图的深度优先搜索和广度优先搜索算法、最小生成树两种算法 --C++实现
一:通用图结构
#ifndef _GRAPH_H
#define _GRAPH_H
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace::std;
#define MAX_COST 0x7FFFFFFF //花费无限大设为整型最大值
///
//通用图结构
template
class graph{
public:
bool is_empty()const;
bool is_full()const;
int get_numvertices()const; //当前顶点数
int get_numedges()const; //当前边数
public:
virtual bool insert_vertex(const T&) = 0; //插入顶点
virtual bool insert_edge(const T&, const T&, E) = 0; //插入边
virtual int get_firstneighbor(const T&)const = 0; //得到第一个邻接顶点
virtual int get_nextneighbor(const T&, const T&)const = 0; //某邻接顶点的下一个邻接顶点
virtual void print_graph()const = 0;
virtual int get_vertex_index(const T&)const = 0; //得到顶点序号
virtual void depth_first(const T&) = 0;
virtual void broad_first(const T&) = 0;
virtual void min_spantree_kruskal() = 0;
virtual void min_spantree_prim(const T&) = 0;
protected:
static const int VERTICES_DEFAULT_SIZE = 10; //默认图顶点数
int max_vertices;
int num_vertices;
int num_edges;
};
template
bool graph::is_empty()const
{
return num_edges == 0;
}
template
bool graph::is_full()const
{
return num_vertices >= max_vertices
|| num_edges >= max_vertices*(max_vertices-1)/2; //判满,分为顶点满和边满
}
template
int graph::get_numvertices()const
{
return num_vertices;
}
template
int graph::get_numedges()const
{
return num_edges;
}
///
#define VERTICES_DEFAULT_SIZE graph::VERTICES_DEFAULT_SIZE
#define num_vertices graph::num_vertices
#define num_edges graph::num_edges
#define max_vertices graph::max_vertices
///
#endif /*graph.h*/
二:邻接矩阵图结构
#pragma once
#include "graph.h"
//图的邻接矩阵表示法
template
class graph_mtx : public graph{
public:
graph_mtx(int);
~graph_mtx();
public:
bool insert_vertex(const T&);
bool insert_edge(const T&, const T&, E);
int get_firstneighbor(const T&)const;
int get_nextneighbor(const T&, const T&)const;
int get_vertex_index(const T&)const;
T& get_vertex_symbol(const int)const;
void print_graph()const;
void depth_first(const T&);
void broad_first(const T&);
void min_spantree_kruskal();
void min_spantree_prim(const T&);
protected:
void depth_first(const T&, bool *);
private:
T* vertices_list; //顶点线性表
E **edge; //内部矩阵
};
template
graph_mtx::graph_mtx(int sz = VERTICES_DEFAULT_SIZE)
{
max_vertices = sz > VERTICES_DEFAULT_SIZE ? sz
: VERTICES_DEFAULT_SIZE;
vertices_list = new T[max_vertices];
edge = new int*[max_vertices]; //动态申请二维数组
for(int i=0; i
graph_mtx::~graph_mtx()
{
for(int i=0; i
bool graph_mtx::insert_vertex(const T& vert)
{
if(this->is_full()) //派生类函数调用父类函数,用this或加作用域
return false;
vertices_list[num_vertices++] = vert;
return true;
}
template
bool graph_mtx::insert_edge(const T& vert1, const T& vert2, E cost = MAX_COST)//由于权值存在默认值,get_neighbor的操作需判断是否等于MAX_COST,否则不能正常取得邻接顶点
{
if(this->is_full()) //判满
return false;
int index_v1 = get_vertex_index(vert1); //得到顶点序号
int index_v2 = get_vertex_index(vert2);
if(index_v1 == -1 || index_v2 == -1 )
return false;
edge[index_v1][index_v2] = edge[index_v2][index_v1] = cost; //无向图
++num_edges;
return true;
}
template
int graph_mtx::get_firstneighbor(const T& vert)const
{
int index = get_vertex_index(vert);
if(index != -1){
for(int i=0; i
int graph_mtx::get_nextneighbor(const T& vert1, const T& vert2)const
{
int index_v1 = get_vertex_index(vert1);
int index_v2 = get_vertex_index(vert2);
if(index_v1 != -1 && index_v2 != -1){
for(int i=index_v2+1; i
int graph_mtx::get_vertex_index(const T& vert)const
{
for(int i=0; i
T& graph_mtx::get_vertex_symbol(const int index)const
{
assert(index >= 0 && index < this->get_numvertices());
//assert(index >= 0 && index < num_vertices); //error,由于num_vertices本身是我们用宏替换父类该元素,在这里使用会出现双重宏
return vertices_list[index];
}
template
void graph_mtx::print_graph()const
{
if(this->is_empty()){
cout << "nil graph" << endl; //空图输出nil
return;
}
for(int i=0; i
void graph_mtx::depth_first(const T& vert) //深度优先,认准一条路往死走,无路可走再回退
{
int num = this->get_numvertices();
bool *visited = new bool[num];
memset(visited, 0, sizeof(bool)*num); //首先全部赋值为假,遍历过后为真,防止图死循环
depth_first(vert, visited);
cout << "end.";
delete []visited;
}
template
void graph_mtx::depth_first(const T& vert, bool *visited)
{
cout << vert << "-->";
int index = get_vertex_index(vert);
visited[index] = true;
int neighbor_index = get_firstneighbor(vert);
while(neighbor_index != -1){
if(!visited[neighbor_index])
depth_first(get_vertex_symbol(neighbor_index), visited); //递归
neighbor_index = get_nextneighbor(vert,
get_vertex_symbol(neighbor_index));
}
}
template
void graph_mtx::broad_first(const T& vert)
{
int num = this->get_numvertices();
bool *visited = new bool[num];
int index = get_vertex_index(vert);
assert(index != -1);
memset(visited, 0, sizeof(bool)*num);
queue que; //通过队列,将元素以次入队
que.push(index);
cout << vert << "-->";
visited[index] = true;
while(!que.empty()){
int index_tmp = que.front();
que.pop();
int neighbor_index = get_firstneighbor(get_vertex_symbol(index_tmp));
while(neighbor_index != -1){
if(!visited[neighbor_index]){
cout << get_vertex_symbol(neighbor_index) << "-->";
visited[neighbor_index] = true; //遍历过后为真,防止图死循环
que.push(neighbor_index);
}
neighbor_index = get_nextneighbor(get_vertex_symbol(index_tmp),
get_vertex_symbol(neighbor_index));
}
}
cout << "end.";
delete []visited;
}
//
//min_spactree_kruskal
template
struct _mst_edge{ //最小生成树边的结构体,为一组边,cost为花费
int begin;
int end;
E cost;
};
template
int compare(const void* vp1, const void* vp2)
{
return (*(_mst_edge *)vp1).cost - (*(_mst_edge *)vp2).cost;
}
bool _is_same(int *father, int begin, int end) //判断是否在同一张子图中
{
while(father[begin] != begin)
begin = father[begin];
while(father[end] != end)
end = father[end];
return begin == end; //以最后一个元素是否存在父子关系判断
}
void mark_same(int *father, int begin, int end)
{
while(father[begin] != begin)
begin = father[begin];
while(father[end] != end)
end = father[end];
father[end] = begin; //让最后一个元素连接起来,使它们成为同一子图的元素
}
template
void graph_mtx::min_spantree_kruskal()
{
int num = this->get_numvertices();
_mst_edge *mst_edge = new _mst_edge[num*(num-1)/2];
int k = 0;
for(int i=0; i), compare); //调用快速排序函数
int *father = new int[num]; //初始化使所有元素的父指向自己
for(int i=0; i"
<< get_vertex_symbol(mst_edge[i].end)
<< ":" << mst_edge[i].cost << endl;
mark_same(father, mst_edge[i].begin, mst_edge[i].end); //加入后做标记
}
delete []father;
delete []mst_edge;
}
//
//min_spantree_prim
template
void graph_mtx::min_spantree_prim(const T& vert)
{
int num = this->get_numvertices();
int *lowcost = new int[num]; //最小花费数组
int *mst = new int[num]; //起始位置数组 为一组边,起始为mst[i]
int index = get_vertex_index(vert);
assert(index != -1);
for(int i=0; i"
<< get_vertex_symbol(min_index) << ":" << min << endl;
lowcost[min_index] = 0; //花费为0,相当于加入已生成树中
for(int j=0; j 三:测试部分
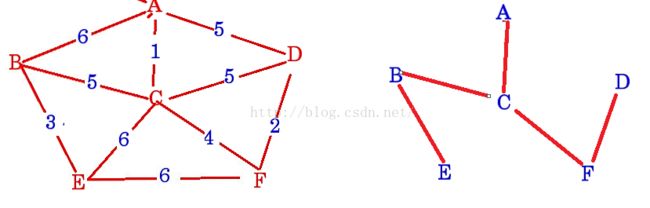
测试用图:
测试代码:
#include "graph.h"
#include "graph_mtx.h"
#define VERTEX_SIZE 4
int main()
{
graph_mtx gm;
gm.insert_vertex('A');
gm.insert_vertex('B');
gm.insert_vertex('C');
gm.insert_vertex('D');
gm.insert_vertex('E');
gm.insert_vertex('F');
gm.insert_edge('A', 'B', 6);
gm.insert_edge('A', 'C', 1);
gm.insert_edge('A', 'D', 5);
gm.insert_edge('B', 'C', 5);
gm.insert_edge('B', 'E', 3);
gm.insert_edge('C', 'D', 5);
gm.insert_edge('C', 'F', 4);
gm.insert_edge('D', 'F', 2);
gm.insert_edge('E', 'F', 6);
gm.insert_edge('C', 'E', 6);
gm.print_graph();
cout << "depth_first traverse:" << endl;
gm.depth_first('A');
cout << endl;
cout << "broad_first traverse:" << endl;
gm.broad_first('A');
cout << endl;
cout << "min_spantree_kruskal :" << endl;
gm.min_spantree_kruskal();
cout << "min_spantree_prim :" << endl;
gm.min_spantree_prim('A');
return 0;
}
测试结果: