pytorch框架学习(8)——nn网络层
文章目录
- 1. 卷积层
- 1.2 1d/2d/3d卷积
- 1.3 卷积-nn.Conv2d()
- 1.4 转置卷积-ConvTranspose
- 2. 池化层——Pooling Layer
- 3. 线性层——Linear Layer
- 4. 激活函数层——Activation Layer
1. 卷积层
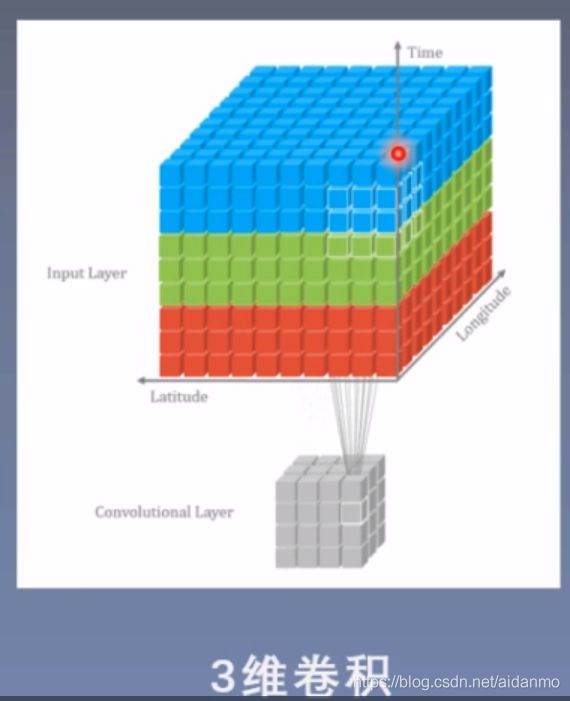
1.2 1d/2d/3d卷积
-
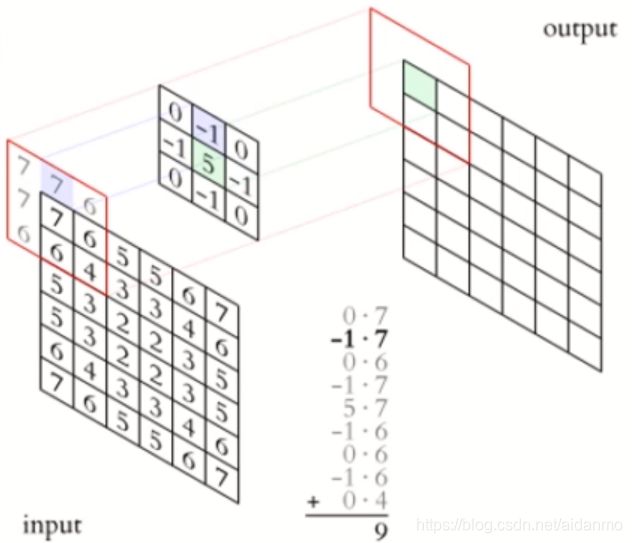
卷积运算:卷积核在输入信号(图像)上滑动,相应位置上进行乘加
-
卷积过程类似于用一个模板去图像上寻找与它相似的区域,与卷积核模式越相似,激活值越高,从而实现特征提取。
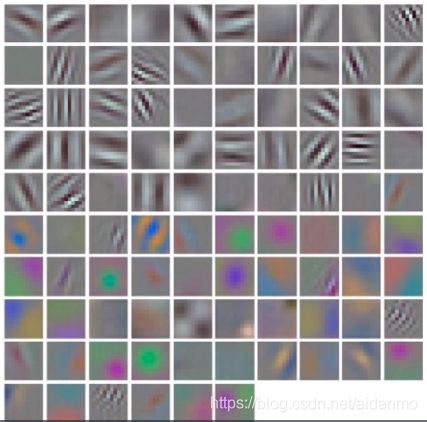
上图是AlexNet卷积核可视化图像,发现卷积核学习到的是边缘,条纹,色彩这一些细节模式。
1.3 卷积-nn.Conv2d()
- nn.Conv2d
- 功能:对多个二维信号进行二维卷积
- in_channels:输入通道数
- out_channels:输出通道数,等价于卷积核个数
- kernel_size:卷积核尺寸
- stride:步长
- padding:填充个数
- dilation:空洞卷积大小
- groups:分组卷积设置
- bias:偏置
- 尺寸计算:
简化版: o u t s i z e = I n s i z e − k e r n e l s i z e s t r i d e + 1 out_{size} = \frac{In_{size} - kernel_{size}}{stride} + 1 outsize=strideInsize−kernelsize+1
# load img
path_img = os.path.join(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__)), 'lena.png')
img = Image.open(path_img).convert('RGB')
# convert to tensor
img_transform = transforms.Compose([transforms.ToTensor()])
img_tensor = img_transform(img)
img_tensor.unsqueeze_(dim=0) # C*H*W to B*C*H*W
# 创建卷积层
# 2d
flag = 1
# flag = 0
if flag:
conv_layer = nn.Conv2d(3, 1, 3) # input:(i, o, size)
nn.init.xavier_normal_(conv_layer.weight.data) # 正态分布初始化
# calculation
img_conv = conv_layer(img_tensor)
卷积前尺寸:torch.Size([1, 3, 512, 512])
卷积后尺寸:torch.Size([1, 1, 510, 510])
1.4 转置卷积-ConvTranspose
- 转置卷积用于对图像进项上采样
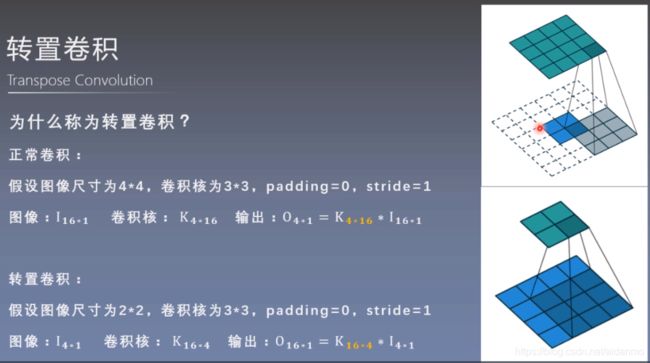
- nn.ConvTranspose2d
- 功能:转置卷积实现上采样
- in_channels:输入通道数
- out_channels:输出通道数
- kernel_size:卷积核尺寸
- stride:步长
- padding:填充个数
- dilation:空洞卷积大小
- groups:分组卷积设置
- bias:偏置
- 尺寸计算:
简化版: o u t s i z e = ( i n s i z e − 1 ) ∗ s t r i d e + k e r n e l s i z e out_{size} = (in_{size} - 1) * stride + kernel_{size} outsize=(insize−1)∗stride+kernelsize
# transposed
flag = 1
# flag = 0
if flag:
conv_layer = nn.ConvTranspose2d(3, 1, 3, stride=2)
nn.init.xavier_normal_(conv_layer.weight.data)
# calculation
img_conv = conv_layer(img_tensor)
卷积前尺寸:torch.Size([1, 3, 512, 512])
卷积后尺寸:torch.Size([1, 1, 1025, 1025])
2. 池化层——Pooling Layer
- 池化运算:对信号进行“收集”并“总结”,类似水池收集水资源,因而得名池化层。
- 收集:多变少
- 总结:最大值/平均值

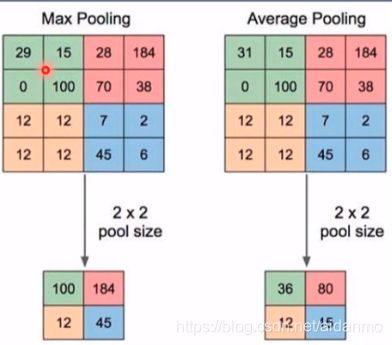
- nn.MaxPool2d
- 功能:对二维信号进行最大值池化
- kernel_size:池化核尺寸
- stride:步长
- padding:填充个数
- dilation:池化核间隔大小
- ceil_mode:尺寸向上取整
- return_indices:记录池化像素索引
maxpool_layer = nn.MaxPool2d((2, 2), stride=(2, 2))
img_pool = maxpool_layer(img_tensor)
池化前尺寸:torch.Size([1, 3, 512, 512])
池化后尺寸:torch.Size([1, 3, 256, 256])
- nn.AvgPool2d
- 功能:对二维信号进行平均值池化
- kernel_size:池化核尺寸
- stride:步长
- padding:填充个数
- ceil_mode:尺寸向上取整
- count_include_pad:填充值用于计算
- divisor_override:除法因子
avgpool_layer = nn.AvgPool2d((2, 2), stride=(2, 2))
img_pool = avgpool_layer(img_tensor)
池化前尺寸:torch.Size([1, 3, 512, 512])
池化后尺寸:torch.Size([1, 3, 256, 256])
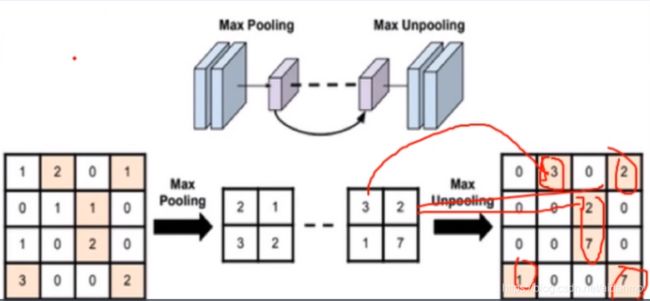
# pooling
img_tensor = torch.randint(high=5, size=(1, 1, 4, 4), dtype=torch.float)
maxpool_layer = nn.MaxPool2d((2, 2), stride=(2, 2), return_indices=True)
img_pool, indices = maxpool_layer(img_tensor) # indices为坐标信息
# unpooling
img_reconstruct = torch.randn_like(img_pool, dtype=torch.float)
maxunpool_layer = nn.MaxUnpool2d((2, 2), stride=(2, 2))
img_unpool = maxunpool_layer(img_reconstruct, indices)
执行结果:
raw_img:
tensor([[[[0., 4., 4., 3.],
[3., 3., 1., 1.],
[4., 2., 3., 4.],
[1., 3., 3., 0.]]]])
img_pool:
tensor([[[[4., 4.],
[4., 4.]]]])
img_reconstruct:
tensor([[[[-1.0276, -0.5631],
[-0.8923, -0.0583]]]])
img_unpool:
tensor([[[[ 0.0000, -1.0276, -0.5631, 0.0000],
[ 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000],
[-0.8923, 0.0000, 0.0000, -0.0583],
[ 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000]]]])
3. 线性层——Linear Layer
- 线性层又称全连接层,其每个神经元与上一层所有神经元相连,实现对前一层的线性组合,线性变换。

计算方式如下:

- nn.Linear
- 功能:对一维信号(向量)进行线性组合
- in_features:输入结点数
- out_features:输出结点数
- bias:是否需要偏置
- 计算公式: y = x W T + b i a s y = xW^T + bias y=xWT+bias
inputs = torch.tensor([[1., 2, 3]])
linear_layer = nn.Linear(3, 4)
linear_layer.weight.data = torch.tensor([[1., 1., 1.],
[2., 2., 2.],
[3., 3., 3.],
[4., 4., 4.]])
linear_layer.bias.data.fill_(0.5)
output = linear_layer(inputs)
print(inputs, inputs.shape)
print(linear_layer.weight.data, linear_layer.weight.data.shape)
print(output, output.shape)
结果为:
tensor([[1., 2., 3.]]) torch.Size([1, 3])
tensor([[1., 1., 1.],
[2., 2., 2.],
[3., 3., 3.],
[4., 4., 4.]]) torch.Size([4, 3])
tensor([[ 6.5000, 12.5000, 18.5000, 24.5000]], grad_fn=<AddmmBackward>) torch.Size([1, 4])
4. 激活函数层——Activation Layer
- 激活函数对特征进行非线性变换,赋予多层神经网络具有深度的意义。

如果没有激活函数层,那么多个线性层的叠加相当于一个线性层。 - nn.Sigmoid
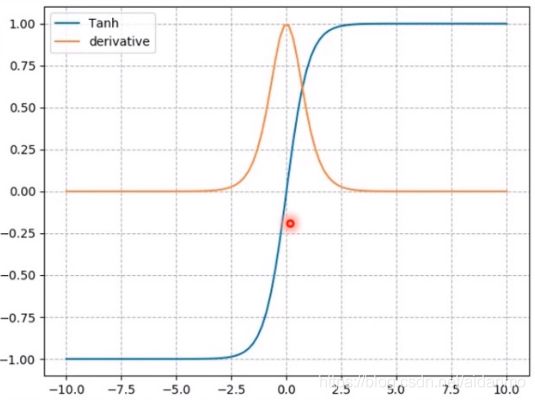
- nn.tanh
- 公式: y = s i n x c o s x = e x − e − x e x + e − x = 2 1 + e − 2 x + 1 y = \frac{sinx}{cosx} = \frac{e^x-e^{-x}}{e^x+e^{-x}} = \frac{2}{1+e^{-2x}}+1 y=cosxsinx=ex+e−xex−e−x=1+e−2x2+1
- 梯度公式:KaTeX parse error: Expected group after '^' at position 2: y^̲' = 1-y^2
- 特性:
- nn.ReLU
- nn.LeakyReLU
- negative_slope:负半轴斜率
- nn.PReLU
- init:可学习斜率
- nn.RReLU