Python浅谈之总结(整理)
一、简介
Python各方面的编程内容总结下来并不断更新,以便以后使用时查询。
二、详解
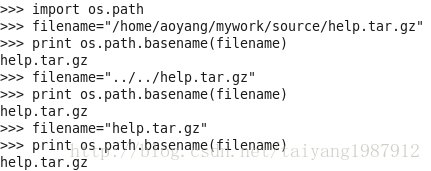
1、Python获取路径文件名
(1)split()函数进行字符串分割
(2)basename()函数
2、Python下的SQlite数据库
Python2.5集成了pysqlite数据库接口程序(sqlite3 模块),这是Python标准库第一次将一个数据库接口程序纳入标准库。SQLite操作的例子:
>>> import sqlite3
>>> cxn = sqlite3.connect('sqlite.db')
>>> cur = cxn.cursor()
>>> cur.execute('CREATE TABLE users(login VARCHAR(8), uid INTEGER)')
>>> cur.execute('INSERT INTO users VALUES("john", 100)')
>>> cur.execute('INSERT INTO users VALUES("jane", 110)')
>>> cur.execute('SELECT * FROM users')
>>> for eachUser in cur.fetchall():
... print eachUser
...
(u'john', 100)
(u'jane', 110)
>>> cur.execute('DROP TABLE users')
>>> cur.close()
>>> cxn.commit()
>>> cxn.close() #!/usr/bin/env python
import os
from random import randrange as rrange
COLSIZ = 10
DB_EXC = None
def connect(dbDir, dbName):
global DB_EXC
try:
import sqlite3
except ImportError, e:
try:
from pysqlite2 import dbapi2 as sqlite3
except ImportError, e:
return None
DB_EXC = sqlite3
if not os.path.isdir(dbDir):
os.mkdir(dbDir)
cxn = sqlite3.connect(os.path.join(dbDir, dbName))
return cxn
def create(cur):
try:
cur.execute('''
CREATE TABLE users (
login VARCHAR(8),
uid INTEGER,
prid INTEGER)
''')
except DB_EXC.OperationalError, e:
drop(cur)
create(cur)
drop = lambda cur: cur.execute('DROP TABLE users')
NAMES = (
('aaron', 8312), ('angela', 7603), ('dave', 7306),
('davina',7902), ('elliot', 7911), ('ernie', 7410),
('jess', 7912), ('jim', 7512), ('larry', 7311),
('leslie', 7808), ('melissa', 8602), ('pat', 7711),
('serena', 7003), ('stan', 7607), ('faye', 6812),
('amy', 7209),
)
def randName():
pick = list(NAMES)
while len(pick) > 0:
yield pick.pop(rrange(len(pick)))
def insert(cur):
cur.executemany("INSERT INTO users VALUES(?, ?, ?)",
[(who, uid, rrange(1,5)) for who, uid in randName()])
getRC = lambda cur: cur.rowcount if hasattr(cur, 'rowcount') else -1
def update(cur):
fr = rrange(1,5)
to = rrange(1,5)
cur.execute(
"UPDATE users SET prid=%d WHERE prid=%d" % (to, fr))
return fr, to, getRC(cur)
def delete(cur):
rm = rrange(1,5)
cur.execute('DELETE FROM users WHERE prid=%d' % rm)
return rm, getRC(cur)
def dbDump(cur):
cur.execute('SELECT * FROM users')
print '%s%s%s' % ('LOGIN'.ljust(COLSIZ),
'USERID'.ljust(COLSIZ), 'PROJ#'.ljust(COLSIZ))
for data in cur.fetchall():
print '%s%s%s' % tuple([str(s).title().ljust(COLSIZ) \
for s in data])
def main():
print '*** Connecting to sqlite database'
cxn = connect('sqlitedir', 'test.db')
if not cxn:
print 'ERROR: %r not supported, exiting' % db
return
cur = cxn.cursor()
print '*** Creating users table'
create(cur)
print '*** Inserting names into table'
insert(cur)
dbDump(cur)
print '*** Randomly moving folks',
fr, to, num = update(cur)
print 'from one group (%d) to another (%d)' % (fr, to)
print '\t(%d users moved)' % num
dbDump(cur)
print '*** Randomly choosing group',
rm, num = delete(cur)
print '(%d) to delete' % rm
print '\t(%d users removed)' % num
dbDump(cur)
print '*** Dropping users table'
drop(cur)
cur.close()
cxn.commit()
cxn.close()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()3、print函数输出
>>> str = 'hello world'
>>> print str
hello world
>>> print 'length of (%s) is %d' %(str, len(str))
length of (hello world) is 11
>>> hex = 0xFF
>>> print 'hex = %x, dec = %d, oct=%o' % (hex, hex, hex)
hex = ff, dec = 255, oct=377
>>> import math
>>> print 'pi = %10.3f' % math.pi
pi = 3.142
>>> print 'pi = %-10.3f' % math.pi
pi = 3.142
>>> print 'pi = %06d' % int(math.pi)
pi = 000003
>>> precise = 4
>>> print ("%.*s" % (4,"python"))
pyth
>>> print ("%10.3s " % ("python"))
pyt
>>> lst = [1,2,3,4,'python']
>>> print lst
[1, 2, 3, 4, 'python']
>>> for i in range(0,6):
... print i,
...
0 1 2 3 4 5
>>> import sys
>>> sys.stdout.write('hello world\n')
hello world
4、Python中文支持
添加一行声明文件编码的注释(python默认使用ASCII编码),必须将编码注释放在第一行或者第二行。# -*- coding:utf-8 -*- #coding=utf-8 #coding=gbk
# -*- coding: gbk -*-
5、将python的py文件编译成保密的pyc文件
由于python程序的py文件很容易泄露源代码,所以python可以编译成保密的pyc文件。python的pyc文件是一种二进制文件,py文件变成pyc文件后,加载的速度有所提高,而且pyc是一种跨平台的字节码,是由python的虚拟机来执行的,这个是类似于JAVA或者.NET的虚拟机的概念。
编pyc文件也是可以反编译的,不同版本编译后的pyc文件是不同的,根据python源码中提供的opcode,可以根据pyc文件反编译出py文件源码,网上可以找到一个反编译python2.3版本的pyc文件的工具,不过该工具从python2.4开始就要收费了,如果需要反编译出新版本的pyc文件的话,就需要自己动手了,不过你可以自己修改python的源代码中的opcode文件,重新编译python,从而防止不法分子的破解。
(1)编译py文件到pyc文件的方法:在命令行输入:python -m py_compile myFile.py 就可以生成对应的pyc文件了(有时会将pyc的后缀改为py,通过file命令可以看出为byte-compiled)。
(2)内置的类库来实现把py文件编译为pyc文件,这个模块就是py_compile模块。
生成单个pyc文件:
import py_compile
py_compile.compile(r'/tmp/test.py')file:表示需要编译的py文件的路径
cfile:表示编译后的pyc文件名称和路径,默认为直接在file文件名后加c 或者 o,o表示优化的字节码
dfile:这个参数英文看不明白,请各位大大赐教。(鄙视下自己)原文:it is used as the name of the source file in error messages instead of file
doraise:可以是两个值,True或者False,如果为True,则会引发一个PyCompileError,否则如果编译文件出错,则会有一个错误,默认显示在sys.stderr中,而不会引发异常
批量生成pyc文件:
若工程都是在一个目录下的,一般不会说仅仅编译一个py文件而已,而是需要把整个文件夹下的py文件都编译为pyc文件,python又提供了另一个模块:compileall 。使用方法如下:
import compileall
compileall.compile_dir(r'/tmp/code/')compile_dir函数的说明:compile_dir(dir[, maxlevels[, ddir[, force[, rx[, quiet]]]]])
dir:表示需要编译的文件夹位置
maxlevels:表示需要递归编译的子目录的层数,默认是10层,即默认会把10层子目录中的py文件编译为pyc
ddir:it is used as the base path from which the filenames used in error messages will be generated。
force:如果为True,则会强制编译为pyc,即使现在的pyc文件是最新的,还会强制编译一次,pyc文件中包含有时间戳,python编译器会根据时间来决定,是否需要重新生成一次pyc文件
rx:表示一个正则表达式,比如可以排除掉不想要的目录,或者只有符合条件的目录才进行编译
quiet:如果为True,则编译后,不会在标准输出中,打印出信息。
代码片段:
#-*- coding=utf-8
'''
#编译目录下所有py文件为 pyc文件
import compileall
compileall.compile_dir(r"/tmp/code/")
'''
#编译 单个py文件为 pyc文件
import py_compile
py_compile.compile(r"/tmp/code/test.py")