《程序设计与算法》之【深度优先搜索】
- 深度优先搜索
- 例题
- 城堡问题(百练2815)
- 踩方格(百练4892)
- Roads(百练1724)
- 生日蛋糕(百练1190)
深度优先搜索
从起点出发,走过的点要做标记,发现有没走过的点,就随意挑一个往前走,走不 了就回退,此种路径搜索策略就称为“深度优先搜索”,简称“深搜”。
(1)判断从V出发是否能走到终点:
bool Dfs(V) {
if( V 为终点)
return true;
if( V 为旧点)
return false;
将V标记为旧点;
对和V相邻的每个节点U {
if( Dfs(U) == true)
return true;
}
return false;
}int main() {
将所有点都标记为新点;
起点 = 1
终点 = 8
cout << Dfs(起点);
}(2)判断从V出发是否能走到终点,如果能,要记录路径:
Node path[MAX_LEN]; //MAX_LEN取节点总数即可
int depth;
bool Dfs(V) {
if( V为终点){
path[depth] = V;
return true;
}
if( V 为旧点)
return false;
将V标记为旧点;
path[depth]=V;
++depth;
对和V相邻的每个节点U {
if( Dfs(U) == true)
return true;
}
--depth;
return false;int main() {
将所有点都标记为新点;
depth = 0;
if( Dfs(起点)) {
for(int i = 0;i <= depth; ++ i)
cout << path[i] << endl;
}
}城堡问题(百练2815)
题目描述
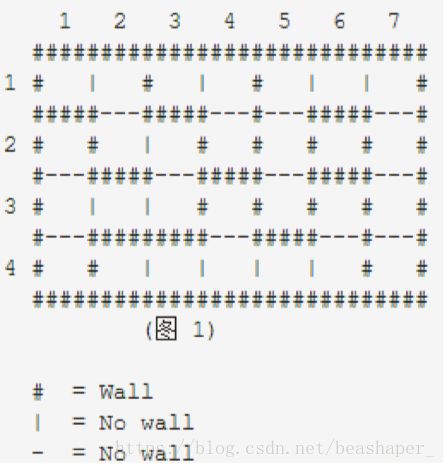
上图是一个城堡地形图,请你编写一个程序,计算城堡一共有多少个房间,最大的房间有多大。城堡被分割成m*n(m<=50,n<=50)个方块,每个方块可以有0~4面墙。
输入:
- 程序从标准输入设备读入数据。
- 第一行是两个整数,分别是南北向、东西向的方块数。
- 在接下来的输入行里,每个方块用一个数字(0≤p≤50)描述。用一个数字表示方块周围的墙,1表示西墙,2表示北墙,4表示东墙,8表示南墙。
- 每个方块用代表其周围墙的数字之和表示。城堡的内墙被计算两次,方块(1,1)的南墙同时也是方块(2,1)的北墙。
- 输入的数据保证城堡至少有两个房间。
输出:
- 城堡的房间数、城堡中最大房间所包括的方块数。
- 结果显示在标准输出设备上。
样例输入:
4
7
11 6 11 6 3 10 6
7 9 6 13 5 15 5
1 10 12 7 13 7 5
13 11 10 8 10 12 13
样例输出:
5
9解题思路
- 把方块看作是节点,相邻两个方块之间如果没有墙,则在方块之间连一条边,这样城堡就能转换成一个图。
- 求房间个数,实际上就是在求图中有多少个极大连通子图。
- 一个连通子图,往里头加任何一个图里的其他点,就会变得不连通,那么这个连通子图就是极大连通子图。
- 对每一个房间,深度优先搜索,从而给这个房间能够到达的所有位置染色。最后统计一共用了几种颜色,以及每种颜色的数量。
比如
1 1 2 2 3 3 3
1 1 1 2 3 4 3
1 1 1 5 3 5 3
1 5 5 5 5 5 3从而一共有5个房间,最大的房间(1)占据9个格子。
解答
#include 踩方格(百练4892)
题目描述
有一个方格矩阵,矩阵边界在无穷远处。我们做如下假设:
a. 每走一步时,只能从当前方格移动一格,走到某个相邻的方格上;
b. 走过的格子立即塌陷无法再走第二次;
c. 只能向北、东、西三个方向走;
请问:如果允许在方格矩阵上走n步(n<=20),共有多少种不同的方案。 2种走法只要有一步不一样,即被认为是不同的方案。
解题思路
递归
从 (i,j) 出发,走n步的方案数,等于以下三项之和:
- 从(i+1,j)出发,走n-1步的方案数。前提:(i+1,j)还没走过
- 从(i,j+1)出发,走n-1步的方案数。前提:(i,j+1)还没走过
- 从(i,j-1)出发,走n-1步的方案数。前提:(i,j-1)还没走过
解答
#include Roads
题目描述
N个城市,编号1到N。城市间有R条单向道路。每条道路连接两个城市,有长度和过路费两个属性。Bob只有K块钱,他想从城市1走到城市N。问最短共需要走多长的路。如果到不了N ,输出-1。
2<=N<=100
0<=K<=10000
1<=R<=10000
每条路的长度 L, 1 <= L <= 100
每条路的过路费T , 0 <= T <= 100
解题思路
从城市 1开始深度优先遍历整个图,找到所有能过到达 N 的走法,选一个最优的。
最优性剪枝:
1) 如果当前已经找到的最优路径长度为L ,那么在继续搜索的过程中,总长度已经大于 等于L的走法,就可以直接放弃,不用走到底了。
另一种通用的最优性剪枝思想 —保存中间计算结果用于最优性剪枝:
2) 用midL[k][m] 表示:走到城市k时总过路费为m的条件下,最优路径的长度。若在 后续的搜索中,再次走到k时,如果总路费恰好为m,且此时的路径长度已经超过 midL[k][m],则不必再走下去了。
解答
#include 生日蛋糕(百练1190)
题目描述
要制作一个体积为Nπ的M层生日蛋糕,每层都是一个圆柱体。 设从下往上数第i(1 <= i <= M)层蛋糕是半径为Ri, 高度为Hi的圆柱。当i < M时 ,要求Ri > Ri+1且Hi > Hi+1。
由于要在蛋糕上抹奶油,为尽可能节约经费,我们希望蛋糕外表面(最下一层的 下底面除外)的面积Q最小。
令Q = Sπ
请编程对给出的N和M,找出蛋糕的制作方案(适当的Ri和Hi的值),使S最小 。 (除Q外,以上所有数据皆为正整数)
解题思路
- 深度优先搜索,搜索什么?
- 枚举每一层可能的高度和半径。
- 如何确定搜索范围?
- 底层蛋糕的最大可能半径和最大可能高度
- 搜索顺序,哪些地方体现搜索顺序?
- 从底层往上搭蛋糕,而不是从顶层往下搭
- 如何剪枝?
- 剪枝1:搭建过程中发现已建好的面积已经不小于目前求得的最优表面积,或者预见到搭完后面积一定会不小于目前最优表面积,则停止搭建(最优性剪枝)
- 剪枝2:搭建过程中预见到再往上搭,高度已经无法安排,或者半径已经无法安排,则停止搭建(可行性剪枝)
- 剪枝3:搭建过程中发现还没搭的那些层的体积,一定会超过还缺的体积,则停止搭建(可行性剪枝)
- 剪枝4:搭建过程中发现还没搭的那些层的体积,最大也到不了还缺的体积,则停止搭建(可行性剪枝)
解答
#include