Springboot对接InfluxDB
Springboot对接InfluxDB
1、InfluxDB的安装与配置
2、InfluxDB基本操作
3、Springboot对接InfluxDB
4、InfluxDB小总结
5、telagraf+influxdb+grafana搭建监控系统
6、Grafana的基本使用
写在前面
InfluxDB开放了HTTP API,所以使用代码对接InfluxDB也是基于HTTP的API进行访问
引入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.influxdbgroupId>
<artifactId>influxdb-javaartifactId>
<version>2.15version>
dependency>
springboot与集成influxdb比较简单,只需要引入以上的依赖即可
配置InfluxDB
spring:
influx:
url: http://localhost:8086 #influxdb服务器的地址
user: test #用户名
password: 123456 #密码
database: mydb #指定的数据库
- InfluxDB默认没有开启权限验证,所以可以直接访问其HTTP API
- 要开启其访问权限验证,需要在其配置文件 /etc/influxdb/influxdb.conf 修改[http]模块下的配置
[http]
enabled = true #开启HTTP API
bind-address = ":8086" #绑定的端口号
auth-enabled = true #开启授权
log-enabled = true #开启日志
开启后进行influxdb重启
systemctl restart influxdb
此时再使用CLI或者HTTP API都需要权限验证了
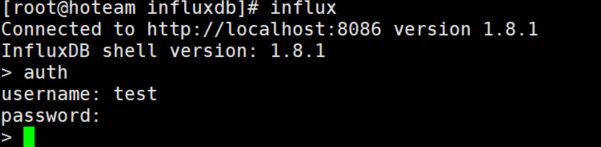
当然开启权限之前要先有一个用户,关于用户的创建以及权限的修改见另一篇博客,此处不再赘述
InfluxDB基本操作
代码实现
当上面的环境搭建好了之后,就可以进入开发阶段了,这里我使用的是springboot2.x版本,新建一个Controller进行开发
@Resource
private InfluxDB influxDB; //注入influxDB
开始使用
- 写入数据
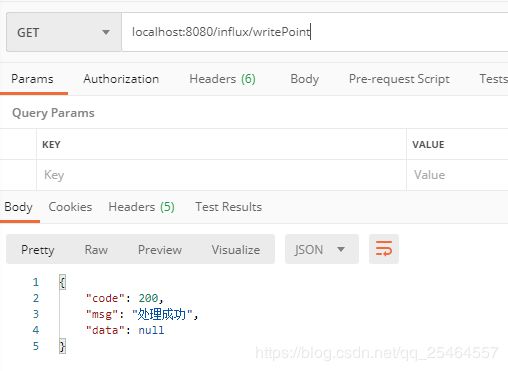
@RequestMapping("writePoint")
public Result insertPoint(){
try{
influxDB.setDatabase("mydb");
//新建一个Point,指定表名,和tag以及field
//由于是链式调用可以增加多个Tag和Field
Point point = Point.measurement(MEASURMENT_NAME)
.tag("host","server03")
.tag("region","zh-east")
.addField("value",1.0)
.time(System.currentTimeMillis(),TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)
.build();
influxDB.write(point);
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
return Result.error();
}
return Result.ok();
}
@RequestMapping("writePoint2")
public Result insertPoint2(){
try{
influxDB.setDatabase("mydb");
PointBean pointBean = new PointBean(
System.currentTimeMillis(),
"out","server04",
"zh-east",0.6f
);
Point point = Point.measurementByPOJO(PointBean.class).addFieldsFromPOJO(pointBean).build();
influxDB.write(point);
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
return Result.error();
}
return Result.ok();
}
实体类的结构
@Measurement(name="cpu_load_short")
public class PointBean {
/**Column中的name为measurement中的列名*/
@Column(name = "time")
private Long time;
/**注解中添加tag = true,表示当前字段内容为tag内容*/
@Column(name = "direction", tag = true)
private String direction;
@Column(name = "host", tag = true)
private String host;
@Column(name = "region", tag = true)
private String region;
@Column(name = "value")
private Float value;
public PointBean(Long time, String direction, String host, String region, Float value) {
this.time = time;
this.direction = direction;
this.host = host;
this.region = region;
this.value = value;
}
}
要用@Measurement注解指定表名
Point point = Point.measurementByPOJO(PointBean.class).addFieldsFromPOJO(pointBean).build();
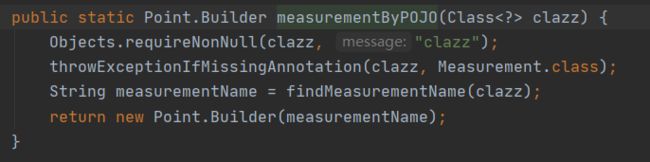
可以看到measurementByPOJO接收的bean必须要有@Measurement注解修饰
- 读取数据
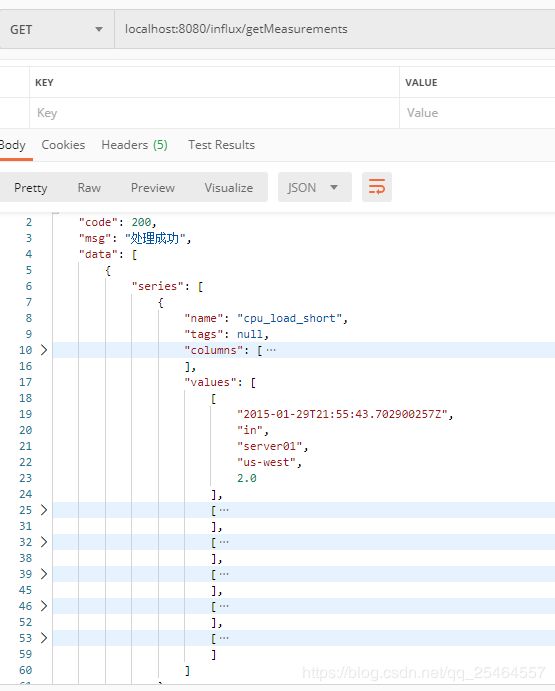
@RequestMapping("getMeasurements")
public Result getMeasurements(){
//构建查询语句,返回QueryResult
QueryResult rs = influxDB.query(new Query("select * from cpu_load_short", "mydb"));
logger.info("query result => {}", rs);
if (!rs.hasError() && !rs.getResults().isEmpty()) {
rs.getResults().forEach(System.out::println);
}
return Result.ok(rs.getResults());
}
总结
InfluxDB的java API实际上是通过访问InfluxDB的HTTP API,只要掌握其中的几个关键类就可以灵活运用,可以进入InfluxDB的接口看其接口的定义,主要是write()和query()方法的运用,可以有多种表现形式,在实际应用中选择适合自己业务的即可