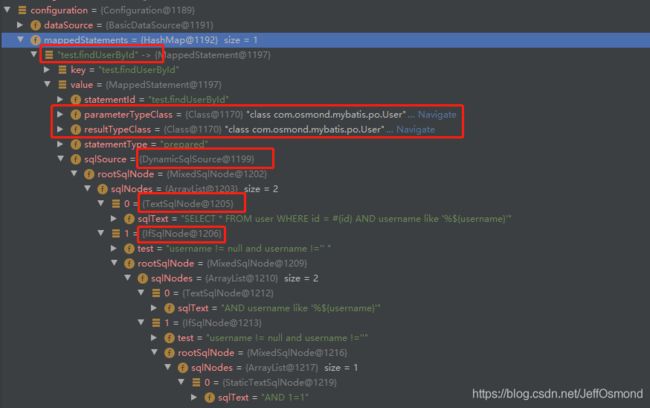
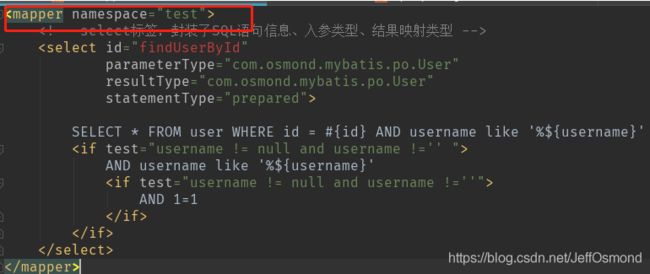
Test:测试UserMapper.xml文件解析
使用之前的测试类测试,结果如下: