android 开发零起步学习笔记(十一):界面切换+几种常用界面切换效果
两种方法实现界面的切换:
方法1、layout切换(通过setContentView切换layout)
方法2、Activity切换
方法3、Android之fragment点击切换和滑动切换
方法1、layout切换(通过setContentView切换layout)
有以下步骤:
①新建一个界面的layout的xml文件
②触发某一控件(如Button),该控件已经加载监听器,监听器通过setContentView函数切换layout
这样的实现整个过程都是在一个Activity上面实现,所有变量都在同一状态,因此所有变量都可以在这个Activity状态中获得。
代码如下:
[java]
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
Button button = (Button) this.findViewById(R.id.button1);
//给按钮设置监听器
button.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
//通过调用setContentView函数切换layout
setContentView(R.layout.login);
}
});
}
另一篇《多个layout界面之间的切换》 http://www.cnblogs.com/tt_mc/archive/2010/06/22/1762794.html
方法2、Activity切换 及切换效果
通过转换到另一个Activity,步骤如下
①建一个Activity类
②把该类注册到AndroidManifest.xml,如下
③在原来的Activity上面通过创建Intent类来进行Activity的切换,代码如下
[java]
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
Button button_activity = (Button) this.findViewById(R.id.button2);
button_activity.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener()){
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Intent intent = new Intent(MainActivity.this, LoginActivity.class);
startActivity(intent);
}
});
}
--------------Activity切换的几种方法-----------------------------
1.无参数Activity跳转
Intent it = new Intent(Activity.Main.this, Activity2.class);
startActivity(it);
2.向下一个Activity传递数据(使用Bundle和Intent.putExtras)
Intent it = new Intent(Activity.Main.this, Activity2.class);
Bundle bundle=new Bundle();
bundle.putString("name", "This is from MainActivity!");
it.putExtras(bundle); // it.putExtra(“test”, "shuju”);
startActivity(it); // startActivityForResult(it,REQUEST_CODE);
对于数据的获取可以采用:
Bundle bundle=getIntent().getExtras();
String name=bundle.getString("name");
3.向上一个Activity返回结果(使用setResult,针对startActivityForResult(it,REQUEST_CODE)启动的Activity)
Intent intent=getIntent();
Bundle bundle2=new Bundle();
bundle2.putString("name", "This is from ShowMsg!");
intent.putExtras(bundle2);
setResult(RESULT_OK, intent);
4.回调上一个Activity的结果处理函数(onActivityResult)
@Override
protected void onActivityResult(int requestCode, int resultCode, Intent data) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onActivityResult(requestCode, resultCode, data);
if (requestCode==REQUEST_CODE){
if(resultCode==RESULT_CANCELED)
setTitle("cancle");
else if (resultCode==RESULT_OK) {
String temp=null;
Bundle bundle=data.getExtras();
if(bundle!=null) temp=bundle.getString("name");
setTitle(temp);
}
}
}
{它包括两个部分:
一部分是第一个activity退出时的动画;
另外一部分时第二个activity进入时的动画;
在Android的2.0版本之后,有了一个函数来帮我们实现这个动画。这个函数就是overridePendingTransition
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.SplashScreen);
new Handler().postDelayed(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
Intent mainIntent = new Intent(SplashScreen.this, AndroidNews.class);
SplashScreen.this.startActivity(mainIntent);
SplashScreen.this.finish();
overridePendingTransition(R.anim.mainfadein,
R.anim.splashfadeout);
}
}, 3000);
}
上面的代码只是闪屏的一部分。
getWindow (). setWindowAnimations ( int );
这可没有上个好但是也可以 。
实现淡入淡出的效果1
overridePendingTransition(R.anim.splash_screen_fade, R.anim.splash_screen_hold);
实现淡入淡出的效果2
由左向右滑入的效果
实现zoomin和zoomout,即类似iphone的进入和退出时的效果
overridePendingTransition(R.anim.zoomin, R.anim.zoomout);
新建zoomin.xml文件
Android:pivotX="50%p" android:pivotY="50%p"
Android:duration="@android:integer/config_mediumAnimTime" />
新建zoomout.xml文件
Android:zAdjustment="top">
Android:pivotX="50%p" android:pivotY="50%p"
Android:duration="@android:integer/config_mediumAnimTime" />
学了一小段时间的Android,主要接触的是UI设计,打交道最多莫过于fragment了吧。在Android3.0引入了fragment的概念后,几乎在所以的Android的应用中都可以看见其身影,已经有很多前辈高人都已经详细介绍过fragmrnt,我这里就不多说什么了。
这里本来是想模仿一下微信的切换效果,怎奈水平不足,这里就献丑贴出半成品的代码,希望有大神能指点一下。废话不多说,上代码。先从简单的开始吧,这里是我一共用了3个fragment,这里就只贴出第一个的fragment的布局,别的两个基本一样,比较简朴。
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:gravity="center_horizontal|center_vertical"
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
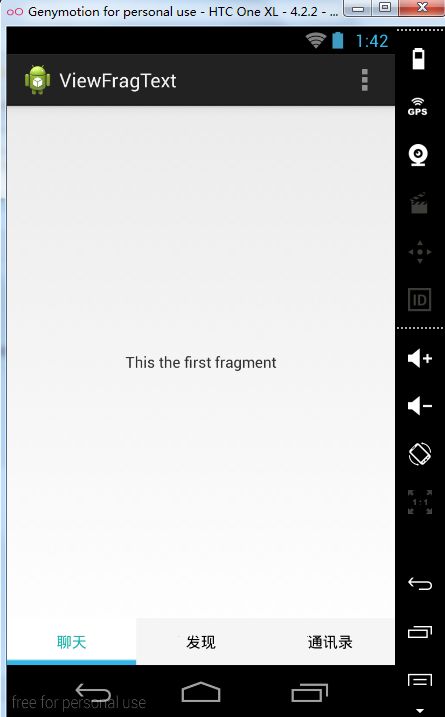
android:text="This the first fragment"
/>
接下来的是使用fragment片段,这里也只贴出第一个的。
package com.example.fragments;
import com.example.viewfragtext.R;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.v4.app.Fragment;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
public class Fragmentone extends Fragment
{
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container,
Bundle savedInstanceState) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment1, container, false);
}
}
接下来便要开始实现切换的功能,这里是底部切换组件(tabfoot)的布局。
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="44dp"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:background="@drawable/tabfootbg"
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/lay1"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
style="@style/Linearlayout_Style"
>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/fratext1"
android:text="@string/chat"
android:textColor="@color/black"
/>
<LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/lay2"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
style="@style/Linearlayout_Style">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/fratext2"
android:text="@string/find"
android:textColor="@color/black"/>
<LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/lay3"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
style="@style/Linearlayout_Style">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/fratext3"
android:text="@string/tongxunlu"
android:textColor="@color/black"/>
这里分别是自定义的style和color的代码。
#20b2aa
#000000
别的设计都完成了,马上对应的是MainActivity的设计,这是其布局
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<fragment
android:name="com.example.fragments.Fragmentone"
android:id="@+id/fragment1"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1.0"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
/>
<fragment
android:name="com.example.fragments.Fragmenttwo"
android:id="@+id/fragment2"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1.0"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
/>
<fragment
android:name="com.example.fragments.Fragmentthree"
android:id="@+id/fragment3"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1.0"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
/>
最后遍是实现在主活动中实现点击底部切换和滑动的换的功能。这里滑动功能我是采用手势(Gesture)实现的。
1 package com.example.viewfragtext; 2 3 import android.os.Bundle; 4 import android.support.v4.app.Fragment; 5 import android.support.v4.app.FragmentActivity; 6 import android.view.GestureDetector; 7 import android.view.GestureDetector.OnGestureListener; 8 import android.view.Menu; 9 import android.view.MotionEvent; 10 import android.view.View; 11 import android.widget.LinearLayout; 12 import android.widget.TextView; 13 14 public class MainActivity extends FragmentActivity implements OnGestureListener 15 { 16 public static Fragment[] fragments; 17 public static LinearLayout[] linearLayouts; 18 public static TextView[] textViews; 19 /**定义手势检测实例*/ 20 public static GestureDetector detector; 21 /**做标签,记录当前是哪个fragment*/ 22 public int MARK=0; 23 /**定义手势两点之间的最小距离*/ 24 final int DISTANT=50; 25 26 27 @Override 28 protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { 29 super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); 30 setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); 31 //分别实例化和初始化fragement、lineatlayout、textview 32 setfragment(); 33 setlinearLayouts(); 34 settextview(); 35 //创建手势检测器 36 detector=new GestureDetector(this); 37 38 } 39 40 @Override 41 public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) { 42 // Inflate the menu; this adds items to the action bar if it is present. 43 getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.main, menu); 44 return true; 45 } 46 /**初始化fragment*/ 47 public void setfragment() 48 { 49 fragments=new Fragment[3]; 50 fragments[0]=getSupportFragmentManager().findFragmentById(R.id.fragment1); 51 fragments[1]=getSupportFragmentManager().findFragmentById(R.id.fragment2); 52 fragments[2]=getSupportFragmentManager().findFragmentById(R.id.fragment3); 53 getSupportFragmentManager().beginTransaction().hide(fragments[0]).hide(fragments[1]).hide(fragments[2]) 54 .show(fragments[0]).commit(); 55 56 } 57 /**初始化linerlayout*/ 58 public void setlinearLayouts() 59 { 60 linearLayouts=new LinearLayout[3]; 61 linearLayouts[0]=(LinearLayout)findViewById(R.id.lay1); 62 linearLayouts[1]=(LinearLayout)findViewById(R.id.lay2); 63 linearLayouts[2]=(LinearLayout)findViewById(R.id.lay3); 64 linearLayouts[0].setBackgroundResource(R.drawable.lay_select_bg); 65 } 66 /**初始化textview*/ 67 public void settextview() 68 { 69 textViews=new TextView[3]; 70 textViews[0]=(TextView)findViewById(R.id.fratext1); 71 textViews[1]=(TextView)findViewById(R.id.fratext2); 72 textViews[2]=(TextView)findViewById(R.id.fratext3); 73 textViews[0].setTextColor(getResources().getColor(R.color.lightseagreen)); 74 } 75 /**点击底部linerlayout实现切换fragment的效果*/ 76 public void LayoutOnclick(View v) 77 { 78 resetlaybg();//每次点击都重置linearLayouts的背景、textViews字体颜色 79 switch (v.getId()) { 80 case R.id.lay1: 81 getSupportFragmentManager().beginTransaction().hide(fragments[0]).hide(fragments[1]).hide(fragments[2]) 82 .show(fragments[0]).commit(); 83 linearLayouts[0].setBackgroundResource(R.drawable.lay_select_bg); 84 textViews[0].setTextColor(getResources().getColor(R.color.lightseagreen)); 85 MARK=0; 86 break; 87 88 case R.id.lay2: 89 getSupportFragmentManager().beginTransaction().hide(fragments[0]).hide(fragments[1]).hide(fragments[2]) 90 .show(fragments[1]).commit(); 91 linearLayouts[1].setBackgroundResource(R.drawable.lay_select_bg); 92 textViews[1].setTextColor(getResources().getColor(R.color.lightseagreen)); 93 MARK=1; 94 break; 95 case R.id.lay3: 96 getSupportFragmentManager().beginTransaction().hide(fragments[0]).hide(fragments[1]).hide(fragments[2]) 97 .show(fragments[2]).commit(); 98 linearLayouts[2].setBackgroundResource(R.drawable.lay_select_bg); 99 textViews[2].setTextColor(getResources().getColor(R.color.lightseagreen)); 100 MARK=2; 101 break; 102 default: 103 break; 104 } 105 } 106 /**重置linearLayouts、textViews*/ 107 public void resetlaybg() 108 { 109 for(int i=0;i<3;i++) 110 { 111 linearLayouts[i].setBackgroundResource(R.drawable.tabfootbg); 112 textViews[i].setTextColor(getResources().getColor(R.color.black)); 113 } 114 115 } 116 117 @Override 118 public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) { 119 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 120 //将该Activity上触碰事件交给GestureDetector处理 121 return detector.onTouchEvent(event); 122 } 123 @Override 124 public boolean onDown(MotionEvent arg0) { 125 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 126 return false; 127 } 128 129 /**滑动切换效果的实现*/ 130 @Override 131 public boolean onFling(MotionEvent arg0, MotionEvent arg1, float arg2, 132 float arg3) { 133 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 134 resetlaybg(); 135 //当是Fragment0的时候 136 if(MARK==0) 137 { 138 if(arg1.getX()>arg0.getX()+DISTANT) 139 { 140 getSupportFragmentManager().beginTransaction().hide(fragments[0]).hide(fragments[1]).hide(fragments[2]) 141 .show(fragments[1]).commit(); 142 linearLayouts[1].setBackgroundResource(R.drawable.lay_select_bg); 143 textViews[1].setTextColor(getResources().getColor(R.color.lightseagreen)); 144 MARK=1; 145 } 146 else 147 { 148 linearLayouts[0].setBackgroundResource(R.drawable.lay_select_bg); 149 textViews[0].setTextColor(getResources().getColor(R.color.black)); 150 } 151 152 } 153 //当是Fragment1的时候 154 else if (MARK==1) 155 { 156 if(arg1.getX()>arg0.getX()+DISTANT) 157 { 158 getSupportFragmentManager().beginTransaction().hide(fragments[0]).hide(fragments[1]).hide(fragments[2]) 159 .show(fragments[2]).commit(); 160 linearLayouts[2].setBackgroundResource(R.drawable.lay_select_bg); 161 textViews[2].setTextColor(getResources().getColor(R.color.lightseagreen)); 162 MARK=2; 163 } 164 else if(arg0.getX()>arg1.getX()+DISTANT) 165 { 166 getSupportFragmentManager().beginTransaction().hide(fragments[0]).hide(fragments[1]).hide(fragments[2]) 167 .show(fragments[0]).commit(); 168 linearLayouts[0].setBackgroundResource(R.drawable.lay_select_bg); 169 textViews[0].setTextColor(getResources().getColor(R.color.lightseagreen)); 170 MARK=0; 171 } 172 else 173 { 174 linearLayouts[1].setBackgroundResource(R.drawable.lay_select_bg); 175 textViews[1].setTextColor(getResources().getColor(R.color.black)); 176 } 177 } 178 //当是Fragment2的时候 179 else if(MARK==2) 180 { 181 if(arg0.getX()>arg1.getX()+DISTANT) 182 { 183 getSupportFragmentManager().beginTransaction().hide(fragments[0]).hide(fragments[1]).hide(fragments[2]) 184 .show(fragments[1]).commit(); 185 linearLayouts[1].setBackgroundResource(R.drawable.lay_select_bg); 186 textViews[1].setTextColor(getResources().getColor(R.color.lightseagreen)); 187 MARK=1; 188 } 189 else 190 { 191 linearLayouts[2].setBackgroundResource(R.drawable.lay_select_bg); 192 textViews[2].setTextColor(getResources().getColor(R.color.black)); 193 } 194 } 195 return false; 196 } 197 198 @Override 199 public void onLongPress(MotionEvent arg0) { 200 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 201 202 } 203 204 @Override 205 public boolean onScroll(MotionEvent arg0, MotionEvent arg1, float arg2, 206 float arg3) { 207 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 208 return false; 209 } 210 211 @Override 212 public void onShowPress(MotionEvent arg0) { 213 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 214 215 } 216 217 @Override 218 public boolean onSingleTapUp(MotionEvent arg0) { 219 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 220 return false; 221 } 222 223 }
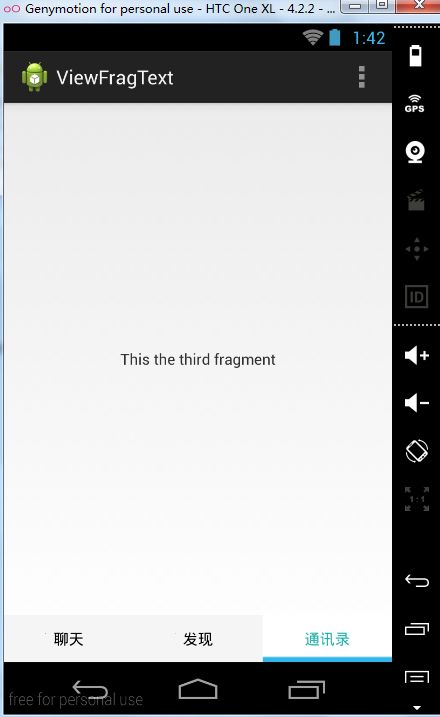
最后的效果图
转载请注明出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/zhrxidian/p/3801545.html
Android页面切换方法和区别
通用的页面跳转方法有两种:
1、Intent
Intent适合Activity与Activity之间的跳转,按返回键可以直接返回前一页面
缺点:需要到Manifest注册Activity
2、setContentView
适合同一Activity里的不同View之间跳转
优点:按返回键不会返回到前一页面,需要自己添加按键监听代码来实现
只切换Layout运行速度会快点,因为启动activity是最耗时的。
数据传递也简单,不用Intent.setExtra之类的。
缺点是所有控件的事件处理、加载之类的操作全集中由activity管理,拆分不够清晰
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.KeyEvent;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.*;
public class IntentTest extends Activity {
private LinearLayout mainView=null;
private Button button1=null;
private Button button2=null;
private LinearLayout layout=null;
private TextView tv=null;
/*
* 由于setContentVeiw()函数返回是void,系统中没有提供获取当前View的函数
* 所以此处添加一个整形变量用来指示当前View的id
*/
private int currentViewId;
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
//tv初始化
tv=new TextView(this);
tv.setText("这是layout里面的tv");
//layout初始化
layout=new LinearLayout(this);
layout.setId(100);//这里需要指定id,否则默认的id会和mainView一样,都是-1
layout.setLayoutParams(new LinearLayout.LayoutParams(-1,-1));
layout.addView(tv);
//button1初始化
button1=new Button(this);
button1.setLayoutParams(new LinearLayout.LayoutParams(-2,-2));
button1.setText("Intent方式跳转");
button1.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener(){
public void onClick(View v) {
/*此处用Intent来实现Activity与Activity之间的跳转*/
Intent intent=new Intent();
intent.setClass(IntentTest.this,MyActivity.class);
//Intent intent=new Intent(IntentTest.this,MyActivity.class);
startActivity(intent);
}
});
//button2初始化
button2=new Button(this);
button2.setLayoutParams(new LinearLayout.LayoutParams(-2,-2));
button2.setText("setContentView方式跳转");
button2.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener(){
public void onClick(View v) {
//此处用setContentView方式来实现统一Activity不同View跳转
setCurrentView(layout);
}
});
//mianView初始化
mainView=new LinearLayout(this);
mainView.setId(1000);//指定id
mainView.setLayoutParams(new LinearLayout.LayoutParams(-1,-1));
mainView.setOrientation(LinearLayout.VERTICAL);
mainView.addView(button1);
mainView.addView(button2);
//显示mainView
setCurrentView(mainView);
}
/*
* 这里重写onKeyDown()函数,实现返回键的监听
* 如果通过显示的View对keyListener进行监听,则返回键监听不到
* 所以此处是通过在Activity里面重写onKeyDown()函数来实现监听
* 此处如果不拦截监听的话,在显示layout后按返回键则直接执行退出程序
*/
public boolean onKeyDown(int keyCode, KeyEvent event) {
if (keyCode == KeyEvent.KEYCODE_BACK) {
if(currentViewId==layout.getId()){
setCurrentView(mainView);
}else{
System.exit(0);
}
return false;
}
return false;
}
/*自定义函数setCurrentView()*/
public void setCurrentView(View view){
currentViewId=view.getId();
//此处用setContentView方式来实现统一Activity不同View跳转
setContentView(view);
}
}
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class MyActivity extends Activity{
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
TextView tv=new TextView(this);
tv.setText("我是MyActivity里的tv");
setContentView(tv);
}
}