string类的模拟之深浅拷贝
浅拷贝:浅拷贝只拷贝指针,但拷贝后两个指针指向同一个内存空间,或者可以说,原对象和拷贝对象共用一个实体,任何一个对象的改变都会引起另一个的改变。当类成员不包括指针何引用时,浅拷贝并无问题;但对于指针与引用成员,当对象的生命周期结束后,浅拷贝会造成同一块内存单元被释放两次,导致内存泄漏。
深拷贝:不但对指针进行拷贝,而且对指针指向的内容进行拷贝,经深拷贝后的指针指向两个不同地址。
调用拷贝构造函数后,浅拷贝依然还有联系,深拷贝的两个对象完全独立。浅拷贝类似于文件创建快捷方式,而深拷贝好比文件复制。编译器默认提供的默认拷贝构造函数是浅拷贝,深拷贝的构造函数需自己实现。
//浅拷贝
class String
{
public:
String(const char* pStr = "")//构造函数
:_pStr(new char[strlen(pStr)+1])
{
strcpy(_pStr,pStr);
}
String(const String& s)//拷贝构造函数
{
_pStr = s._pStr;
}
String& operator=(String& s)//赋值运算符重载
{
if(_pStr != s._pStr)//判断是不是自己给自己赋值
{
_pStr = s._pStr;
}
return *this;
}
~String()//析构函数
{
if(NULL != _pStr)
{
delete []_pStr;
_pStr = NULL;
}
}
private:
char* _pStr;
};
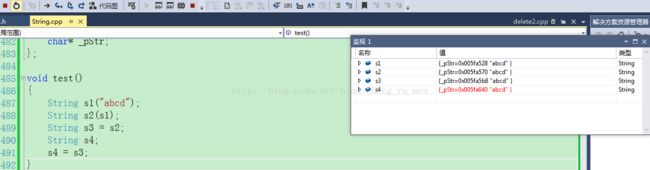
void test()
{
String s1("abcd");
String s2(s1);
String s3 = s2;//调用拷贝构造函数(编译器会s2直接初始化s3)
String s4;//s4对象已经存在了
s4 = s3;//编译器会调用赋值运算符重载将s3的值赋给s4
}
int main()
{
test();
return 0;
} 
S1,S2,S3,S4,指针指向的是同一块空间,根据栈帧的开辟原则,先对S4,进行析构,然后S4的空间被释放,S4,接着被置空,接下来堆S3进行析构时,程序崩溃。
既然如此,我们采用深拷贝的方法来构造对象,使得每个对象都拥有独立的内存空间,在内存释放是不会发生多次析构的问题。
class String //深拷贝
{
public:
String(const char* pStr = "")//构造函数
:_pStr(new char[strlen(pStr)+1])
{
strcpy(_pStr,pStr);
}
String(const String& s)//拷贝构造
:_pStr(new char[strlen(s._pStr)+1])
{
strcpy(_pStr,s._pStr);
}
String& operator=(const String& s)//赋值运算符重载
{
if(_pStr != s._pStr)//判断自赋值
{
char* temp = new char[strlen(s._pStr)+1];//先开辟一段新空间
strcpy(temp,s._pStr);//将原对象的值赋给新空间
delete []_pStr;//释放当前对象
_pStr = temp;//将当前对象指向新开辟的空间
}
return *this;
}
~String()//析构
{
if(NULL != _pStr)
{
delete[]_pStr;
_pStr = NULL;
}
}
private:
char* _pStr;
};
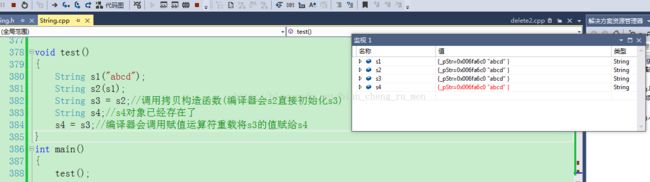
void test()
{
String s1("abcd");
String s2(s1);
String s3 = s2;//调用拷贝构造函数(编译器会s2直接初始化s3)
String s4;//s4对象已经存在了
s4 = s3;//编译器会调用赋值运算符重载将s3的值赋给s4
}
int main()
{
test();
system("pause");
return 0;
} 我们可以看到没个对象都新开辟了一块内存,在析构的时候不会因为析构多次二发生内存泄漏。
深拷贝的现代写法,基本思想利用临时对象来构造出需要拷贝的对象,然后将个对象的内容交换。(可以看做是一种剥夺)//深拷贝(简洁版2)
class String
{
public:
String(const char* pStr = "")//构造函数
:_pStr(new char[strlen(pStr)+1])
{
if(0 == *pStr)
{
*_pStr = '\0';
}
else
{
strcpy(_pStr,pStr);
}
}
String(String& s)//拷贝构造
:_pStr(NULL)//防止交换后temp指向随机空间,本函数调用结束导致内存泄漏以致崩溃
{
String temp(s._pStr);//如果不给出临时变量,交换后s的值将为NULL
std::swap(_pStr,temp._pStr);
}
//1
String& operator=(const String &s)//赋值运算符重载
{
if(_pStr != s._pStr)
{
String temp(s._pStr);//如果不给出临时变量,交换后s的值将为NULL
std::swap(_pStr,temp._pStr);
}
return *this;
}
/* 2
String& operator=(const String& s)
{
if (this != &s)
{
String temp(s);
std::swap(_pStr, temp._pStr);
}
return *this;
}*/
/* 3
String& operator=(String temp)
{
std::swap(_pStr, temp._pStr);
return *this;
}*/
~String()//析构函数
{
if(NULL == _pStr)
{
return;
}
else
{
delete[]_pStr;
_pStr = NULL;
}
}
private:
char* _pStr;
};
void test()
{
String s1("abcd");
String s2(s1);
String s3 = s2;//调用拷贝构造函数(编译器会s2直接初始化s3)
String s4;//s4对象已经存在了
s4 = s3;//编译器会调用赋值运算符重载将s3的值赋给s4
}
int main()
{
test();
system("pause");
return 0;
} String.cpp
#include
#include
#include
#include "String.h"
using namespace std;
现代写法 ----- 剥夺 -------利用构造函数创建,然后交换
String::String(const String& s)
:_size(s._size)
, _capacity(s._capacity)
, _str(new char[strlen(s._str) + 1])
{
strcpy(_str, s._str);
}
//String::String(const String& s)
//:_str(NULL)
//{
// //构造函数
// String tmp(s._str);
// //交换
// swap(_str, tmp._str);
//}
String& String::operator=(const String& s)
{
//if (this != &s)//自赋值
//{
// delete[]_str; //释放原有空间
// _str = new char[strlen(s._str) + 1];
// strcpy(_str, s._str);
// _size = s._size;
// _capacity = s._capacity;
//}
//return *this;
String tmp(s._str);
swap(_str, tmp._str);
return *this;
//swap(_str, s._str); //不为错,额外的内存开销
//return *this;
}
String::~String()
{
if (_str != NULL)
{
delete[]_str;
_str = NULL; //可置可不置空
_size = 0;
_capacity = 0;
}
}
const char* String::c_str()
{
return _str;
}
void String::Swap(String& s) //s1.Swap(s2);
{
assert(this != &s);
swap(_str, s._str);
swap(_size, s._size);
swap(_capacity, s._capacity);
}
void String::Expand(size_t n)
{
if (n > _capacity)
{
char* tmp = new char[_capacity];
strcpy(tmp, _str);
delete[]_str;
_str = tmp;
_capacity = n;
}
}
void String::PushBack(char ch)
{
if (_size >= _capacity)
{
Expand(_capacity * 2);
}
_str[_size++] = ch;
_str[_size] = '\0';
}
void String::PushBack(const char* str)
{
assert(str);
size_t len = strlen(str);
if (_size + len > _capacity)
{
Expand(_size + len);
}
strcpy(_str + _size, str);
_size += len;
}
void String::PushFront(char ch)
{
if (_size + 1 > _capacity) //增容
{
Expand(_capacity * 2);
}
for (int i = _size + 1; i >= 0; --i) //搬移
{
_str[i + 1] = _str[i];
}
_str[0] = ch;
_size++;
}
void String::PushFront(const char* str)
{
assert(str);
size_t len = strlen(str);
if (len + _size > _capacity)
{
Expand(len + _size);
}
for (int i = _size; i >= 0; --i)
{
_str[i + len] = _str[i];
}
memcpy(_str, str, len);
_size += len;
}
void String::Insert(size_t pos, char ch)
{
assert(pos < _size);
if (_size + 1 > _capacity)
{
Expand(_capacity * 2);
}
for (int i = _size; i >= (int)pos; --i) //强转pos防止发生无限循环
{
_str[i + 1] = _str[i];
}
_str[pos] = ch;
_size++;
}
void String::Insert(size_t pos, const char* str)
{
assert(str);
assert(pos <= _size);
size_t len = strlen(str);
if (len + _size > _capacity)
{
Expand(_size + len);
}
for (int i = _size; i >= (int)pos; --i)
{
_str[i + len] = _str[i];
}
while (*str != '\0')
{
_str[pos++] = *(str++);
}
_size += len;
}
void String::Erase(size_t pos, size_t n)
{
//1.pos
assert(pos < _size);
//pos+n
if (pos + n >= _size)
{
_str[pos] = '\0';
_size = pos;
}
else
{
strcpy(_str + pos, _str + pos + n);
_size -= n;
}
}
size_t String::Find(char ch, size_t pos)
{
for (size_t i = pos; i < _size; i++)
{
if (ch == _str[i]) return i;
}
return -1;
}
size_t String::Find(const char* str, size_t pos)
{
assert(str != NULL);
assert(pos < _size);
assert(_size > strlen(str));
const char* src = _str + pos;
while (*src != '\0')//标记母串的查找位置
{
const char* match = str;
const char* cur = src;
while (*match != '\0' && *match == *cur)//子串没有走到结尾
//子串的当前字符不等于母串
{
match++;
cur++;
}
if (*match == '\0')
{
return src - _str;
}
src++;
}
return -1;
}
void String::Replace(size_t pos, int len, const char* sub2)
{
//pos > _size == _size < _size
//len > strlen(sub2) pos + len > size
//sub2
}
bool String::operator>(const String& s)const
{
size_t i = 0;
while (_str[i] != '\0' && s._str[i] != '\0')
{
if (_str[i] == s._str[i])
i++;
else if (_str[i] > s._str[i])
return true;
else
return false;
}
if (_str[i] != '\0')
return true;
else
return false;
}
bool String::operator>=(const String& s)const
{
return *this > s || *this == s;
}
bool String::operator<(const String& s)const
{
return !(*this >= s);
}
bool String::operator<=(const String& s)const
{
return !(*this > s);
}
bool String::operator==(const String& s)const
{
size_t i = 0;
while (_str[i] != '\0' && s._str[i] != '\0')
{
if (_str[i] == s._str[i])
i++;
else
return false;
}
if (_str[i] == '\0' && s._str[i] == '\0')
return true;
else
return false;
}
bool String::operator!=(const String& s)const
{
return !(*this == s);
}
String String::operator+(char ch)
{
String tmp(*this); //构造
tmp.PushBack(ch);
return tmp;
}
String& String::operator+=(char ch)
{
PushBack(ch);
return *this;
}
String String::operator+(const char* str)
{
String tmp(*this);
tmp.PushBack(str);
return tmp;
}
String& String::operator+=(const char* str)
{
PushBack(str);
return *this;
}
void TestString()
{
String s1("change world");
cout << s1.Find("wor")< #pragma
#include
#define NULL 0
class String
{
public:
String(const char* str = "")
:_str(new char[strlen(str) + 1])
, _size(strlen(str))
, _capacity(strlen(str)) //size和capacity保持一致'\0'不算给_capacity
{
strcpy(_str, str);
}
String(const String& s);
String& operator=(const String& s);
~String();
const char* c_str();
void Swap(String& s);
void Expand(size_t n);
void PushBack(char ch);
void PushBack(const char* str);
void PushFront(char ch);
void PushFront(const char* str);
void Insert(size_t pos, char ch);
void Insert(size_t pos, const char* str);
void Erase(size_t pos, size_t n = 1);
void Replace(size_t pos, int len, const char* sub2);
size_t Find(char ch, size_t pos);
size_t Find(const char* str, size_t pos = 0);
String operator+(char ch);
String& operator+=(char ch);
String operator+(const char* str);
String& operator+=(const char* str);
bool operator>(const String& s)const;
bool operator>=(const String& s)const;
bool operator<(const String& s)const;
bool operator<=(const String& s)const;
bool operator==(const String& s)const;
bool operator!=(const String& s)const;
private:
size_t _size;
size_t _capacity;
char* _str;
};