图网络embeding transE及node2vec方法
1、 transE 表示学习
知识图谱中的事实是用三元组 (h,l,t)(h,l,t)(h,l,t) 表示的,那么如何用低维稠密向量来表示它们,才能得到这种依赖关系呢?transE算法的思想非常简单,它受word2vec平移不变性的启发,希望h+l≈t
参考:https://github.com/Anery/transE
import codecs
import random
import math
import numpy as np
import copy
import time
entity2id = {}
relation2id = {}
def data_loader(file):
file1 = file + "train.txt"
file2 = file + "entity2id.txt"
file3 = file + "relation2id.txt"
with open(file2, 'r') as f1, open(file3, 'r') as f2:
lines1 = f1.readlines()
lines2 = f2.readlines()
for line in lines1:
line = line.strip().split('\t')
if len(line) != 2:
continue
entity2id[line[0]] = line[1]
for line in lines2:
line = line.strip().split('\t')
if len(line) != 2:
continue
relation2id[line[0]] = line[1]
entity_set = set()
relation_set = set()
triple_list = []
with codecs.open(file1, 'r') as f:
content = f.readlines()
for line in content:
triple = line.strip().split("\t")
if len(triple) != 3:
continue
h_ = entity2id[triple[0]]
t_ = entity2id[triple[1]]
r_ = relation2id[triple[2]]
triple_list.append([h_,t_,r_])
entity_set.add(h_)
entity_set.add(t_)
relation_set.add(r_)
return entity_set, relation_set, triple_list
def distanceL2(h,r,t):
#为方便求梯度,去掉sqrt
return np.sum(np.square(h + r - t))
def distanceL1(h,r,t):
return np.sum(np.fabs(h+r-t))
class TransE:
def __init__(self, entity_set, relation_set, triple_list,
embedding_dim=100, learning_rate=0.01, margin=1, L1=True):
self.embedding_dim = embedding_dim
self.learning_rate = learning_rate
self.margin = margin
self.entity = entity_set
self.relation = relation_set
self.triple_list = triple_list
self.L1=L1
self.loss = 0
def emb_initialize(self):
relation_dict = {}
entity_dict = {}
for relation in self.relation:
r_emb_temp = np.random.uniform(-6/math.sqrt(self.embedding_dim) ,
6/math.sqrt(self.embedding_dim) ,
self.embedding_dim)
relation_dict[relation] = r_emb_temp / np.linalg.norm(r_emb_temp,ord=2)
for entity in self.entity:
e_emb_temp = np.random.uniform(-6/math.sqrt(self.embedding_dim) ,
6/math.sqrt(self.embedding_dim) ,
self.embedding_dim)
entity_dict[entity] = e_emb_temp / np.linalg.norm(e_emb_temp,ord=2)
self.relation = relation_dict
self.entity = entity_dict
def train(self, epochs):
nbatches = 100
batch_size = len(self.triple_list) // nbatches
print("batch size: ", batch_size)
for epoch in range(epochs):
start = time.time()
self.loss = 0
for k in range(nbatches):
# Sbatch:list
Sbatch = random.sample(self.triple_list, batch_size)
Tbatch = []
for triple in Sbatch:
# 每个triple选3个负样例
# for i in range(3):
corrupted_triple = self.Corrupt(triple)
if (triple, corrupted_triple) not in Tbatch:
Tbatch.append((triple, corrupted_triple))
self.update_embeddings(Tbatch)
end = time.time()
print("epoch: ", epoch , "cost time: %s"%(round((end - start),3)))
print("loss: ", self.loss)
#保存临时结果
if epoch % 20 == 0:
with codecs.open("entity_temp", "w") as f_e:
for e in self.entity.keys():
f_e.write(e + "\t")
f_e.write(str(list(self.entity[e])))
f_e.write("\n")
with codecs.open("relation_temp", "w") as f_r:
for r in self.relation.keys():
f_r.write(r + "\t")
f_r.write(str(list(self.relation[r])))
f_r.write("\n")
print("写入文件...")
with codecs.open("entity_50dim_batch400", "w") as f1:
for e in self.entity.keys():
f1.write(e + "\t")
f1.write(str(list(self.entity[e])))
f1.write("\n")
with codecs.open("relation50dim_batch400", "w") as f2:
for r in self.relation.keys():
f2.write(r + "\t")
f2.write(str(list(self.relation[r])))
f2.write("\n")
print("写入完成")
def Corrupt(self,triple):
corrupted_triple = copy.deepcopy(triple)
seed = random.random()
if seed > 0.5:
# 替换head
rand_head = triple[0]
while rand_head == triple[0]:
rand_head = random.sample(self.entity.keys(),1)[0]
corrupted_triple[0]=rand_head
else:
# 替换tail
rand_tail = triple[1]
while rand_tail == triple[1]:
rand_tail = random.sample(self.entity.keys(), 1)[0]
corrupted_triple[1] = rand_tail
return corrupted_triple
def update_embeddings(self, Tbatch):
copy_entity = copy.deepcopy(self.entity)
copy_relation = copy.deepcopy(self.relation)
for triple, corrupted_triple in Tbatch:
# 取copy里的vector累积更新
h_correct_update = copy_entity[triple[0]]
t_correct_update = copy_entity[triple[1]]
relation_update = copy_relation[triple[2]]
h_corrupt_update = copy_entity[corrupted_triple[0]]
t_corrupt_update = copy_entity[corrupted_triple[1]]
# 取原始的vector计算梯度
h_correct = self.entity[triple[0]]
t_correct = self.entity[triple[1]]
relation = self.relation[triple[2]]
h_corrupt = self.entity[corrupted_triple[0]]
t_corrupt = self.entity[corrupted_triple[1]]
if self.L1:
dist_correct = distanceL1(h_correct, relation, t_correct)
dist_corrupt = distanceL1(h_corrupt, relation, t_corrupt)
else:
dist_correct = distanceL2(h_correct, relation, t_correct)
dist_corrupt = distanceL2(h_corrupt, relation, t_corrupt)
err = self.hinge_loss(dist_correct, dist_corrupt)
if err > 0:
self.loss += err
grad_pos = 2 * (h_correct + relation - t_correct)
grad_neg = 2 * (h_corrupt + relation - t_corrupt)
if self.L1:
for i in range(len(grad_pos)):
if (grad_pos[i] > 0):
grad_pos[i] = 1
else:
grad_pos[i] = -1
for i in range(len(grad_neg)):
if (grad_neg[i] > 0):
grad_neg[i] = 1
else:
grad_neg[i] = -1
# head系数为正,减梯度;tail系数为负,加梯度
h_correct_update -= self.learning_rate * grad_pos
t_correct_update -= (-1) * self.learning_rate * grad_pos
# corrupt项整体为负,因此符号与correct相反
if triple[0] == corrupted_triple[0]: # 若替换的是尾实体,则头实体更新两次
h_correct_update -= (-1) * self.learning_rate * grad_neg
t_corrupt_update -= self.learning_rate * grad_neg
elif triple[1] == corrupted_triple[1]: # 若替换的是头实体,则尾实体更新两次
h_corrupt_update -= (-1) * self.learning_rate * grad_neg
t_correct_update -= self.learning_rate * grad_neg
#relation更新两次
relation_update -= self.learning_rate*grad_pos
relation_update -= (-1)*self.learning_rate*grad_neg
#batch norm
for i in copy_entity.keys():
copy_entity[i] /= np.linalg.norm(copy_entity[i])
for i in copy_relation.keys():
copy_relation[i] /= np.linalg.norm(copy_relation[i])
# 达到批量更新的目的
self.entity = copy_entity
self.relation = copy_relation
def hinge_loss(self,dist_correct,dist_corrupt):
return max(0,dist_correct-dist_corrupt+self.margin)
if __name__=='__main__':
file1 = "FB15k/"
entity_set, relation_set, triple_list = data_loader(file1)
print("load file...")
print("Complete load. entity : %d , relation : %d , triple : %d" % (len(entity_set),len(relation_set),len(triple_list)))
transE = TransE(entity_set, relation_set, triple_list,embedding_dim=50, learning_rate=0.01, margin=1,L1=True)
transE.emb_initialize()
transE.train(epochs=1001)
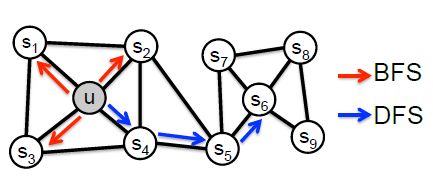
2、node2vec 图嵌入方法
随机游走,集合了deepwalk dfs及line bfs的方法,
参考:https://github.com/eliorc/node2vec
pip install node2vec
import networkx as nx
from node2vec import Node2Vec
# Create a graph
graph = nx.fast_gnp_random_graph(n=100, p=0.5)
# Precompute probabilities and generate walks - **ON WINDOWS ONLY WORKS WITH workers=1**
node2vec = Node2Vec(graph, dimensions=64, walk_length=30, num_walks=200, workers=4) # Use temp_folder for big graphs
# Embed nodes
model = node2vec.fit(window=10, min_count=1, batch_words=4) # Any keywords acceptable by gensim.Word2Vec can be passed, `diemnsions` and `workers` are automatically passed (from the Node2Vec constructor)
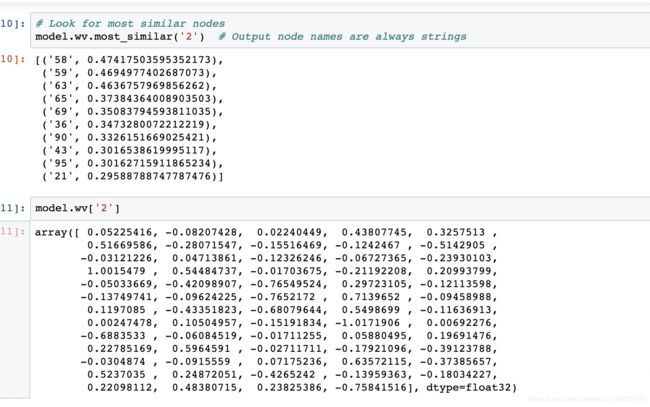
# Look for most similar nodes
model.wv.most_similar('2') # Output node names are always strings
# Save embeddings for later use
model.wv.save_word2vec_format(EMBEDDING_FILENAME)
# Save model for later use
model.save(EMBEDDING_MODEL_FILENAME)
# Embed edges using Hadamard method
from node2vec.edges import HadamardEmbedder
edges_embs = HadamardEmbedder(keyed_vectors=model.wv)
# Look for embeddings on the fly - here we pass normal tuples
edges_embs[('1', '2')]
''' OUTPUT
array([ 5.75068220e-03, -1.10937878e-02, 3.76693785e-01, 2.69105062e-02,
... ... ....
..................................................................],
dtype=float32)
'''
# Get all edges in a separate KeyedVectors instance - use with caution could be huge for big networks
edges_kv = edges_embs.as_keyed_vectors()
# Look for most similar edges - this time tuples must be sorted and as str
edges_kv.most_similar(str(('1', '2')))
# Save embeddings for later use
edges_kv.save_word2vec_format(EDGES_EMBEDDING_FILENAME)