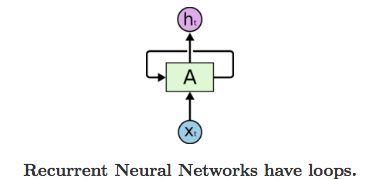
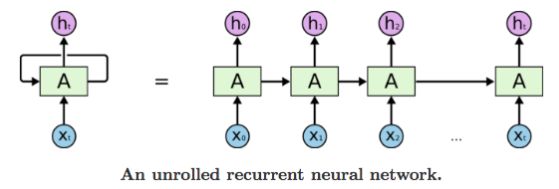
Pytorch学习笔记——nn.RNN()
pytorch 中使用 nn.RNN 类来搭建基于序列的循环神经网络,其构造函数如下:
nn.RNN(input_size, hidden_size, num_layers=1, nonlinearity=tanh, bias=True, batch_first=False, dropout=0, bidirectional=False)
- input_size:The number of expected features in the input
x,即输入特征的维度, 一般rnn中输入的是词向量,那么 input_size 就等于一个词向量的维度。 - hidden_size:The number of features in the hidden state
h,即隐藏层神经元个数,或者也叫输出的维度(因为rnn输出为各个时间步上的隐藏状态)。 - num_layers:Number of recurrent layers. E.g., setting
num_layers=2would mean stacking two RNNs together to form astacked RNN,with the second RNN taking in outputs of the first RNN and computing the final results. Default: 1
即网络的层数。 - nonlinearity:The non-linearity to use. Can be either
'tanh'or'relu'. Default:'tanh',即激活函数。 - bias:If
False, then the layer does not use bias weightsb_ihandb_hh. Default:True,即是否使用偏置。 - batch_first:If
True, then the input and output tensors are provided as(batch, seq, feature). Default:False,即输入数据的形式,默认是 False,如果设置成True,则格式为(seq(num_step), batch, input_dim),也就是将序列长度放在第一位,batch 放在第二位。 - dropout:If non-zero, introduces a
Dropoutlayer on the outputs of each RNN layer except the last layer, with dropout probability equal to :attr:dropout. Default: 0,即是否应用dropout, 默认不使用,如若使用将其设置成一个0-1的数字即可。 - birdirectional:If
True, becomes a bidirectional RNN. Default:False,是否使用双向的 rnn,默认是 False。
nn.RNN() 中最主要的参数是 input_size 和 hidden_size,这两个参数务必要搞清楚。其余的参数通常不用设置,采用默认值就可以了。
- RNN输入输出的shape
-
Inputs: input, h_0
- input of shape(seq_len, batch, input_size): tensor containing the features
of the input sequence. The input can also be a packed variable length
sequence. See :func:torch.nn.utils.rnn.pack_padded_sequence
or :func:torch.nn.utils.rnn.pack_sequence
for details.
- h_0 of shape(num_layers * num_directions, batch, hidden_size): tensor
containing the initial hidden state for each element in the batch.
Defaults to zero if not provided. If the RNN is bidirectional,
num_directions should be 2, else it should be 1. -
Outputs: output, h_n
- output of shape(seq_len, batch, num_directions * hidden_size): tensor containing the output features (h_t) from the last layer of the RNN,
- for eacht. If a :class:torch.nn.utils.rnn.PackedSequencehas
been given as the input, the output will also be a packed sequence.
For the unpacked case, the directions can be separated
usingoutput.view(seq_len, batch, num_directions, hidden_size),with forward and backward being direction0and1respectively.
Similarly, the directions can be separated in the packed case.
- h_n of shape(num_layers * num_directions, batch, hidden_size): tensor containing the hidden state fort = seq_len.
Like output, the layers can be separated using
h_n.view(num_layers, num_directions, batch, hidden_size). -
Shape:
- Input1: :math: ( L , N , H i n ) (L, N, H_{in}) (L,N,Hin) tensor containing input features where
:math: H i n = input_size H_{in}=\text{input\_size} Hin=input_size andLrepresents a sequence length.
- Input2: :math: ( S , N , H o u t ) (S, N, H_{out}) (S,N,Hout) tensor
containing the initial hidden state for each element in the batch.
:math: H o u t = hidden_size H_{out}=\text{hidden\_size} Hout=hidden_size
Defaults to zero if not provided. where :math: S = num_layers ∗ num_directions S=\text{num\_layers} * \text{num\_directions} S=num_layers∗num_directions
If the RNN is bidirectional, num_directions should be 2, else it should be 1.
- Output1: :math: ( L , N , H a l l ) (L, N, H_{all}) (L,N,Hall) where :math: H a l l = num_directions ∗ hidden_size H_{all}=\text{num\_directions} * \text{hidden\_size} Hall=num_directions∗hidden_size
- Output2: :math: ( S , N , H o u t ) (S, N, H_{out}) (S,N,Hout) tensor containing the next hidden state for each element in the batch
输入shape :input_shape = [时间步数, 批量大小, 特征维度] =[num_steps(seq_length), batch_size, input_size]
在前向计算后会分别返回输出 o o o和隐藏状态 h h h,其中输出 o o o指的是隐藏层在各个时间步上计算并输出的隐藏状态,它们通常作为后续输出层的输⼊。需要强调的是,该“输出”本身并不涉及输出层计算,形状为output_shape = [时间步数, 批量大小, 隐藏单元个数]=[num_steps(seq_length), batch_size, hidden_size];隐藏状态指的是隐藏层在最后时间步的隐藏状态:当隐藏层有多层时,每⼀层的隐藏状态都会记录在该变量中;对于像⻓短期记忆(LSTM),隐藏状态是⼀个元组 ( h , c ) (h, c) (h,c),即hidden state和cell state(此处普通rnn只有一个值),隐藏状态 h h h的形状为hidden_shape = [层数, 批量大小,隐藏单元个数] = [num_layers, batch_size, hidden_size]
代码
rnn_layer = nn.RNN(input_size=vocab_size, hidden_size=num_hiddens, )
定义模型, 其中vocab_size = 1027, hidden_size = 256
num_steps = 35
batch_size = 2
state = None # 初始隐藏层状态可以不定义
X = torch.rand(num_steps, batch_size, vocab_size)
Y, state_new = rnn_layer(X, state)
print(Y.shape, len(state_new), state_new.shape)
输出
torch.Size([35, 2, 256]) 1 torch.Size([1, 2, 256])
具体计算过程为:
H t = i n p u t ∗ W x h + H t − 1 ∗ W h h + b i a s H_t = input * W_{x_h} + H_{t-1} * W_{h_h} + bias Ht=input∗Wxh+Ht−1∗Whh+bias
为了便于观察,假设num_step=1,维度变化过程如下:
[batch_size, input_size] * [input_size, hidden_size] + [batch_size, hidden_size] *[hidden_size, hidden_size] +bias
可以发现每个隐藏状态形状都是[batch_size, hidden_size], 起始输出也是一样的。
另外,可以通过查看源代码rnn.py文件来分析:
参考链接:https://blog.csdn.net/orangerfun/article/details/103934290