Android自定义View之扇形饼状图
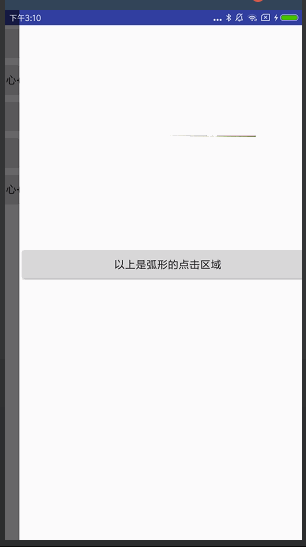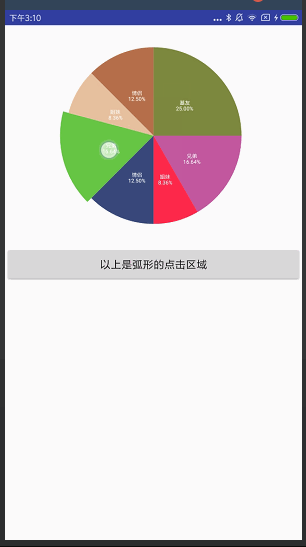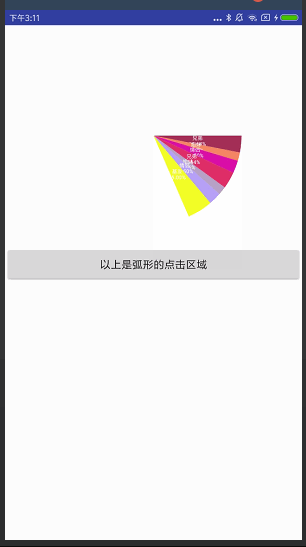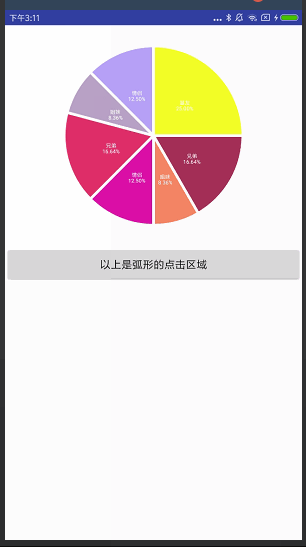
饼状图
Math类介绍
sin:在直角三角形中,∠α(不是直角)的对边与斜边的比叫做∠α的正弦
cos:在直角三角形中,∠α(不是直角)的临边与斜边的比叫做∠α的余弦
Math.toRadians(double angdeg):角度转换为弧度
Math.toDegrees(double angrad):弧度转换为角度
Math.sqrt(double d):开根号
Math.sin(double d):参数d不是度数而是弧度
Math.cos(double d):参数d不是度数而是弧度
Math.atan2(double y, double x):计算出来的结果是一个弧度值,也可以表示相对直角三角形对角的角,其中 x 是临边边长, y 是对边边长。
Arrays.binarySearch(float[] array, float value):如果找到关键字,则返回值为关键字在数组中的位置索引,且索引从0开始;如果没有找到关键字,返回值为 负 的插入点值,所谓插入点值就是第一个比关键字大的元素在数组中的位置索引,而且这个位置索引从1开始
效果图
函数式说明:
/**
* 1:算出弧形和弧形间的间隔各自占多少度数
* 2:通过循环先画每个弧形大小、再通过循环画每个间隔大小
* 3:通过属性动画来实现动态增加
*/
private void goDrawArc(Canvas canvas) {
Log.d("liuyz", "onDraw:" + measureWidth + "x" + measureHeight);
float startAngle = 0;
float lineStartAngle;
float sweepLineAngle;
count = 0;
float linetotal = 360 - data.length * SPACE_DEGREES;
//循环画弧形
for (int i = 0; i < data.length; i++) {
float percent = data[i] / totalNum;
float sweepAngle = data[i] / totalNum * linetotal;//每个扇形的角度
sweepAngle = sweepAngle * animationValue;
sweepLineAngle = SPACE_DEGREES * animationValue;//弧形间的间距
angles[i] = startAngle;
drawArc(canvas, startAngle, sweepAngle, colors[i], i);
startAngle = startAngle + sweepAngle;//这里只计算了弧形区域的开始角度,等把数据计算画成后,还需要加上间隔区域
//当前弧线中心点相对于纵轴的夹角度数,由于扇形的绘制是从三点钟方向开始,所以加90
float arcCenterDegree = 90 + startAngle - sweepAngle / 2;//这里坐标系是从0点开始,顺时针开始计算度数,这里即便第一次startAngle也不是0 而是弧形结束的位置度数
drawData(canvas, arcCenterDegree, i, percent);
startAngle += sweepLineAngle;//需要先把数据画完,才能加间隔区域,否则数据无法显示在正中间
}
startAngle = 0;//每次弧形画完成后,都需要重置再画线,这样可以让白线在弧形上面
//循环画线
for (int i = 0; i < data.length; i++) {
float sweepAngle = data[i] / totalNum * linetotal;//每个扇形的角度
sweepAngle = sweepAngle * animationValue;
sweepLineAngle = SPACE_DEGREES * animationValue;//弧形间的间距
lineStartAngle = startAngle + sweepAngle;
//这里坐标系是从0点开始,顺时针开始计算度数,这里即便第一次startAngle也不是0 而是弧形结束的位置度数
//所以这里需要加上sweepAngle1
float lineAngle1 = lineStartAngle + sweepLineAngle;
drawLine(canvas, lineAngle1, sweepLineAngle, i);
startAngle = startAngle + sweepAngle + sweepLineAngle;//这里只计算了弧形区域的开始角度,等把数据计算画成后,还需要加上间隔区域
}
setClickPosition();
canvas.drawText(totalNum + "", centerX - centerTextBound.width() / 2, centerY + centerTextBound.height() / 2, centerPaint);
}
/**
* 根据旋转的度数,计算出圆上的点相对于自定义View的(0,0)的坐标
*
* @param degree 旋转的度数
* @param radius 半径
*/
private float[] calculatePosition(float degree, float radius) {
//由于Math.sin(double a)中参数a不是度数而是弧度,所以需要将度数转化为弧度
//而Math.toRadians(degree)的作用就是将度数转化为弧度
float x = 0f;
float y = 0f;
//扇形弧线中心点距离圆心的x坐标
//sin 一二正,三四负 sin(180-a)=sin(a)
x = (float) (Math.sin(Math.toRadians(degree)) * radius);
//扇形弧线中心点距离圆心的y坐标
//cos 一四正,二三负
y = (float) (Math.cos(Math.toRadians(degree)) * radius);
//每段弧度的中心坐标(扇形弧线中心点相对于view的坐标)
float startX = centerX + x;
float startY = centerY - y;
float[] position = new float[2];
position[0] = startX;
position[1] = startY;
return position;
}
/**
* 通过count、comparePosition值来判断是否需要放大、缩小弧形区域
*/
private void drawArc(Canvas canvas, float startAngle, float rotateAngle, int color, int i) {
Log.d("huaLine", startAngle + "x" + rotateAngle);
arcPaint.setColor(color);
if (position - 1 == i && !(comparePosition == position)) {
count += 1;
//需要放大时使用rectfTouch
canvas.drawArc(rectfTouch, startAngle, rotateAngle, false, arcPaint);
} else {
count += 0;
canvas.drawArc(rectf, startAngle, rotateAngle, false, arcPaint);
}
}
/**
* 通过count、comparePosition值来判断是否需要放大、缩小弧形区域
*/
private void drawArc(Canvas canvas, float startAngle, float rotateAngle, int color, int i) {
Log.d("huaLine", startAngle + "x" + rotateAngle);
arcPaint.setColor(color);
if (position - 1 == i && !(comparePosition == position)) {
count += 1;
//需要放大时使用rectfTouch
canvas.drawArc(rectfTouch, startAngle, rotateAngle, false, arcPaint);
} else {
count += 0;
canvas.drawArc(rectf, startAngle, rotateAngle, false, arcPaint);
}
}
/**
* 通过间隔弧度,算出弧度两点连线的距离,然后再从圆心开始画直线
*/
private void drawLine(Canvas canvas, float lineStartAngle, float degree, int i) {
float arcCenterDegree = 90 + lineStartAngle - degree / 2;
Log.d("huaLine", degree + "--");
//由于Math.sin(double a)中参数a不是度数而是弧度,所以需要将度数转化为弧度
//sin 对边与斜边的比叫做∠α的正弦
//con 临边与斜边的比叫余弦
//因为画弧形style模式设置为STROKE,所以需要再加上弧形宽度的一半
//根据度数计算出弧形两点连线的距离
double lineWidth = Math.sin(Math.toRadians(degree / 2)) * (radius + cicleWidth / 2) * 2;
linePaint.setStrokeWidth((float) lineWidth);
//弧度中心坐标
float startX = calculatePosition(arcCenterDegree, (radius + cicleWidth / 2))[0];
float startY = calculatePosition(arcCenterDegree, (radius + cicleWidth / 2))[1];
Log.d("huaLine", lineWidth + "--" + startX + "x" + startY);
canvas.drawLine(centerX, centerY, startX, startY, linePaint);
}
/**
* 生成随机颜色
*/
private int randomColor() {
int r = random.nextInt(255);
int g = random.nextInt(255);
int b = random.nextInt(255);
return Color.rgb(r, g, b);
}
/**
* 1:通过atan2函数计算出点击时的角度
* 2:通过象限转换成坐标系的角度
* 3:通过sqrt(开根号)勾股定理计算出点击区域是否在半径内
* 4:通过binarySearch(二分查找)计算出点击的position
*/
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
switch (event.getAction()) {
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
if (!isAnimatorEnd) break;//动画进行时,不能点击
float relative_centerX = centerX;
float relative_centerY = -centerY;
//坐标系 左上正,右下负
float x = event.getX() - relative_centerX;
float y = -event.getY() - relative_centerY;
//angel=Math.atan2(y,x) => x 指定点的 x 坐标的数字,y 指定点的 y 坐标的数字,计算出来的结果angel是一个弧度值,也可以表示相对直角三角形对角的角,其中 x 是临边边长,而 y 是对边边长
//Math.atan2(y,x)函数返回点(x,y)和原点(0,0)之间直线的倾斜角.那么如何计算任意两点间直线的倾斜角呢?只需要将两点x,y坐标分别相减得到一个新的点(x2-x1,y2-y1),转换可以实现计算出两点间连线的夹角Math.atan2(y2-y1,x2-x1)
//函数atan2(y,x)中参数的顺序是倒置的,atan2(y,x)计算的值相当于点(x,y)的角度值
//坐标系 左上正,右下负,结果为正表示从 X 轴逆时针旋转的角度,结果为负表示从 X 轴顺时针旋转的角度
double v = Math.atan2(y, x);
float touchAngle = (float) Math.toDegrees(v);//弧度转换为角度
Log.d("actionDown:", v + "==" + touchAngle);
//当前弧线 起始点 相对于 横轴 的夹角度数,由于扇形的绘制是从三点钟方向开始计为0度,所以需要下面的转换
if (x > 0 && y > 0) {//1象限
touchAngle = 360 - touchAngle;
} else if (x < 0 && y > 0) {//2象限
touchAngle = 360 - touchAngle;
} else if (x < 0 && y < 0) {//3象限
touchAngle = Math.abs(touchAngle);
} else if (x > 0 && y < 0) {//4象限
touchAngle = Math.abs(touchAngle);
}
//取点击半径
float touchRadius = (float) Math.sqrt(x * x + y * y);//sqrt:对数值开根号
if (touchRadius < (radius + cicleWidth / 2)) {
//如果找到关键字,则返回值为关键字在数组中的位置索引,且索引从0开始
//如果没有找到关键字,返回值为 负 的插入点值,所谓插入点值就是第一个比关键字大的元素在数组中的位置索引,
// 而且这个位置索引从1开始。
position = -Arrays.binarySearch(angles, touchAngle) - 1;
invalidate();
}
Log.d("actionDown:", "==" + position);
break;
}
return super.onTouchEvent(event);
}
Dmeo下载
源码下载