solr6.6 创建一个core,并导入索引数据
1、什么是core
core是solr的一个索引库,可以理解为一个数据库,core可以根据需要,创建多个。
2、创建core
例如,创建一个core,名字叫mycore,就可以用一下命令:
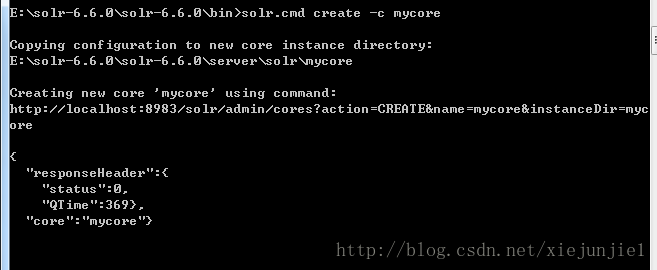
E:\solr-6.6.0\solr-6.6.0\bin>solr.cmd create -c mycore
如果一个core创建成功之后,会有如下信息打印:
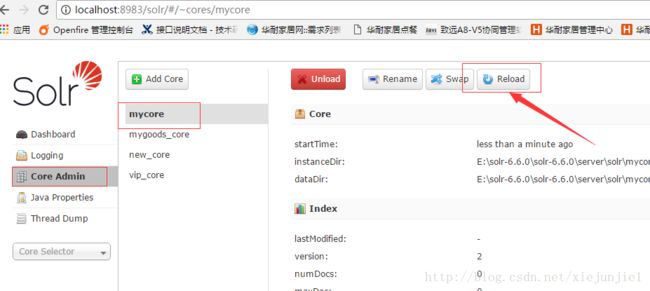
然后会在solr后台看到:
表示一个core已经创建成功!
3、core目录介绍
创建一个core之后,除了在后台看到结果,也会在E:\solr-6.6.0\solr-6.6.0\server\solr目录下创建了一个叫mycore的文件夹。
core里面默认创建如下目录和文件:
conf:是一个放置配置文件,里面有两个文件需要经常修改。
data:是索引数据的保存目录。
core.properties:当前core的属性文件。
4、给core创建索引数据,做个实验
创建一个例子,给core导入索引数据,用于后面的实验。
4.1 创建一个数据库
创建一个数据库,并创建几条数据,表结构:
id自增
vip表示是否vip
point表示点击次数
content随便填一些内容
add_time表示添加时间

添加几条测试数据,content字段整规律一点,用于后面的实验。

4.2 配置solrconfig.xml
sorlconfig.xml文件与managed-shema文件是经常要修改的文件。位于创建的core目录里面的config文件夹里。例如:
E:\solr-6.6.0\solr-6.6.0\server\solr\mycore\conf
在solrconfig.xml文件的后面配置如下信息:
<lib dir="${solr.install.dir:../../../..}/dist/" regex="solr-dataimporthandler-.*\.jar" />
<requestHandler name="/dataimport" class="org.apache.solr.handler.dataimport.DataImportHandler">
<lst name="defaults">
<str name="config">data-config.xmlstr>
lst>
requestHandler>这里的配置表示mycore的数据导入使用solr的DataImportHandler,而这个handler所在的jar位于E:\solr-6.6.0\solr-6.6.0\dist目录里面,解压的时候就有。通过配置lib节点来进行引入
其中data-config.xml 需要在solrconfig.xml同级目录下自己手动创建。
配置之后应该是这样的:
<config>
......篇幅有限,此处省略很多默认内容
<lib dir="${solr.install.dir:../../../..}/dist/" regex="solr-dataimporthandler-.*\.jar" />
<requestHandler name="/dataimport" class="org.apache.solr.handler.dataimport.DataImportHandler">
<lst name="defaults">
<str name="config">data-config.xmlstr>
lst>
requestHandler>
config>
4.2.1 创建data-config.xml 暂时不填写内容,后面再写.
4.3 编写managed_schema
managed_schema里面定义了很多域,其实是使用了lucene中的域。
什么是域?域的作用是定义一个solr索引里面的字段是什么类型,能做什么,怎么做。有点类似数据库中字段的类型。但表示的含义更加的丰富。
在managed_schema后面添加如下代码:
<field name="vip" type="string" indexed="true" stored="true" />
<field name="point" type="int" indexed="true" stored="true" />
<field name="content" type="string" indexed="true" stored="true"/>
<field name="add_time" type="date" indexed="true" stored="true"/>name是这个域的名称,在整个managed_schema文件里面需要唯一,不能重复,这里定义成跟数据库表字段的名称,方便使用。当然,也可以定义成其他名字。
type是表示这个字段的类型是什么,string是字符串类型,int是整形数据类型,date是时间类型,相当于数据库里面的timestamp。
indexed表示是否索引,索引的话就能查询到,否则,搜索的时候,不会出现。
stored表示是否存储到索引库里面。
添加之后的managed_schema是这样的:
"1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
--
Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
(the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
limitations under the License.
-->
--
This is the Solr schema file. This file should be named "schema.xml" and
should be in the conf directory under the solr home
(i.e. ./solr/conf/schema.xml by default)
or located where the classloader for the Solr webapp can find it.
This example schema is the recommended starting point for users.
It should be kept correct and concise, usable out-of-the-box.
For more information, on how to customize this file, please see
http://wiki.apache.org/solr/SchemaXml
PERFORMANCE NOTE: this schema includes many optional features and should not
be used for benchmarking. To improve performance one could
- set stored="false" for all fields possible (esp large fields) when you
only need to search on the field but don't need to return the original
value.
- set indexed="false" if you don't need to search on the field, but only
return the field as a result of searching on other indexed fields.
- remove all unneeded copyField statements
- for best index size and searching performance, set "index" to false
for all general text fields, use copyField to copy them to the
catchall "text" field, and use that for searching.
- For maximum indexing performance, use the ConcurrentUpdateSolrServer
java client.
- Remember to run the JVM in server mode, and use a higher logging level
that avoids logging every request
-->
"example-data-driven-schema" version="1.6">
......篇幅有限,此处省略很多默认的内容
"vip" type="string" indexed="true" stored="true" />
"point" type="int" indexed="true" stored="true" />
"content" type="string" indexed="true" stored="true"/>
"add_time" type="date" indexed="true" stored="true"/>
4.4 编写之前创建的data-config.xml
之所以现在才写data-config.xml是因为这个文件需要managed_schema里面的域与数据库字段进行映射。
<dataConfig>
<dataSource type="JdbcDataSource" driver="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" url="jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/db_jx" user="root" password="root" batchSize="-1" />
<document>
<entity name="mycore_test" query="select id ,vip,point,content,add_time from solr_mycore">
<field column="id" name="id" />
<field column="vip" name="vip" />
<field column="point" name="point" />
<field column="content" name="content" />
<field column="add_time" name="add_time" />
entity>
document>
dataConfig>
dataSource配置数据库信息
document配置数据库查询语句与managed_schema域的对应关系。目的是,在core导入数据的时候,会先通过该配置信息链接到数据库通过查询语句把数据查询出来,通过数据库字段与managed_schema域关联关系创建索引
4.5 开始导入数据
配置好了前面的信息,就可以在后台导入数据,配置信息需要reload一下core才能生效。如果配置文件出现错误,reload的时候也会有错误信息提示。
reload完之后,开始导入。
查询一下,发现已经导入成功