python爬虫之Beautiful Soup基础知识
Beautiful Soup是一个可以从HTML或XML文件中提取数据的python库。它能通过你喜欢的转换器实现惯用的文档导航,查找,修改文档的方式。
需要注意的是,Beautiful Soup已经自动将输入文档转换为Unicode编码,输出文档转换为utf-8编码。因此在使用它的时候不需要考虑编码方式,仅仅需要说明一下原始编码方式就可以了。
一、安装Beautiful Soup库
使用pip命令工具安装Beautiful Soup4库
pip install beautifulsoup4
二、BeautifulSoup库的主要解析器
| 解析器 | 使用方法 | 条件 |
|---|---|---|
| bs4的html解析器 | BeautifulSoup(markup, 'html.parser') | 安装bs4库 |
| lxml的html解析器 | BeautifulSoup(markup, 'lxml') | pip install lxml |
| lxml的lxml解析器 | BeautifulSoup(markup, 'lxml') | pip install lxml |
| html5lib的解析器 | BeautifulSoup(markup, 'html5lib') | pip install html5lib |
具体操作:
html = 'https://www.baidu.com'
bs = BeautifulSoup(html, 'html.parser')
三、BeautifulSoup的简单使用
提取百度搜索页面的部分源代码为例:
百度一下,你就知道
综合requests和使用BeautifulSoup库的html解析器,对其进行解析如下:
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
# 使用requests库加载页面代码
r = requests.get('https://www.baidu.com')
r.encoding = r.apparent_encoding
html = r.text
bs = BeautifulSoup(html, 'html.parser')
print(bs.prettify()) # prettify 方式输出页面
结果如下:
百度一下,你就知道
四、BeautifulSoup类的基本元素
BeautifulSoup将复制的HTML文档转换成一个复杂的树型结构,每个节点都是python对象,所有对象可以归纳为四种Tag,NavigableString,Comment,Beautifulsoup。
| 基本元素 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Tag | 标签,最基本的信息组织单元,分别用<>和标明开头和结尾,格式:bs.a或者bs.p(获取a标签中或者p标签中的内容)。 |
| Name | 标签的名字,格式为.name. |
| Attributes | 标签的属性,字典形式,格式:.attrs. |
| NavigableString | 标签内非属性字符串,<>...中的字符串,格式:.string. |
| Comment | 标签内的注释部分,一种特殊的Comment类型。 |
Tag
任何存在于HTML语法中的标签都可以bs.tag访问获得,如果在HTML文档中存在多个相同的tag对应的内容时,bs.tag返回第一个。示例代码如下:
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
# 使用requests库加载页面代码
r = requests.get('https://www.baidu.com')
r.encoding = r.apparent_encoding
html = r.text
bs = BeautifulSoup(html, 'html.parser')
# 获取第一个a标签的所有内容
print(bs.a) # 新闻
print(type(bs.a)) #
在Tag标签中最重要的就是html页面中的nam和attrs属性,使用方法如下:
print(bs.a.name) # a
# 把a标签的所有属性打印输出出来,返回一个字典类型
print(bs.a.attrs) # {'href': 'http://news.baidu.com', 'name': 'tj_trnews', 'class': ['mnav']}
# 等价 bs.a.get('class')
print(bs.a['class']) # ['mnav']
bs.a['class'] = 'newClass' # 对class属性的值进行修改
print(bs.a) # 新闻
del bs.a['class'] # 删除class属性
print(bs.a) # 新闻
NavigableString
NavigableString中的string方法用于获取标签内部的文字,代码如下:
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
# 使用requests库加载页面代码
r = requests.get('https://www.baidu.com')
r.encoding = r.apparent_encoding
html = r.text
bs = BeautifulSoup(html, 'html.parser')
print(bs.title.string) # 百度一下,你就知道
print(type(bs.title.string)) #
Comment
Comment对象是一个特殊类型的NavigableString对象,其输出的内容不包括注释符号,用于输出注释的内容。
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
html = """"""
bs = BeautifulSoup(html, 'html.parser')
print(bs.a.string) # 新闻
print(type(bs.a.string)) #
BeautifulSoup
bs对象表示的是一个文档的全部内容,大部分时候,可以把它当作Tag对象,支持遍历文档树和搜索文档中描述的大部分方法。
因为Beautifulsoup对象并不是真正的HTML或者XML的tag,所以它没有name和attribute属性。所以BeautifulSoup对象一般包含值为"[document]"的特殊属性.name
print(bs.name) # [document]
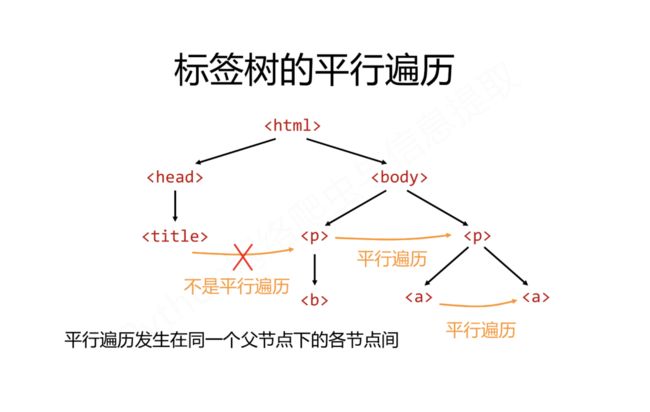
五、基于bs4库的HTML内容的遍历方法
在HTML中有如下特定的基本格式,也是构成HTML页面的基本组成成分。
而在这种基本的格式下有三种基本的遍历流程
- 下行遍历
- 上行遍历
- 平行遍历
三种遍历方式分别是从当前节点出发,对之上、之下、平行的格式以及关系进行遍历。
下行遍历
下行遍历分别有三种遍历属性,如下所示:
| 属性 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| .contents | 子节点的列表,将所有儿子节点存入列表。 |
| .children | 子节点的迭代类型,用于循环遍历儿子节点。 |
| .descendants | 子孙节点的迭代类型,包涵所有子孙节点,用于循环遍历。 |
代码如下:
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
# 使用requests库加载页面代码
r = requests.get('https://www.baidu.com')
r.encoding = r.apparent_encoding
html = r.text
bs = BeautifulSoup(html, 'html.parser')
# 循环遍历儿子节点
for child in bs.body.children:
print(child)
# 循环遍历子孙节点
for child in bs.body.descendants:
print(child)
# 输出子节点,以列表的形式
print(bs.head.contents)
print(bs.head.contents[0]) # 用列表索引来获取它的某一个元素
上行遍历
上行遍历有两种方式,如下所示:
| 属性 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| .parent | 节点的父亲标签。 |
| .parents | 节点先辈标签的迭代类型,用于循环遍历先辈节点,返回一个生成器。 |
代码如下:
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
# 使用requests库加载页面代码
r = requests.get('https://www.baidu.com')
r.encoding = r.apparent_encoding
html = r.text
bs = BeautifulSoup(html, 'html.parser')
for parent in bs.a.parents:
if parent is not None:
print(parent.name)
print(bs.a.parent.name)
平行遍历
平行遍历有四种属性,如下所示:
| 属性 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| .next_sibling | 返回按照HTML文本顺序的下一个平行节点标签。 |
| .previous_sibling | 返回按照HTML文本顺序的上一个平行节点标签。 |
| .next_siblings | 迭代类型,返回按照HTML文本顺序的所有后续平行节点标签。 |
| .previous_siblings | 迭代类型,返回按照HTML文本顺序的前序所有平行节点标签。 |
代码如下:
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
# 使用requests库加载页面代码
r = requests.get('https://www.baidu.com')
r.encoding = r.apparent_encoding
html = r.text
bs = BeautifulSoup(html, 'html.parser')
for sibling in bs.a.next_siblings:
print(sibling)
for sibling in bs.a.previous_siblings:
print(sibling)
其它遍历
| 属性 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| .strings | 如果Tag包含多个字符串,即在子孙节点中有内容,可以用此获取,然后进行遍历。 |
| .stripped_strings | 与strings用法一致,可以去除掉那些多余的空白内容。 |
| .has_attr | 判断Tag是否包含属性。 |
六、文件树搜索
使用bs.find_all(name, attires, recursive, string, **kwargs)方法,用于返回一个列表类型,存储查找的结果。
| 属性 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| name | 对标签的名称的检索字符串。 |
| attrs | 对标签属性值的检索字符串,可标注属性检索。 |
| recursive | 是否对子孙全部检索,默认为True。 |
| string | 用与在信息文本中特定字符串的检索。 |
name参数
如果是指定的字符串:会查找与字符串完全匹配的内容,代码如下:
a_list = bs.find_all("a")
print(a_list)
使用正则表达式:将会使用BeautifulSoup4中的search()方法来匹配,代码如下:
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import re
# 使用requests库加载页面代码
r = requests.get('https://www.baidu.com')
r.encoding = r.apparent_encoding
html = r.text
bs = BeautifulSoup(html, 'html.parser')
t_list = bs.find_all(re.compile("p"))
for item in t_list:
print(item)
传入一个列表:Beautifulsoup4将会与列表中的任一元素匹配到的节点返回,代码如下:
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
# 使用requests库加载页面代码
r = requests.get('https://www.baidu.com')
r.encoding = r.apparent_encoding
html = r.text
bs = BeautifulSoup(html, 'html.parser')
t_list = bs.find_all(["meta", "link"])
for item in t_list:
print(item)
传入一个函数或方法:将会根据函数或者方法来匹配,代码如下:
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
# 使用requests库加载页面代码
r = requests.get('https://www.baidu.com')
r.encoding = r.apparent_encoding
html = r.text
bs = BeautifulSoup(html, 'html.parser')
def name_is_exists(tag):
return tag.has_attr("name")
t_list = bs.find_all(name_is_exists)
for item in t_list:
print(item)
attrs参数
并不是所有的属性都可以使用上面这种方法进行搜索,比如HTML的data属性,用与指定属性搜索。
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
# 使用requests库加载页面代码
r = requests.get('https://www.baidu.com')
r.encoding = r.apparent_encoding
html = r.text
bs = BeautifulSoup(html, 'html.parser')
t_list = bs.find_all(attrs={"class": "mnav"})
for item in t_list:
print(item)
string参数
通过string参数可以搜索文档中的字符串内容,与name参数的可选值一样,string参数接受字符串,正则表达式,列表。
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import re
# 使用requests库加载页面代码
r = requests.get('https://www.baidu.com')
r.encoding = r.apparent_encoding
html = r.text
bs = BeautifulSoup(html, 'html.parser')
t_list = bs.find_all(attrs={"class": "mnav"})
for item in t_list:
print(item)
# text用于搜索字符串
t_list = bs.find_all(text="hao123")
for item in t_list:
print(item)
# text可以通其它参数混合使用用来过滤tag
t_list = bs.find_all("a", text=["hao123", "地图", "贴吧"])
for item in t_list:
print(item)
t_list = bs.find_all(text=re.compile("\d\d"))
for item in t_list:
print(item)
使用find_all()方法,常用到的正则表达式形式import re代码如下:
bs.find_all(string = re.compile('python')) # 指定查找内容
# 或者指定使用正则表达式要搜索的内容
string = re.compile('python') # 字符为python
bs.find_all(string) # 调用方法模版
七、常用的find()方法如下
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| <>find() | 搜索且只返回一个结果,字符串类型,同.find_all()参数。 |
| <>find_parent() | 在先辈节点中返回一个结果,字符串类型,同.find_all()参数。 |
| <>.find_parents() | 在先辈节点中搜索,返回列表类型,同.find_all()参数。 |
| <>.find_next_sibling() | 在后续平行节点中返回一个结果,同.find_all()参数。 |
| <>.find_next_siblings() | 在后续平行节点中搜索,返回列表类型,同.find_all()参数。 |
| <>.find_previous_sibling() | 在前序平行节点中返回一个结果,字符串类型,同.find_all()参数。 |
| <>.find_previous_siblings() | 在前序平行节点中搜索,返回列表类型,同.find_all()参数。 |
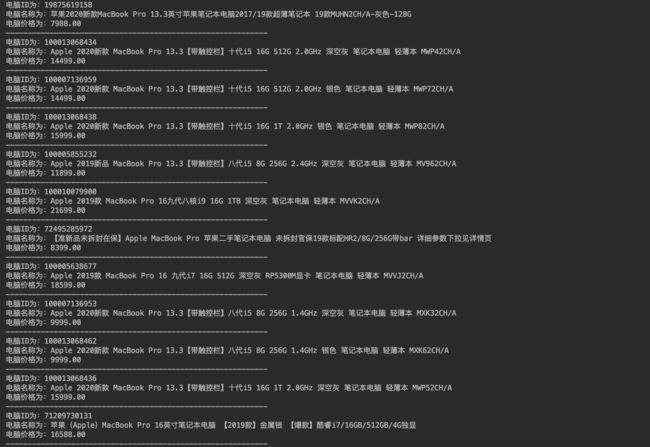
八、爬取京东电脑数据
爬取的例子直接输出到屏幕。
(1)要爬取京东一页的电脑商品信息,下图所示:
(2)所爬取的网页连接:https://search.jd.com/search?keyword=macbook pro&qrst=1&suggest=5.def.0.V09&wq=macbook pro
(3)我们的目的是需要获取京东这一个页面上所有的电脑数据,包括价格,名称,ID等。具体代码如下:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
headers = {
'User-agent': "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) "
"Chrome/66.0.3359.139 Safari/537.36"
}
URL = "https://search.jd.com/search?keyword=macbook%20pro&qrst=1&suggest=5.def.0.V09&wq=macbook%20pro"
r = requests.get(URL, headers=headers)
r.encoding = r.apparent_encoding
html = r.text
bs = BeautifulSoup(html, 'html.parser')
all_items = bs.find_all('li', attrs={"class": "gl-item"})
for item in all_items:
computer_id = item["data-sku"]
computer_name = item.find('div', attrs={'class': 'p-name p-name-type-2'})
computer_price = item.find('div', attrs={'class': 'p-price'})
print('电脑ID为:' + computer_id)
print('电脑名称为:' + computer_name.em.text)
print('电脑价格为:' + computer_price.find('i').string)
print('------------------------------------------------------------')
部分结果如下图所示: