CobarClient源码分析
前言
Cobar Client是一个阿里开源的轻量级分布式数据访问层,基于Ibatis和Spring框架。
最近公司的项目在分表分库时使用此框架,起初不明白为什么使用这么老,没人维护的开源框架。后来想想是根据现有代码,迁移起来简单吧。
既然用了,就还是仔细看下,深入的了解一下CobarClient的原理吧。
正文
Cobar Client就是在spring提供的ibatis的SqlMapClientTemplate的基础上,添加了路由规则,然后根据路由规则找到相应的数据源,提供了自定义的CobarSqlMapClientTemplate。先看一下它的类关系图,如下。
然后我们从CobarSqlMapClientTemplate的queryForList()这个常用方法,来仔细分析一下。
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected List queryForList(final String statementName, final Object parameterObject,
final Integer skipResults, final Integer maxResults) {
//1.如果需要则记录执行的sql
auditSqlIfNecessary(statementName, parameterObject);
long startTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
//2.是否有分区的行为
if (isPartitioningBehaviorEnabled()) {
//3.通过ibatis的namespace + sqlStatement id和参数查找路由规则,然后通过路由规则找到数据源
SortedMap dsMap = lookupDataSourcesByRouter(statementName,
parameterObject);
//如果数据源为空,则调用父类的执行器执行查询
if (!MapUtils.isEmpty(dsMap)) {
SqlMapClientCallback callback = null;
if (skipResults == null || maxResults == null) {
callback = new SqlMapClientCallback() {
public Object doInSqlMapClient(SqlMapExecutor executor)
throws SQLException {
return executor.queryForList(statementName, parameterObject);
}
};
} else {
callback = new SqlMapClientCallback() {
public Object doInSqlMapClient(SqlMapExecutor executor)
throws SQLException {
return executor.queryForList(statementName, parameterObject,
skipResults, maxResults);
}
};
}
//3.执行请求
List 从源码上看,过程很简单,主要有四个步骤,其核心在步骤2。
1.记录执行sql(如果配置了)。
2.根据请求的statement id和参数,找到路由规则,根据路由规则获取数据源。
3.执行请求。
4.合并结果。
先看一下,如何判断是否有分区行为
protected boolean isPartitioningBehaviorEnabled() {
return ((router != null) && (getCobarDataSourceService() != null));
}代码很简单,就看是否配置了数据请求访问路由和多数据源的管理。如果配置了就表明有分区行为,否则没有。
再看一下lookupDataSourcesByRouter方法,看看如何根据请求获取数据源。这个也是核心方法。
protected SortedMap lookupDataSourcesByRouter(final String statementName,
final Object parameterObject) {
SortedMap resultMap = new TreeMap();
if (getRouter() != null && getCobarDataSourceService() != null) {
//getRouter获取数据访问请求路由
//doRoute根据当前请求路由到指定数据库
//IBatisRoutingFact当前请求
//getResourceIdentities获取数据标识
List dsSet = getRouter().doRoute(
new IBatisRoutingFact(statementName, parameterObject)).getResourceIdentities();
if (CollectionUtils.isNotEmpty(dsSet)) {
Collections.sort(dsSet);
for (String dsName : dsSet) {
resultMap.put(dsName, getCobarDataSourceService().getDataSources().get(dsName));
}
}
}
return resultMap;
}
一般的数据访问请求路由是CobarClientInternalRouter,我们在看一下它的doRoute方法。
public RoutingResult doRoute(IBatisRoutingFact routingFact) throws RoutingException {
//如果缓存可用,则从缓存中查找路由结果
if (enableCache) {
synchronized (localCache) {
if (localCache.containsKey(routingFact)) {
RoutingResult result = (RoutingResult) localCache.get(routingFact);
logger.info("return routing result:{} from cache for fact:{}", result, routingFact);
return result;
}
}
}
//设置路由结果
RoutingResult result = new RoutingResult();
result.setResourceIdentities(new ArrayList());
IRoutingRule> ruleToUse = null;
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(getRuleSequences())) {
//getRuleSequences路由规则集合,bean初始化时添加进去
//这个集合会排序,保证规则先匹配到sqlMap级的规则,在匹配namespace级
for (Set>> ruleSet : getRuleSequences()) {
//根据mvel表达式判断当前请求和路由规则是否匹配,如果匹配则结束
ruleToUse = searchMatchedRuleAgainst(ruleSet, routingFact);
if (ruleToUse != null) {
break;
}
}
}
if (ruleToUse != null) {
logger.info("matched with rule:{} with fact:{}", ruleToUse, routingFact);
//将找到数据源添加到路由结果中
result.getResourceIdentities().addAll(ruleToUse.action());
} else {
logger.info("No matched rule found for routing fact:{}", routingFact);
}
//添加到缓存里面
if (enableCache) {
synchronized (localCache) {
localCache.put(routingFact, result);
}
}
//返回结果
return result;
} 总的来说就是初始化时将IRoutingRule(路由规则)的集合添加到路由CobarClientInternalRouter里面,然后mvel表达式逐个验证当前请求是否和路由规则匹配,如果匹配则结束。
在看一下如何处理请求。
public List executeInConcurrency(SqlMapClientCallback action,
SortedMap dsMap) {
List requests = new ArrayList();
//根据数据源的数量,将原来的一个请求封装成对应数量的请求
for (Map.Entry entry : dsMap.entrySet()) {
ConcurrentRequest request = new ConcurrentRequest();
request.setAction(action);
request.setDataSource(entry.getValue());
request.setExecutor(getDataSourceSpecificExecutors().get(entry.getKey()));
requests.add(request);
}
//处理请求
List results = getConcurrentRequestProcessor().process(requests);
return results;
}
再看一下具体的执行。
public List process(List requests) {
List resultList = new ArrayList();
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(requests))
return resultList;
//获取每个请求的数据源的连接
List requestsDepo = fetchConnectionsAndDepositForLaterUse(requests);
//用CountDownLatch来保证每个请求都执行完毕后才返回结果
final CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(requestsDepo.size());
List> futures = new ArrayList>();
try {
//异步的执行每一个请求
for (RequestDepository rdepo : requestsDepo) {
ConcurrentRequest request = rdepo.getOriginalRequest();
final SqlMapClientCallback action = request.getAction();
final Connection connection = rdepo.getConnectionToUse();
futures.add(request.getExecutor().submit(new Callable() {
public Object call() throws Exception {
try {
return executeWith(connection, action);
} finally {
latch.countDown();
}
}
}));
}
try {
latch.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new ConcurrencyFailureException(
"interrupted when processing data access request in concurrency", e);
}
} finally {
//释放资源
for (RequestDepository depo : requestsDepo) {
Connection springCon = depo.getConnectionToUse();
DataSource dataSource = depo.getOriginalRequest().getDataSource();
try {
if (springCon != null) {
if (depo.isTransactionAware()) {
springCon.close();
} else {
DataSourceUtils.doReleaseConnection(springCon, dataSource);
}
}
} catch (Throwable ex) {
logger.info("Could not close JDBC Connection", ex);
}
}
}
//合并结果
fillResultListWithFutureResults(futures, resultList);
return resultList;
} 整体上来说,就是根据数据源的数量将一个请求,封装成多个,然后异步的执行。用CountDownLatch来保证每个执行完毕之后才返回。
至此,整个核心流程就分析结束了。
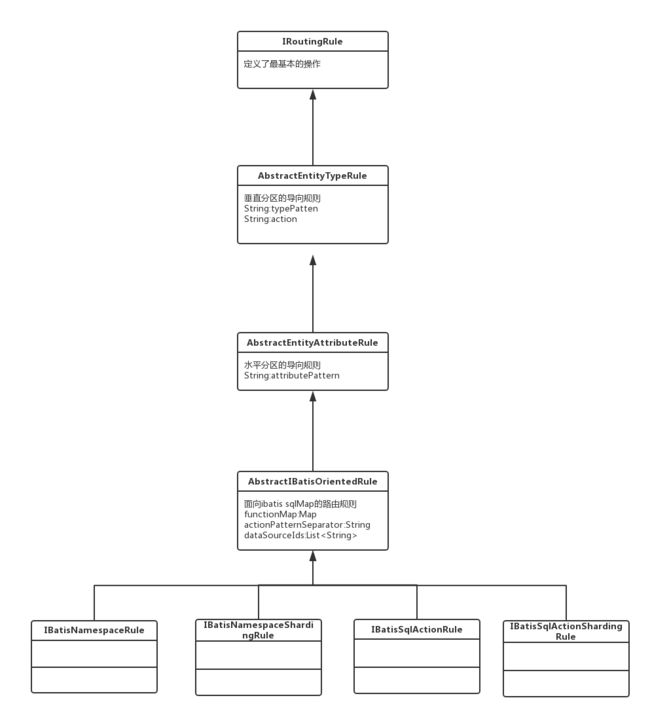
下面再看一下CobarClient的规则定义类关系图。
下面那四种也就是官方文档里说的,四种规则了。整个定义也很简单。
在看一下数据源的架构图。
将数据源注入到CobarSqlMapClientTemplatez中是通过ICobarDataSourceService,完成的。如果配置的HA类型的数据源管理,则会在初始化的时候创建一个线程,监控数据源。
现在看来代码上没有特别神奇之处,不过这是很久之前的代码。看来思想很重要。不过当前还是多看多写。