Actual Cause and General Cause Examples
直觉上的事实样例:
1、a car accident was the cause of Joe's death
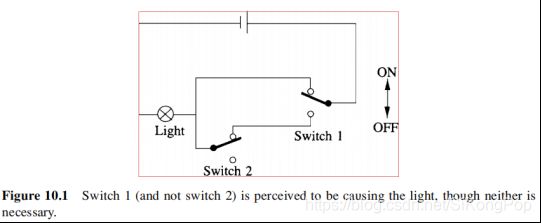
2、Switch light——
3、The Desert Traveler——A desert traveler T has two
enemies. Enemy 1 poisons T’s canteen, and enemy 2, unaware of enemy 1’s action,
shoots and empties the canteen. A week later, T is found dead and the two enemies
confess to action and intention. A jury must decide whose action was the actual cause
of T’s death.
Consider a modification of the desert traveler example in which we do not know
whether the traveler managed to drink any of the poisoned water before the canteen was
emptied.
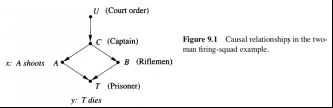
4、The Firing Squad——
5、Fire house——
If fire A burned the house before fire B, then we would consider
fire A “the actual cause” of the damage, even though fire B would have done the same
were it not for A.
6、Vote——
A vote takes place, involving two people. The measure Y is passed
if at least one of them votes in favor. In fact, both of them vote in favor, and the
measure passes.
7、Plaintiff and defendant——
For example, according to common judicial standard, judgment in favor of the plaintiff should be made if and only if
it is “more probable than not” that the defendant’s action was the cause of the plaintiff’s damage (or death).
8、Long distance shoot——
For instance, aiming a gun at and shooting a person from 1,000 meters away will not qualify as an explanation for that person’s death, owing to the very low tendency of shots fired from such long distances to hit their marks.
9、Match oxygen——
For example, the presence of oxygen in the room would qualify as an explanation for the fire that broke out, simply because the fire would not have occurred were it not for the oxygen. That we judge the match struck, not the oxygen, to be the actual cause of the fire indicates that we go beyond the singular event at hand (where each factor alone is both necessary and sufficient) and consider situations of the same general type – where oxygen alone is obviously insufficient to start a fire.
10、Betting against a Fair Coin
We must bet heads or tails on the outcome of a fair coin toss; we win a dollar if we guess correctly and lose if we don’t. Suppose we bet heads and win a dollar, without glancing at the actual outcome of the coin. Was our bet a necessary cause (or a sufficient cause, or both) for winning?
11、Clinical trial
Such a network ensues, for example, in a controlled (i.e., randomized) clinical trial when we find that a treatment X has no effect
on the distribution of subjects’ response Y, which may stand for either recovery (Y=0) or death (Y=1). Assume that a given subject, Joe, has taken the treatment and died; we ask whether Joe’s death occurred because of the treatment, despite the treatment, or regardless of the treatment. In other words, we ask for the probability Q that Joe would have died had he not been treated.
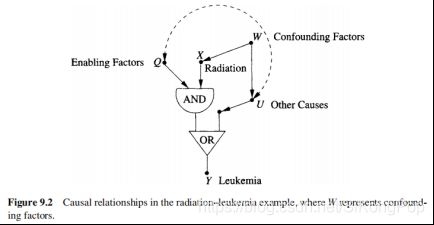
12、The Effect of Radiation on Leukemia
Consider the following data comparing leukemia deaths in children in southern Utah with high and low exposure to radiation from the fallout of nuclear tests in Nevada. Given these data, we wish to estimate the probabilities that high exposure to radiation was a necessary (or sufficient, or both) cause of death due to leukemia.
13、
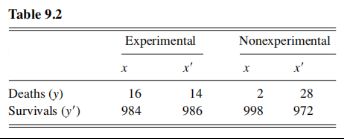
A lawsuit is filed against the manufacturer of drug x, charging that the drug is likely to have caused the death of Mr. A, who took the drug to relieve symptom S associated with disease D.
The manufacturer claims that experimental data on patients with symptom S show conclusively that drug x may cause only a minor increase in death rates. However, the plaintiff argues that the experimental study is of little relevance to this case because it represents the effect of the drug on all patients, not on patients like Mr. A who actually died while using drug x. Moreover, argues the plaintiff, Mr. A is unique in that he used the drug on his own volition, unlike subjects in the experimental study who took the drug to comply with experimental protocols. To support this argument, the plaintiff furnishes nonexperimental data indicating that most patients who chose drug x would have been alive were it not for the drug. The manufacturer counterargues by stating that: (1) counterfactual speculations regarding whether patients would or would not have died are purely metaphysical and should be avoided (Dawid 2000); and (2) nonexperimental data should be dismissed a priori on the grounds that such data may be highly confounded by extraneous factors. The court must now decide, based on both the experimental and nonexperimental studies, what the probability is that drug x was in fact the cause of Mr. A’s death.