HDU4456————Crowd(离散化,坐标转化,二维树状数组)
Crowd
Time Limit: 5000/2000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 2403 Accepted Submission(s): 575
Problem Description
City F in the southern China is preparing lanterns festival celebration along the streets to celebrate the festival.
Since frequent accidents had happened last year when the citizens went out to admire the colorful lanterns, City F is planning to develop a system to calculate the degree of congestion of the intersection of two streets.
The map of City F is organized in an N×N grid (N north-south streets and N west-east street). For each intersection of streets, we define a density value for the crowd on the intersection.
Initially, the density value of every intersection is zero. As time goes by, the density values may change frequently. A set of cameras with new graphical recognition technology can calculate the density value of the intersection easily in a short time.
But the administrator of the police office is planning to develop a system to calculate the degree of congestion. For some consideration, they come up with a conception called "k-dimension congestion degree". The "k-dimension congestion degree" of intersection (x0,y0) is represented as "c(x0,y0,k)", and it can be calculated by the formula below:
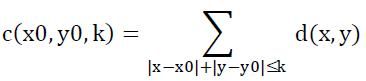
Here, d(x,y) stands for the density value on intersection (x,y) and (x,y) must be in the N×N grid. The formula means that all the intersections in the range of manhattan distance k from (x0,y0) effect the k-dimension congestion degree of (x0,y0) equally, so we just simply sum them up to get the k-dimension congestion degree of (x0,y0).
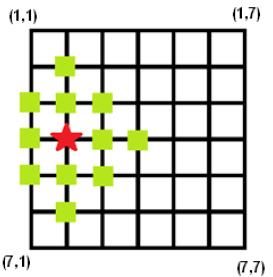
The figure below shows a 7×7 grid, and it shows that if you want to get the 2-dimension congestion degree of intersection (4,2),you should sum up the density values of all marked intersections.
Since frequent accidents had happened last year when the citizens went out to admire the colorful lanterns, City F is planning to develop a system to calculate the degree of congestion of the intersection of two streets.
The map of City F is organized in an N×N grid (N north-south streets and N west-east street). For each intersection of streets, we define a density value for the crowd on the intersection.
Initially, the density value of every intersection is zero. As time goes by, the density values may change frequently. A set of cameras with new graphical recognition technology can calculate the density value of the intersection easily in a short time.
But the administrator of the police office is planning to develop a system to calculate the degree of congestion. For some consideration, they come up with a conception called "k-dimension congestion degree". The "k-dimension congestion degree" of intersection (x0,y0) is represented as "c(x0,y0,k)", and it can be calculated by the formula below:
Here, d(x,y) stands for the density value on intersection (x,y) and (x,y) must be in the N×N grid. The formula means that all the intersections in the range of manhattan distance k from (x0,y0) effect the k-dimension congestion degree of (x0,y0) equally, so we just simply sum them up to get the k-dimension congestion degree of (x0,y0).
The figure below shows a 7×7 grid, and it shows that if you want to get the 2-dimension congestion degree of intersection (4,2),you should sum up the density values of all marked intersections.
Input
These are multiple test cases.
Each test case begins with a line with two integers N, M, meaning that the city is an N×N grid and there will be M queries or events as time goes by. (1 ≤ N ≤10 000, 1 ≤ M ≤ 80 000) Then M lines follow. Each line indicates a query or an event which is given in form of (p, x, y, z), here p = 1 or 2, 1 ≤ x ≤ N, 1 ≤ y ≤ N.
The meaning of different p is shown below.
1. p = 1 the value of d(x,y) is increased by z, here -100 ≤ z ≤ 100.
2. p = 2 query the value of c(x,y,z), here 0 ≤ z ≤ 2N-1.
Input is terminated by N=0.
Each test case begins with a line with two integers N, M, meaning that the city is an N×N grid and there will be M queries or events as time goes by. (1 ≤ N ≤10 000, 1 ≤ M ≤ 80 000) Then M lines follow. Each line indicates a query or an event which is given in form of (p, x, y, z), here p = 1 or 2, 1 ≤ x ≤ N, 1 ≤ y ≤ N.
The meaning of different p is shown below.
1. p = 1 the value of d(x,y) is increased by z, here -100 ≤ z ≤ 100.
2. p = 2 query the value of c(x,y,z), here 0 ≤ z ≤ 2N-1.
Input is terminated by N=0.
Output
For each query, output the value for c(x,y,z) in a line.
Sample Input
8 5 1 8 8 1 1 1 1 -2 2 5 5 6 1 5 5 3 2 2 3 9 3 2 1 3 2 -9 2 3 2 0 0
Sample Output
1 1 -9
一个棋盘,可以对上面的点进行两种操作,给某个点赋值,或者查询某个点周围曼哈顿距离小于等于k的点的值的和。
如果说查询的是某个矩形,显然就可以直接用二维树状数组。
但是实际上是一个菱形。
所以就需要用到坐标转化。
使得X=x-y,Y=x+y,那么就可以把菱形转化成一个矩形
然后用map离散化一下就行
不过MLE了= =不知道为什么
不知道是不是不能用map离散化
#include
#include
#include
#include