本地安装的python库同步到pycharm中
将pip命令行安装的库同步导入到pycharm中
一、利用pip安装第三方库
安装第三方python库的两种方法:
1.用pip命令进行安装。
2.利用第三方软件Aconda
可以参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/jesselzj/p/7086521.html(Windows10+Python3下安装NumPy+SciPy+Matplotlib )
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_40174045/article/details/81106190(Python3.7安装numpy与scipy库(win10))
pip命令安装:1)在线安装 2)离线安装
离线安装:http://www.lfd.uci.edu/~gohlke/pythonlibs/
注意:四个包的安装顺序是:numpy+mkl scipy matplotlib sklearn
A.在上面的网址中找到需要的.whl文件。
【注意】文件名中的cp**应与安装的版本相匹配。如安装Python3.4,应下载对应的cp34的.whl文件。并且注意系统的位数,本文环境是64bit。
B.将下载好的.whl文件放在python安装路径下的Scripts目录下,如:本机F:\Python3.7_64bit\Scripts。
C.在dos环境下,利用cmd命令行,用pip install命令安装对应的wheel包。
【注意】需要提前安装好wheel,利用 pip install wheel命令行安装wheel。
执行命令 >pip install F:\XXX\XX\Scripts\**.whl
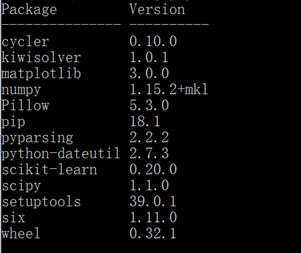
安装成功,执行 pip list命令,可以看到包的目录,如:
注意:四个软件的安装顺序是:numpy+mkl scipy matplotlib sklearn
二、同步本地库到pycharm中
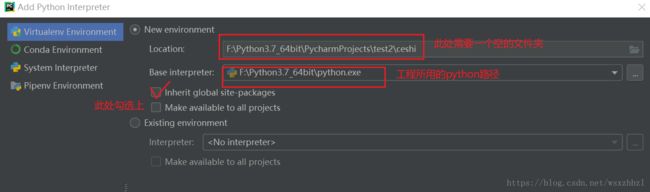
利用pycharm创建一个新的工程,
Files-Settings-Project-Project Interpreter
右上角设置中,选择Add,添加新的解释器。
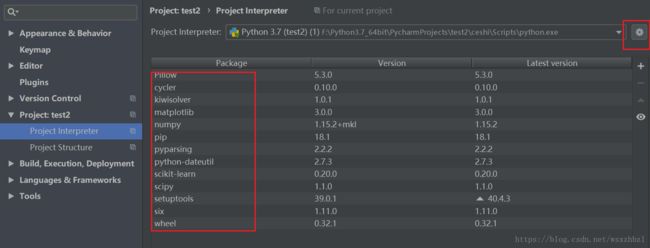
apply之后,可以看到本地安装的库添加进工程内。
测试一下库安装是否成功:
测试代码来自:http://www.cnblogs.com/jasonfreak/p/5441512.html 感谢作者。
from numpy import array
from numpy.random import normal
from matplotlib import pyplot
def gen_data():
heights = []
weights = []
grades = []
N = 10000
for i in range(N):
while True:
# 身高服从均值172,标准差为6的正态分布
height = normal(172, 6)
if 0 < height:
break
while True:
# 体重由身高作为自变量的线性回归模型产生,误差服从标准正态分布
weight = (height - 80) * 0.7 + normal(0, 1)
if 0 < weight:
break
while True:
# 分数服从均值为70,标准差为15的正态分布
score = normal(70, 15)
if 0 <= score and score <= 100:
grade = 'E' if score < 60 else (
'D' if score < 70 else ('C' if score < 80 else ('B' if score < 90 else 'A')))
break
heights.append(height)
weights.append(weight)
grades.append(grade)
return array(heights), array(weights), array(grades)
# 绘制柱状图
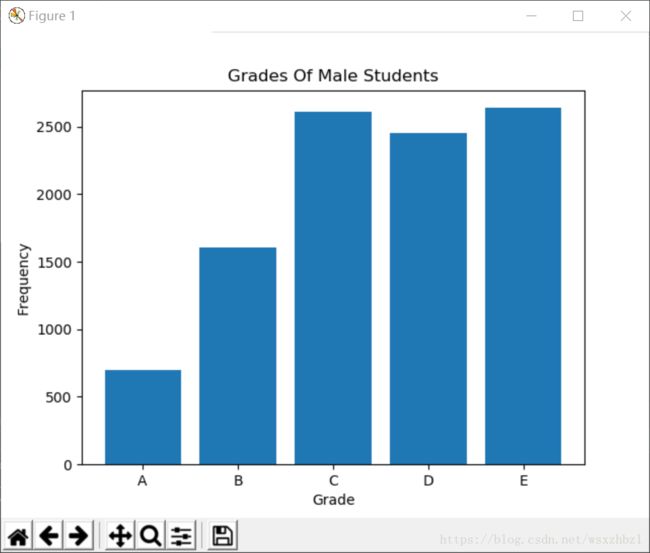
def draw_bar(grades):
xticks = ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E']
grade_group = {}
# 对每一类成绩进行频数统计
for grade in grades:
grade_group[grade] = grade_group.get(grade, 0) + 1
# 创建柱状图
# 第一个参数为柱的横坐标
# 第二个参数为柱的高度
# 参数align为柱的对齐方式,以第一个参数为参考标准
pyplot.bar(range(5), [grade_group.get(xtick, 0) for xtick in xticks], align='center')
# 设置柱的文字说明
# 第一个参数为文字说明的横坐标
# 第二个参数为文字说明的内容
pyplot.xticks(range(5), xticks)
# 设置横坐标的文字说明
pyplot.xlabel('Grade')
# 设置纵坐标的文字说明
pyplot.ylabel('Frequency')
# 设置标题
pyplot.title('Grades Of Male Students')
# 绘图
pyplot.show()
# 绘制饼形图
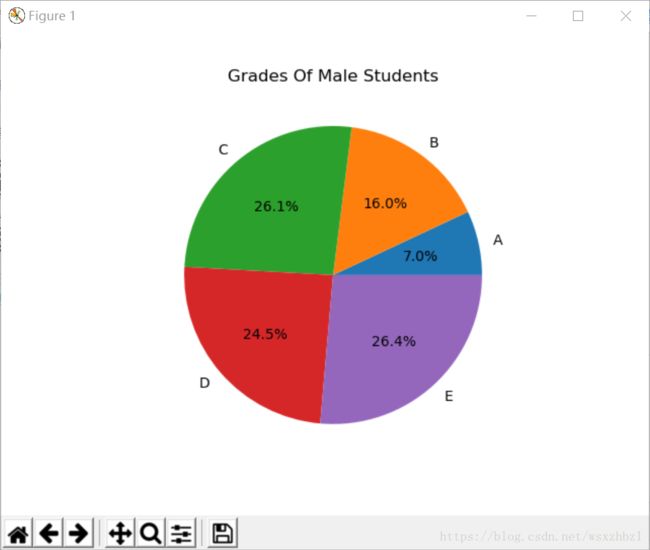
def draw_pie(grades):
labels = ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E']
grade_group = {}
for grade in grades:
grade_group[grade] = grade_group.get(grade, 0) + 1
# 创建饼形图
# 第一个参数为扇形的面积
# labels参数为扇形的说明文字
# autopct参数为扇形占比的显示格式
pyplot.pie([grade_group.get(label, 0) for label in labels], labels=labels, autopct='%1.1f%%')
pyplot.title('Grades Of Male Students')
pyplot.show()
# 绘制直方图
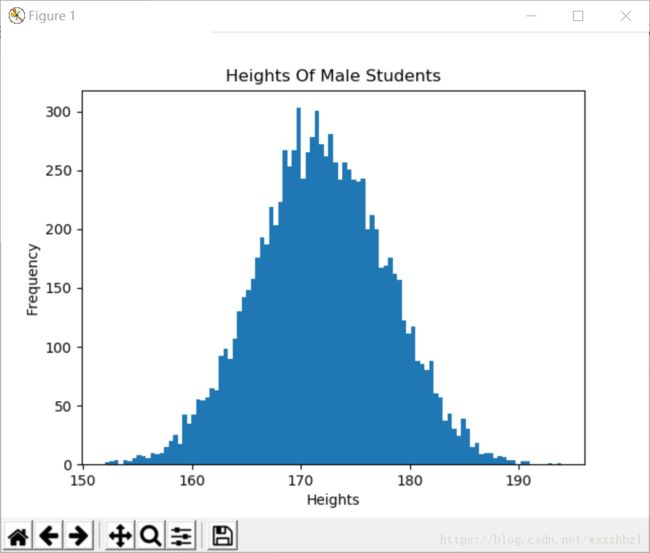
def draw_hist(heights):
# 创建直方图
# 第一个参数为待绘制的定量数据,不同于定性数据,这里并没有事先进行频数统计
# 第二个参数为划分的区间个数
pyplot.hist(heights, 100)
pyplot.xlabel('Heights')
pyplot.ylabel('Frequency')
pyplot.title('Heights Of Male Students')
pyplot.show()
# 绘制累积曲线
def draw_cumulative_hist(heights):
# 创建累积曲线
# 第一个参数为待绘制的定量数据
# 第二个参数为划分的区间个数
# normed参数为是否无量纲化
# hist type参数为'step',绘制阶梯状的曲线
# cumulative参数为是否累积
pyplot.hist(heights, 20, normed=True, histtype='step', cumulative=True)
pyplot.xlabel('Heights')
pyplot.ylabel('Frequency')
pyplot.title('Heights Of Male Students')
pyplot.show()
# 绘制散点图
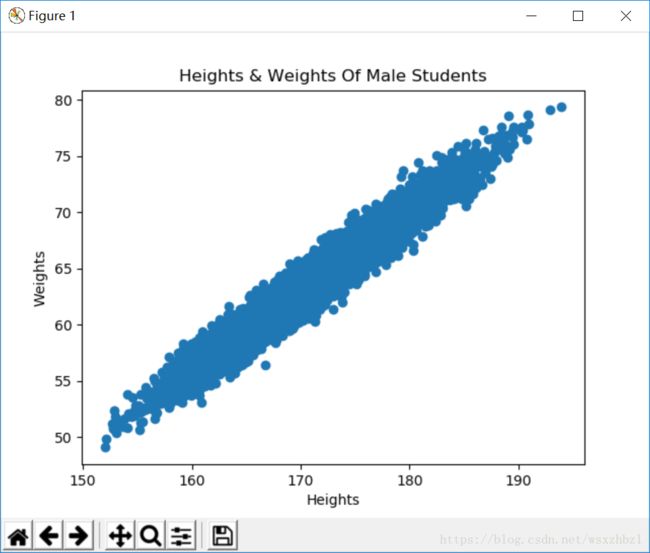
def draw_scatter(heights, weights):
# 创建散点图
# 第一个参数为点的横坐标
# 第二个参数为点的纵坐标
pyplot.scatter(heights, weights)
pyplot.xlabel('Heights')
pyplot.ylabel('Weights')
pyplot.title('Heights & Weights Of Male Students')
pyplot.show()
# 绘制箱形图
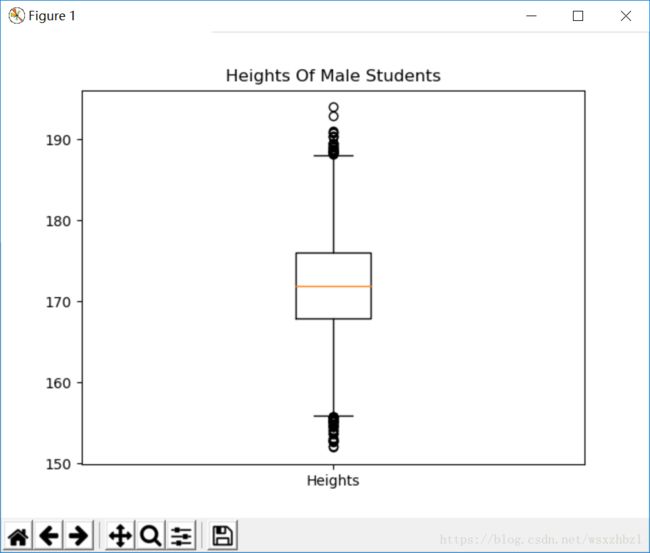
def draw_box(heights):
# 创建箱形图
# 第一个参数为待绘制的定量数据
# 第二个参数为数据的文字说明
pyplot.boxplot([heights], labels=['Heights'])
pyplot.title('Heights Of Male Students')
pyplot.show()
data = gen_data()
print(data)
heights = data[0]
weights = data[1]
grades = data[2]
draw_bar(grades)
draw_pie(grades)
draw_hist(heights)
draw_cumulative_hist(heights)
draw_scatter(heights, weights)
draw_box(heights)
注意:function命名时采用lowercase。即采用小写命名。可以加下划线。
运行结果: