贪心科技机器学习训练营(八)
先把来源写上
来源:贪心学院,https://www.zhihu.com/people/tan-xin-xue-yuan/activities
这次是贝叶斯
先回忆下是啥东西
- 贝叶斯分类算法
- 贝叶斯分类流程
- 贝叶斯算法对文本进行分类实例
- SVM实现人脸识别
- 深入理解SVM
- svm的三个核函数
- SVM支持向量机(上)
- SVM支持向量机(下)
回忆下了tfidf
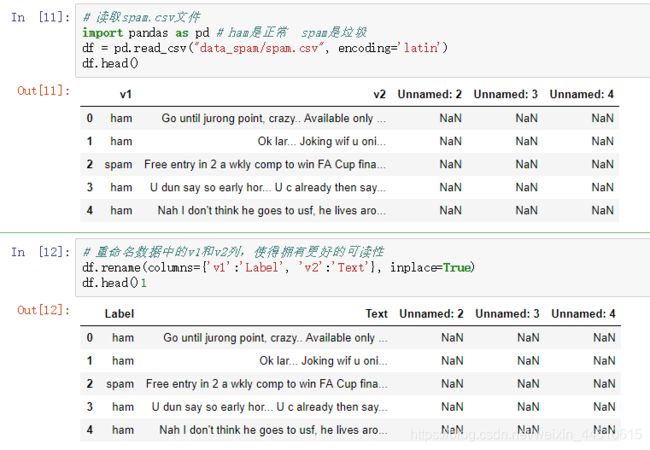
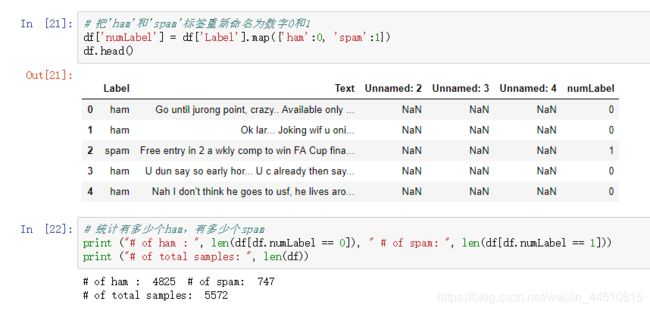
垃圾邮件分类
之前做过文本分类案例,效率差得离谱
这个
# 统计文本的长度信息
text_lengths = [len(df.loc[i,'Text']) for i in range(len(df))]
print ("the minimum length is: ", min(text_lengths))
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.mlab as mlab
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 100是柱子数
plt.hist(text_lengths, 100, facecolor='blue', alpha=0.5)
plt.xlim([0,200])
plt.show()
# 导入英文呢的停用词库
from nltk.corpus import stopwords
# 词袋
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import CountVectorizer
# what is stop wordS? he she the an a that this ...
stopset = set(stopwords.words("english"))
# 构建文本的向量 (基于词频的表示)
#vectorizer = CountVectorizer(stop_words=stopset,binary=True)
vectorizer = CountVectorizer()
# sparse matrix
X = vectorizer.fit_transform(df.Text)
y = df.numLabel
# 把数据分成训练数据和测试数据
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.20, random_state=100)
print ("训练数据中的样本个数: ", X_train.shape[0], "测试数据中的样本个数: ", X_test.shape[0])
训练数据中的样本个数: 4457 测试数据中的样本个数: 1115
# 利用朴素贝叶斯做训练
from sklearn.naive_bayes import MultinomialNB
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
clf = MultinomialNB(alpha=1.0, fit_prior=True)
clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_pred = clf.predict(X_test)
print("accuracy on test data: ", accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred))
# 打印混淆矩阵
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
print(confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pred, labels=[0, 1]))
accuracy on test data: 0.9757847533632287
[[952 18]
[ 9 136]]
文本分类之 - 情感分析
# 导入英文呢的停用词库
#import nltk
#nltk.download('stopwords')
from nltk.corpus import stopwords
# 词袋模型 特征选择
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import CountVectorizer
# what is stop wordS? he she the an a that this ...
# 加载停用词 集合
stopset = set(stopwords.words("english"))
# 构建文本的向量 (基于词频的表示)
vectorizer = CountVectorizer(stop_words=stopset,binary=True)
# vectorizer = CountVectorizer()
# sparse matrix
X = vectorizer.fit_transform(df.Text)
y = df.numLabel
# 利用朴素贝叶斯做训练
from sklearn.naive_bayes import MultinomialNB
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
clf = MultinomialNB(alpha=1.0, fit_prior=True)
clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_pred = clf.predict(X_test)
print("accuracy on test data: ", accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred))
# 打印混淆矩阵
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
print(confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pred, labels=[0, 1]))
accuracy on test data: 0.9757847533632287
[[952 18]
[ 9 136]]
文本分类之 - 情感分析
读取数据
def read_data(path, is_pos=None):
"""
给定文件的路径,读取文件
path: path to the data
is_pos: 是否数据是postive samples.
return: (list of review texts, list of labels)
"""
reviews, labels = [], []
with open(path, 'r',encoding='utf-8') as file:
review_start = False
# 放文本的
review_text = []
for line in file:
# 去空格
line = line.strip()
# 没有就继续
if not line: continue
#
if not review_start and line.startswith("":
review_start = False
reviews.append(" ".join(review_text))
review_text = []
continue
if review_start:
review_text.append(line)
if is_pos:
labels = [1]*len(reviews)
elif not is_pos is None:
labels = [0]*len(reviews)
return reviews, labels
def process_file():
"""
读取训练数据和测试数据,并对它们做一些预处理
"""
train_pos_file = "data_sentiment/train.positive.txt"
train_neg_file = "data_sentiment/train.negative.txt"
test_comb_file = "data_sentiment/test.combined.txt"
# 读取文件部分,把具体的内容写入到变量里面
train_pos_cmts, train_pos_lbs = read_data(train_pos_file, True)
train_neg_cmts, train_neg_lbs = read_data(train_neg_file, False)
train_comments = train_pos_cmts + train_neg_cmts
train_labels = train_pos_lbs + train_neg_lbs
test_comments, test_labels = read_data(test_comb_file)
return train_comments, train_labels, test_comments, test_labels
train_comments, train_labels, test_comments, test_labels = process_file()
def load_stopwords(path):
"""
从外部文件中导入停用词
"""
stopwords = set()
with open(path, 'r') as in_file:
for line in in_file:
stopwords.add(line.strip())
return stopwords
def clean_non_chinese_symbols(text):
"""
处理非中文字符
"""
text = re.sub('[!!]+', "!", text)
text = re.sub('[??]+', "?", text)
text = re.sub("[a-zA-Z#$%&\'()*+,-./:;:<=>@,。★、…【】《》“”‘’[\\]^_`{|}~]+", " UNK ", text)
return re.sub("\s+", " ", text)
def clean_numbers(text):
"""
处理数字符号 128 190 NUM
"""
return re.sub("\d+", ' NUM ', text)
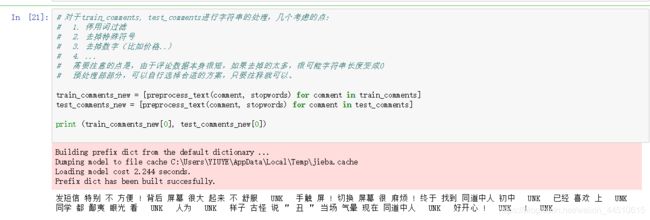
def preprocess_text(text, stopwords):
"""
文本的预处理过程
"""
text = clean_non_chinese_symbols(text)
text = clean_numbers(text)
text = " ".join([term for term in jieba.cut(text) if term and not term in stopwords])
return text
path_stopwords = "./data_sentiment/stopwords.txt"
stopwords = load_stopwords(path_stopwords)
# 利用tf-idf从文本中提取特征,写到数组里面.
# 参考:https://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.feature_extraction.text.TfidfVectorizer.html
tfidf = TfidfVectorizer()
X_train = tfidf.fit_transform(train_comments_new) # 训练数据的特征
y_train = train_labels # 训练数据的label
X_test = tfidf.transform(test_comments_new) # 测试数据的特征
y_test = test_labels# 测试数据的label
print (np.shape(X_train), np.shape(X_test), np.shape(y_train), np.shape(y_test))
# 8064, 23101) (2500, 23101) (8064,) (2500,)
from sklearn.naive_bayes import MultinomialNB
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
clf = MultinomialNB()
# 利用朴素贝叶斯做训练
clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_pred = clf.predict(X_test)
print("accuracy on test data: ", accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred))
# accuracy on test data: 0.6368
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
clf = LogisticRegression(solver='liblinear')
clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_pred = clf.predict(X_test)
print("accuracy on test data: ", accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred))
# accuracy on test data: 0.7136