MySQL学习笔记(4)—— 数据查询语言DQL
文章目录
- 一、查询
- 1. 简单查询
- 2. 条件查询
- (1)单条件查询
- (2)多条件查询
- (3)IN和LIKE的使用
- 二、MySQL内置函数
- 1. 函数now()
- 2. 函数date_format()
- 3. 聚合函数
- 4. 函数ifnull()
- 5. case when
- 三、查询结果排序与分页
- 1. 排序的应用场景
- 2. order by的使用
- 3. limit的使用
- 四、GROUP BY与HAVING的使用
- 1. 应用场景
- 2. group by的使用
- 3. having的使用
- 五、GROUP_CONCAT函数的使用
- 1. 应用场景
- 2. group_concat的使用
- 六、使用DISTINCT去重
- 七、表连接(内连接、外连接、自连接)
- 1. 什么是表连接
- 2. 表连接的几种方式
- 3. 各种表连接的区别
- (1)内连接
- (2)左连接
- (3)自连接
- 4. 示例
- 八、子查询EXISTS和IN
- 1. 子查询in
- 2. 子查询exists
一、查询
1. 简单查询
-
在SQL中,使用select语句来查询数据。不同的关系数据库,select语法会有细微差别
-
mysql中查询语法
SELECT column_name1, column_name2 FROM table_name [WHERE where_condition] [GROUP BY {col_name | expr | position}, ... [WITH ROLLUP]] [HAVING where_condition] [ORDER BY {col_name | expr | position} [ASC | DESC], ... [WITH ROLLUP]] [LIMIT {[offset,] row_count | row_count OFFSET offset}] -
示例
# 查询所有属性/字段(列) mysql> select * from contacts; +----+------+-----------+ | id | name | phone | +----+------+-----------+ | 1 | 小明 | 123456789 | | 3 | 李四 | 123151361 | +----+------+-----------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec) # 查询特定的属性/字段(列) mysql> select name,phone from contacts; +------+-----------+ | name | phone | +------+-----------+ | 小明 | 123456789 | | 李四 | 123151361 | +------+-----------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec) # 带where条件的查询 mysql> select phone from contacts where name = '李四'; +-----------+ | phone | +-----------+ | 123151361 | +-----------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
2. 条件查询
- 使用
select中的where子句进行条件查询 - 在SQL中,
insert、update、delete和select后面都能带where子句,用于插入、修改、删除或查询指定条件的记录
(1)单条件查询
(2)多条件查询
-
在where子句中,使用
and、or可以把两个或多个过滤条件结合起来。 -
语法:
SELECT 属性名 FROM 表名 WHERE condition1 AND condition2 OR condition3 -
示例
-
先建个测试表
create table employee( id int not null auto_increment primary key, name varchar(30) comment '姓名', sex varchar(1) comment '性别', salary int comment '薪资(元)' )ENGINE=InnoDB default charset=utf8; insert into employee(name,sex,salary) values('张三','男',5500); insert into employee(name,sex,salary) values('李洁','女',4500); insert into employee(name,sex,salary) values('李小梅','女',4200); insert into employee(name,sex,salary) values('欧阳辉','男',7500); insert into employee(name,sex,salary) values('李芳','女',8500); insert into employee(name,sex,salary) values('张江','男',6800); insert into employee(name,sex,salary) values('李四','男',12000); insert into employee(name,sex,salary) values('王五','男',3600); insert into employee(name,sex,salary) values('马小龙','男',6000); insert into employee(name,sex,salary) values('龙五','男',8000); insert into employee(name,sex,salary) values('冯小芳','女',10000); insert into employee(name,sex,salary) values('马小龙','女',4000); -
开始查询
mysql> select * from employee where sex != '男'; +----+--------+------+--------+ | id | name | sex | salary | +----+--------+------+--------+ | 2 | 李洁 | 女 | 4500 | | 3 | 李小梅 | 女 | 4200 | | 5 | 李芳 | 女 | 8500 | | 11 | 冯小芳 | 女 | 10000 | | 12 | 马小龙 | 女 | 4000 | +----+--------+------+--------+ 5 rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql> select * from employee where salary>10000; +----+------+------+--------+ | id | name | sex | salary | +----+------+------+--------+ | 7 | 李四 | 男 | 12000 | +----+------+------+--------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) mysql> select * from employee where salary between 10000 and 12000; +----+--------+------+--------+ | id | name | sex | salary | +----+--------+------+--------+ | 7 | 李四 | 男 | 12000 | | 11 | 冯小芳 | 女 | 10000 | +----+--------+------+--------+ 2 rows in set (0.12 sec) mysql> select * from employee where sex='男' and salary between 10000 and 12000; +----+------+------+--------+ | id | name | sex | salary | +----+------+------+--------+ | 7 | 李四 | 男 | 12000 | +----+------+------+--------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) -
(3)IN和LIKE的使用
-
运算符 IN 允许我们在 WHERE 子句中过滤某个字段的多个值
- 语法:
SELECT column_name FROM table_name WHERE column_name IN(value1, value2, …);
- 语法:
-
在where子句中,有时候我们需要查询包含xxx 字符串的所有记录,这时就需要用到运算符like
-
语法:
SELECT column_name FROM table_name WHERE column_name LIKE ‘%value%’; -
LIKE子句中的
%类似于正则表达式中的*匹配任意0个或多个字符 -
LIKE子句中的
_匹配任意单个字符 -
LIKE子句中如果没有
%和_,就相当于运算符=的效果 -
示例:找出姓张的人的信息
mysql> select * from employee where name like '张%'; +----+------+------+--------+ | id | name | sex | salary | +----+------+------+--------+ | 1 | 张三 | 男 | 5500 | | 5 | 张江 | 男 | 6800 | +----+------+------+--------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
-
二、MySQL内置函数
-
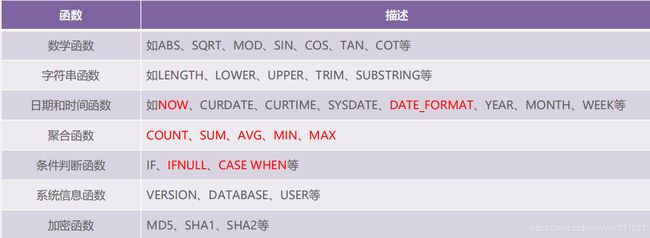
我们通常说的MySQL函数指的是MySQL数据库提供的内置函数,包括数学函数、字符串函数、日期和时间函数、聚合函数、条件判断函数等,这些内置函数可以帮助用户更方便地处理表中的数据,简化用户的操作
-
部分简单函数示例
mysql> select abs(-10); +----------+ | abs(-10) | +----------+ | 10 | +----------+ 1 row in set (0.03 sec) mysql> select length('123456789'); +---------------------+ | length('123456789') | +---------------------+ | 9 | +---------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) mysql> select length('123456789') from dual; #从虚拟表dual中获取,加不加没区别 +---------------------+ | length('123456789') | +---------------------+ | 9 | +---------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
1. 函数now()
-
now()用于返回当前的日期和时间
mysql> select now(); +---------------------+ | now() | +---------------------+ | 2020-06-23 19:23:53 | +---------------------+ 1 row in set (0.10 sec) -
应用场景:在实际应用中,大多数业务表都会带一个创建时间create_time字段,用于记录每一条数据的产生时间。在向表中插入数据时,就可以在insert语句中使用now()函数
insert into user(id, name, create_time) values(1, 'zhangsan', now());
2. 函数date_format()
-
函数
date_format()用于以指定的格式显示日期/时间mysql> select date_format(now(),'%y/%m/%d %H:%i:%s'); +----------------------------------------+ | date_format(now(),'%y/%m/%d %H:%i:%s') | +----------------------------------------+ | 20/06/23 19:26:41 | +----------------------------------------+ 1 row in set (0.09 sec) -
应用场景:在实际应用中,一般会按照标准格式存储日期/时间,如 2019-12-13 14:15:16 。在查询使用数据时,往往会有不同的格式要求,这时就需要使用date_format()函数进行格式转换
select name, date_format(birthday, '%Y/%m/%d') from user;
3. 聚合函数
-
聚合函数是对一组值进行计算,并返回单个值
-
示例
mysql> select * from employee; +----+--------+------+--------+ | id | name | sex | salary | +----+--------+------+--------+ | 1 | 张三 | 男 | 5500 | | 2 | 李洁 | 女 | 4500 | | 3 | 李小梅 | 女 | 4200 | | 4 | 欧阳辉 | 男 | 7500 | | 5 | 李芳 | 女 | 8500 | | 6 | 张江 | 男 | 6800 | | 7 | 李四 | 男 | 12000 | | 8 | 王五 | 男 | 3600 | | 9 | 马小龙 | 男 | 6000 | | 10 | 龙五 | 男 | 8000 | | 11 | 冯小芳 | 女 | 10000 | | 12 | 马小龙 | 女 | 4000 | +----+--------+------+--------+ 12 rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql> select sum(salary) from employee; +-------------+ | sum(salary) | +-------------+ | 80600 | +-------------+ 1 row in set (0.10 sec) mysql> select avg(salary) from employee; +-------------+ | avg(salary) | +-------------+ | 6716.6667 | +-------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) mysql> select count('女员工') from employee where sex='女'; +-----------------+ | count('女员工') | +-----------------+ | 5 | +-----------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) # 以下是一个错误示例,如果没有min(salary),会选出所有名字, # 这里因为min(salary)只有一个,所以通过限制name也只显示了一个。 # 但这个其实不是薪资最少者的名字 mysql> select name,min(salary) from employee; +------+-------------+ | name | min(salary) | +------+-------------+ | 张三 | 3600 | +------+-------------+ 1 row in set (0.10 sec) # 这是找出薪资最低员工的正确写法,后面还会详细说明 mysql> select * from employee order by salary asc limit 1; +----+------+------+--------+ | id | name | sex | salary | +----+------+------+--------+ | 8 | 王五 | 男 | 3600 | +----+------+------+--------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
4. 函数ifnull()
-
函数
ifnull()用于处理NULL值 -
ifnull(v1,v2):如果 v1 的值不为 NULL,则返回 v1,否则返回 v2。mysql> select ifnull(1/0,0); +---------------+ | ifnull(1/0,0) | +---------------+ | 0.0000 | +---------------+ 1 row in set (0.04 sec) mysql> select ifnull(1,0); +-------------+ | ifnull(1,0) | +-------------+ | 1 | +-------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
5. case when
-
case when是流程控制语句,可以在SQL语句中使用case when来获取更加准确和直接的结果 -
SQL中的case when类似于编程语言中的if else或者switch
-
语法
#case when的语法有2种 CASE [col_name] WHEN [value1] THEN [result1]…ELSE [default] END CASE WHEN [expr] THEN [result1]…ELSE [default] END -
示例
mysql> select -> id,name, -> case sex -> when '男' then 'F' -> when '女' then 'M' -> else 'UNKNOWN' -> end as sex_code, -> salary -> from employee; +----+--------+----------+--------+ | id | name | sex_code | salary | +----+--------+----------+--------+ | 1 | 张三 | F | 5500 | | 2 | 李小梅 | M | 4200 | | 3 | 欧阳辉 | F | 7500 | | 4 | 李芳 | M | 8500 | | 5 | 张江 | F | 6800 | | 6 | 李四 | F | 12000 | | 7 | 王五 | F | 3600 | | 8 | 马小龙 | F | 6000 | | 9 | 龙五 | F | 8000 | | 10 | 冯小芳 | M | 10000 | | 11 | 马小龙 | M | 4000 | +----+--------+----------+--------+ 11 rows in set (0.00 sec)
三、查询结果排序与分页
1. 排序的应用场景
- 使用select选出数据后,往往还需要对数据进行一些处理
- 学生按身高从高到低进行排列
- 双十一,某商城的商品交易量排行榜
- 博客中的文章按时间先后顺序显示
2. order by的使用
-
在SQL中,使用
order by对查询结果集进行排序,可以按照一列或多列进行排序。 -
语法
#order by语法 SELECT column_name1, column_name2 FROM table_name1, table_name2 ORDER BY column_name, column_name [ASC|DESC]ASC表示按(字段)升序排列,DESC表示按降序排列- 默认情况下,对列按升序排列
-
示例
mysql> select * from employee order by salary asc; +----+--------+------+--------+ | id | name | sex | salary | +----+--------+------+--------+ | 8 | 王五 | 男 | 3600 | | 12 | 马小龙 | 女 | 4000 | | 3 | 李小梅 | 女 | 4200 | | 2 | 李洁 | 女 | 4500 | | 1 | 张三 | 男 | 5500 | | 9 | 马小龙 | 男 | 6000 | | 6 | 张江 | 男 | 6800 | | 4 | 欧阳辉 | 男 | 7500 | | 10 | 龙五 | 男 | 8000 | | 5 | 李芳 | 女 | 8500 | | 11 | 冯小芳 | 女 | 10000 | | 7 | 李四 | 男 | 12000 | +----+--------+------+--------+ 12 rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql> select * from employee order by salary desc; +----+--------+------+--------+ | id | name | sex | salary | +----+--------+------+--------+ | 7 | 李四 | 男 | 12000 | | 11 | 冯小芳 | 女 | 10000 | | 5 | 李芳 | 女 | 8500 | | 10 | 龙五 | 男 | 8000 | | 4 | 欧阳辉 | 男 | 7500 | | 6 | 张江 | 男 | 6800 | | 9 | 马小龙 | 男 | 6000 | | 1 | 张三 | 男 | 5500 | | 2 | 李洁 | 女 | 4500 | | 3 | 李小梅 | 女 | 4200 | | 12 | 马小龙 | 女 | 4000 | | 8 | 王五 | 男 | 3600 | +----+--------+------+--------+ 12 rows in set (0.00 sec) # 两个字段一起排 mysql> select * from employee order by sex desc,salary desc; +----+--------+------+--------+ | id | name | sex | salary | +----+--------+------+--------+ | 7 | 李四 | 男 | 12000 | | 10 | 龙五 | 男 | 8000 | | 4 | 欧阳辉 | 男 | 7500 | | 6 | 张江 | 男 | 6800 | | 9 | 马小龙 | 男 | 6000 | | 1 | 张三 | 男 | 5500 | | 8 | 王五 | 男 | 3600 | | 11 | 冯小芳 | 女 | 10000 | | 5 | 李芳 | 女 | 8500 | | 2 | 李洁 | 女 | 4500 | | 3 | 李小梅 | 女 | 4200 | | 12 | 马小龙 | 女 | 4000 | +----+--------+------+--------+ 12 rows in set (0.00 sec)
3. limit的使用
-
在
SELECT语句中使用LIMIT子句来约束要返回的记录数,通常使用LIMIT实现分页 -
语法
#limit语法 SELECT column_name1, column_name2 FROM table_name1, table_name2 LIMIT [offset,] row_countoffset指定要返回的第一行的偏移量。第一行(第一条记录)的偏移量是0,而不是1row_count指定要返回的最大行数(返回多少条记录)- 例:
LIMIT 0,20返回最初20条记录
-
分页公式
limit (page-1)\*row_count, row_count
-
示例
mysql> select * from employee limit 3; +----+--------+------+--------+ | id | name | sex | salary | +----+--------+------+--------+ | 1 | 张三 | 男 | 5500 | | 2 | 李小梅 | 女 | 4200 | | 3 | 欧阳辉 | 男 | 7500 | +----+--------+------+--------+ 3 rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql> select * from employee order by salary desc limit 0,5; +----+--------+------+--------+ | id | name | sex | salary | +----+--------+------+--------+ | 6 | 李四 | 男 | 12000 | | 10 | 冯小芳 | 女 | 10000 | | 4 | 李芳 | 女 | 8500 | | 9 | 龙五 | 男 | 8000 | | 3 | 欧阳辉 | 男 | 7500 | +----+--------+------+--------+ 5 rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql> select * from employee order by salary desc limit 10,5; +----+------+------+--------+ | id | name | sex | salary | +----+------+------+--------+ | 7 | 王五 | 男 | 3600 | | 12 | 哈哈 | 男 | NULL | +----+------+------+--------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec) # 综合order和limit,找出工资最多的人 mysql> select * from employee order by salary desc limit 1; +----+------+------+--------+ | id | name | sex | salary | +----+------+------+--------+ | 6 | 李四 | 男 | 12000 | +----+------+------+--------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
四、GROUP BY与HAVING的使用
1. 应用场景
- 用
select语句结合where查询条件获取需要的数据,但在实际的应用中,还会遇到下面这类需求- 公司想知道每个部门有多少名员工-----需按部分分组
- 班主任想统计各科第一名的成绩------需按科目分组
- 某门店想掌握男、女性会员的人数及平均年龄-----需按年龄分组
2. group by的使用
-
从字面上理解,
group by表示根据某种规则对数据进行分组,它必须配合聚合函数进行使用,对数据进行分组后可以用聚合函数进行处理(count、sum、avg、max和min等) -
语法
#group by语法 SELECT column_name, aggregate_function(column_name) FROM table_name GROUP BY column_nameaggregate_function表示聚合函数group by可以对一列或多列进行分组
-
注意: 标准SQL中,select选出的,要么是用于分组的元素/字段,要么是聚合函数
-
示例
-
先准备数据
create table employee( id int not null auto_increment primary key, name varchar(30) comment '姓名', sex varchar(1) comment '性别', salary int comment '薪资(元)', dept varchar(30) comment '部门' )ENGINE=InnoDB default charset=utf8; insert into employee(name,sex,salary,dept) values('张三','男',5500,'A'); insert into employee(name,sex,salary,dept) values('李洁','女',4500,'C'); insert into employee(name,sex,salary,dept) values('李小梅','女',4200,'A'); insert into employee(name,sex,salary,dept) values('欧阳辉','男',7500,'C'); insert into employee(name,sex,salary,dept) values('李芳','女',8500,'A'); insert into employee(name,sex,salary,dept) values('张江','男',6800,'A'); insert into employee(name,sex,salary,dept) values('李四','男',12000,'B'); insert into employee(name,sex,salary,dept) values('王五','男',3600,'B'); insert into employee(name,sex,salary,dept) values('马小龙','男',6000,'A'); insert into employee(name,sex,salary,dept) values('龙五','男',8000,'C'); insert into employee(name,sex,salary,dept) values('冯小芳','女',10000,'C'); insert into employee(name,sex,salary,dept) values('马小龙','女',4000,'A'); -
使用group by分组,再用聚合函数处理
mysql> select sex,count(*) from employee group by sex; +------+----------+ | sex | count(*) | +------+----------+ | 女 | 4 | | 男 | 7 | +------+----------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql> select dept,count(*) from employee group by dept; +------+----------+ | dept | count(*) | +------+----------+ | A | 6 | | B | 3 | | C | 2 | +------+----------+ 3 rows in set (0.00 sec) # 这里sex字段不是用于分组的,非标准SQL写法,不推荐 mysql> select sex,count(*) from employee group by dept; +------+----------+ | sex | count(*) | +------+----------+ | 男 | 6 | | 男 | 3 | | 男 | 2 | +------+----------+ 3 rows in set (0.00 sec) # 用as给查出的字段起别名 mysql> select salary as s,max(salary) as S from employee group by dept; +-------+-------+ | s | S | +-------+-------+ | 5500 | 8500 | | 12000 | 12000 | | 7500 | 8000 | +-------+-------+ 3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
-
3. having的使用
-
在 SQL 中增加
HAVING子句原因是,WHERE关键字无法与聚合函数一起使用。HAVING子句可以对分组后的各组数据进行筛选- where子句:对group by分组前的数据进行过滤
- having子句:对group by分组后的数据进行过滤
-
语法
#having语法 SELECT column_name, aggregate_function(column_name) FROM table_name WHERE column_name operator value GROUP BY column_name HAVING aggregate_function(column_name) operator value -
示例(用having在分组结果上进一步过滤)
mysql> select dept,count(*) from employee group by dept having count(*)<5; +------+----------+ | dept | count(*) | +------+----------+ | B | 3 | | C | 2 | +------+----------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql> select dept,max(salary) from employee group by dept having max(salary)>=10000; +------+-------------+ | dept | max(salary) | +------+-------------+ | B | 12000 | | C | 10000 | +------+-------------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
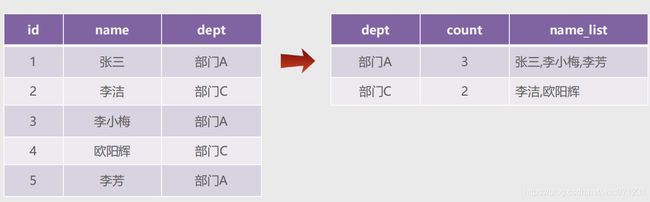
五、GROUP_CONCAT函数的使用
1. 应用场景
2. group_concat的使用
-
配合
group by一起使用,用于将某一列的值按指定的分隔符进行拼接,MySQL默认的分隔符为逗号 -
语法
#group_concat语法 group_concat([distinct] column_name [order by column_name asc/desc ] [separator '分隔符']) from table_name GROUP BY column_namedistinct:选择要不要去重
-
示例
mysql> select dept,group_concat(name) from employee group by dept; +------+-------------------------------------+ | dept | group_concat(name) | +------+-------------------------------------+ | A | 张三,马小龙,马小龙,张江,李芳,李小梅 | | B | 王五,李四 | | C | 欧阳辉,龙五,冯小芳 | +------+-------------------------------------+ 3 rows in set (0.34 sec) mysql> select dept,group_concat(name separator '_') from employee group by dept; +------+-------------------------------------+ | dept | group_concat(name separator '_') | +------+-------------------------------------+ | A | 张三_马小龙_马小龙_张江_李芳_李小梅 | | B | 王五_李四 | | C | 欧阳辉_龙五_冯小芳 | +------+-------------------------------------+ 3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
六、使用DISTINCT去重
-
distinct用于在查询中返回列的唯一不同值(去重复),支持单列或多列。在实际的应用中,表中的某一列含有重复值是很常见的,如employee表的dept列。如果在查询数据时,希望得到某列的所有不同值,可以使用distinct -
语法
#distinct语法 SELECT DISTINCT column_name, column_name FROM table_name; -
示例
mysql> select distinct dept from employee; +------+ | dept | +------+ | A | | C | | B | +------+ 3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
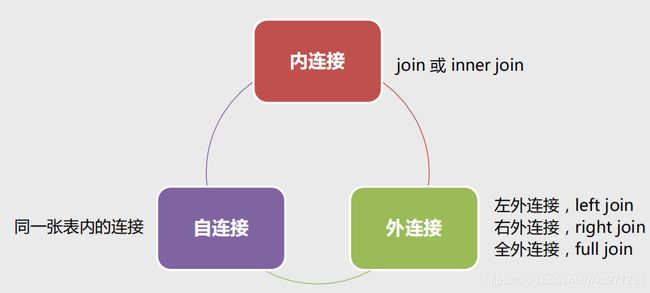
七、表连接(内连接、外连接、自连接)
1. 什么是表连接
-
表连接(JOIN)是在多个表之间通过一定的连接条件,使表之间发生关联,进而能从多个表之间获取数据
-
语法
#表连接语法 SELECT table1.column, table2.column FROM table1, table2 WHERE table1.column1 = table2.column2; # 连接条件(不一定是等于)
2. 表连接的几种方式
3. 各种表连接的区别
- 注:
- mysql中不支持全连接
- 这个表格中给出的示例用了
join表示连接条件- 内连接也可以用
where子句实现 - 左连接/右连接不能用
where实现
- 内连接也可以用
- 不使指定连接条件,得到两个表的笛卡尔积。就是用一个表的每一个元组连接第二个表的每一个元组。这个在实际使用中没啥用
(1)内连接
(2)左连接
(3)自连接
-
自连接是一种特殊的表连接,它是指相互连接的表在物理上同为一张表,但是逻辑上是多张表。自连接通常用于表中的数据有层次结构,如区域表、菜单表、商品分类表等。
-
语法
#自连接语法 SELECT A.column1, B.column2 FROM table A, table B WHERE 连接条件;
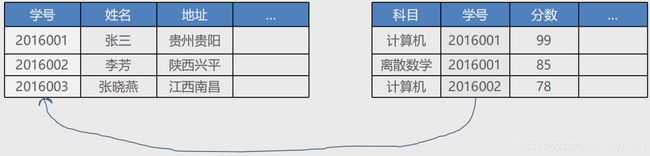
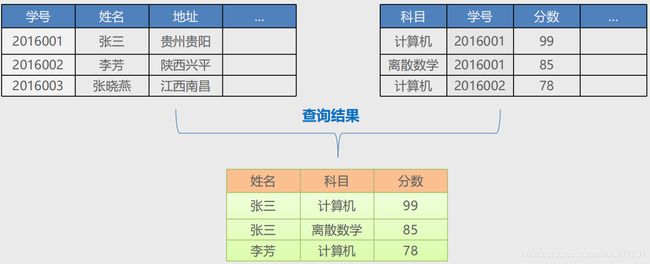
4. 示例
-
准备表
create table student( stu_no varchar(20) not null primary key comment '学号', name varchar(30) comment '姓名', address varchar(150) comment '地址' ); insert into student(stu_no,name,address) values('2016001','张三','贵州'); insert into student(stu_no,name,address) values('2016002','李芳','陕西'); insert into student(stu_no,name,address) values('2016003','张晓燕','江西'); create table score( id int not null auto_increment primary key, course varchar(50) comment '科目', stu_no varchar(20) comment '学号', score int comment '分数', foreign key(stu_no) references student(stu_no) ); insert into score(course,stu_no,score) values('计算机','2016001',99); insert into score(course,stu_no,score) values('离散','2016001',85); insert into score(course,stu_no,score) values('计算机','2016002',78); -
内连接
# 使用join指示连接条件 mysql> select A.stu_no,A.name,B.course,B.score -> from student A -> join score B on(A.stu_no = B.stu_no); # 这里写inner join效果一样 +---------+------+--------+-------+ | stu_no | name | course | score | +---------+------+--------+-------+ | 2016001 | 张三 | 计算机 | 99 | | 2016001 | 张三 | 离散 | 85 | | 2016002 | 李芳 | 计算机 | 78 | +---------+------+--------+-------+ 3 rows in set (0.33 sec) # 使用where子句指示连接条件 mysql> select A.stu_no,A.name,B.course,B.score -> from student A,score B -> where A.stu_no = B.stu_no; +---------+------+--------+-------+ | stu_no | name | course | score | +---------+------+--------+-------+ | 2016001 | 张三 | 计算机 | 99 | | 2016001 | 张三 | 离散 | 85 | | 2016002 | 李芳 | 计算机 | 78 | +---------+------+--------+-------+ 3 rows in set (0.00 sec) -
左连接
mysql> select A.stu_no,A.name,B.course,B.score -> from student A -> left join score B on(A.stu_no = B.stu_no); # 注意这里的left +---------+--------+--------+-------+ | stu_no | name | course | score | +---------+--------+--------+-------+ | 2016001 | 张三 | 计算机 | 99 | | 2016001 | 张三 | 离散 | 85 | | 2016002 | 李芳 | 计算机 | 78 | | 2016003 | 张晓燕 | NULL | NULL | +---------+--------+--------+-------+ 4 rows in set (0.00 sec) -
自连接
-
准备表
create table area( id int not null auto_increment primary key comment '区域id', pid int not null comment '父id(0-省份)', # 如果pid为0则是省;否则pid为所属省id name varchar(30) comment '名称' ); insert into area(id,pid,name) values(1,0,'贵阳'); insert into area(id,pid,name) values(2,1,'贵州'); # 属于贵阳 insert into area(id,pid,name) values(3,1,'遵义'); # 属于贵阳 insert into area(id,pid,name) values(4,0,'广东'); insert into area(id,pid,name) values(5,4,'广州'); # 属于广东 insert into area(id,pid,name) values(6,4,'深圳'); # 属于广东 -
示例
mysql> select A.id,A.name,B.name as province -> from area A,area B -> where A.pid = B.id and A.pid != 0; +----+------+----------+ | id | name | province | +----+------+----------+ | 2 | 贵州 | 贵阳 | | 3 | 遵义 | 贵阳 | | 5 | 广州 | 广东 | | 6 | 深圳 | 广东 | +----+------+----------+ 4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
-
八、子查询EXISTS和IN
1. 子查询in
-
之前的课程中,我们已经学习过运算符
IN,它允许我们在WHERE子句中过滤某个字段的多个值#where子句使用in语法 SELECT column_name FROM table_name WHERE column_name IN(value1, value2, …) -
如果运算符
in后面的值是来源于某个查询结果,并非是指定的几个值,这时就需要用到子查询。子查询又称为内部查询或嵌套查询,即在 SQL 查询的WHERE子句中嵌入查询语句#子查询in语法 SELECT column_name FROM table_name WHERE column_name [not] IN( SELECT column_name FROM table_name [WHERE] ); -
示例
# 查询所有选课了的学生(先从score表B中找出所有学号,再从student中找出学号属于那些的学生信息) mysql> select A.* -> from student A -> where A.stu_no in (select B.stu_no from score B); +---------+------+---------+ | stu_no | name | address | +---------+------+---------+ | 2016001 | 张三 | 贵州 | | 2016002 | 李芳 | 陕西 | +---------+------+---------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec) # 查选了离散的学生 mysql> select A.* -> from student A -> where A.stu_no in (select B.stu_no from score B where B.course = '离散') ; +---------+------+---------+ | stu_no | name | address | +---------+------+---------+ | 2016001 | 张三 | 贵州 | +---------+------+---------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
2. 子查询exists
-
EXISTS是子查询中用于测试内部查询是否返回任何行的布尔运算符。将主查询的数据放到子查询中做条件验证,根据验证结果(TRUE或FALSE)来决定主查询的数据结果是否保留 -
语法
#where子句使用exists语法 SELECT column_name1 FROM table_name1 WHERE [not] EXISTS (SELECT * FROM table_name2 WHERE condition); -
示例
# 这里子查询没限制,从A中查出的每个元组送入子查询比较,都不会返回false mysql> select A.* -> from student A -> where exists(select * from score B); +---------+--------+---------+ | stu_no | name | address | +---------+--------+---------+ | 2016001 | 张三 | 贵州 | | 2016002 | 李芳 | 陕西 | | 2016003 | 张晓燕 | 江西 | +---------+--------+---------+ 3 rows in set (0.00 sec) # 查询所有选课了的学生(注意这里子查询加了限制,可以把没选课的张晓燕过滤出去) mysql> select A.* -> from student A -> where exists(select * from score B where A.stu_no = B.stu_no); +---------+------+---------+ | stu_no | name | address | +---------+------+---------+ | 2016001 | 张三 | 贵州 | | 2016002 | 李芳 | 陕西 | +---------+------+---------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec) # 查询所有没选课的学生(用not exists) mysql> select A.* -> from student A -> where not exists(select * from score B where A.stu_no = B.stu_no); +---------+--------+---------+ | stu_no | name | address | +---------+--------+---------+ | 2016003 | 张晓燕 | 江西 | +---------+--------+---------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)