MySQL中binlog cache使用流程解惑
水平有限整理自己的学习笔记,如果有误请谅解。
最近老是看到有朋友报错如下:
ERROR 1197 (HY000): Multi-statement transaction required more than 'max_binlog_cache_size' bytes of storage; increase this mysqld variable and try again
虽然错误提示非常明确,但是我还是对binlog cache的使用方式进行了学习整理下来,这部分也是我一直疑惑的地方,也希望通过本文接触读者的疑惑。
本文约定:
- binlog cache:实际上就是参数binlog_cache_size指定的大小,它指定的是一段内存空间用于存储生成的binlog event,是事物级别的参数。
- binlog cache 临时文件:实际上就是参数max_binlog_cache_size指定的大小,它指定是一个临时磁盘文件存储由于binlog cache不足溢出的binlog event,其名字由"ML"打头,是事物级别的参数。
- binlog file:代表就是我们平时说的binglog 文件,由max_binlog_size指定大小。
- binlog event:代表是各种各样的binlog中的记录比如MAP_EVENT/QUERY EVENT/XID EVENT/WRITE EVENT等。
本文源码版本:
- percona 5.7.14
一、通常事物binlog event的写入流程
这里首先给出写入过程,让大家有一个大概的理解。
注意这个流程都是对于一个事物来讲的。一旦事物提交,binlog cache和binlog 临时文件都会释放掉,因为binlog已经固化到了binlog file。同时如果事物中包含多个DML语句,那么他们共享的一套的binlog cache和binlog 临时文件。
- 事物开启。
- 执行dml语句,在dml语句第一次执行的时候会分配内存空间binlog cache。
- 执行dml语句期间生成的event不断写入到binlog cache。
- 如果binlog cache的空间已经满了,则将binlog cache的数据写入到binlog临时文件,同时清空binlog cache。如果binlog临时文件的大小大于了max_binlog_cache_size的设置则抛错ERROR 1197 (HY000)。
- 事物提交,整个binlog cache和binlog临时文件数据全部写入到binlog file中进行固化,释放binlog cache和binlog临时文件。但是注意此时binlog cache的内存空间留用供下次事物使用,但是binlog临时文件被截断为0,保留文件描述符。其实也就是IO_CACHE(参考后文)保留,并且保留IO_CACHE中的分配的内存空间,和物理文件描述符。
- 断开连接,这个过程会释放IO_CACHE同时释放其持有的binlog cache内存空间以及持有的binlog 临时文件。
本文研究就是步骤3和步骤4的写入过程,和binlog cache以及binlog 临时文件的实现方式。同时本文不描述binlog_stmt_cache_size和max_binlog_stmt_cache_size的作用,因为他们和binlog_cache_size、max_binlog_cache_size参数的函数一致,只是存储是非事物语句的binlog event,但是在讨论数据结构的时候还是给出部分解释。
二、相关数据结构简介
-
binlog_cache_mngr类:
这个类中包含了两个cache实际上就是binlog cache和binlog stmt cache,如下:- binlog_stmt_cache_data stmt_cache;
- binlog_trx_cache_data trx_cache;
其中包含一些方法用于访问这两个cache。同时将整个binlog event写入到binlog file的方法也在其中叫做flush,栈帧如下:
#0 binlog_cache_mngr::flush (this=0x7fff58ca17c0, thd=0x7fff58012930, bytes_written=0x7ffff0358918, wrote_xid=0x7ffff0358917)
at /root/mysql5.7.14/percona-server-5.7.14-7/sql/binlog.cc:739
#1 0x0000000001857152 in MYSQL_BIN_LOG::flush_thread_caches (this=0x2e02c80, thd=0x7fff58012930) at /root/mysql5.7.14/percona-server-5.7.14-7/sql/binlog.cc:8484
#2 0x0000000001857383 in MYSQL_BIN_LOG::process_flush_stage_queue (this=0x2e02c80, total_bytes_var=0x7ffff0358a88, rotate_var=0x7ffff0358a87,
out_queue_var=0x7ffff0358a78) at /root/mysql5.7.14/percona-server-5.7.14-7/sql/binlog.cc:8546
#3 0x000000000185899f in MYSQL_BIN_LOG::ordered_commit (this=0x2e02c80, thd=0x7fff58012930, all=false, skip_commit=false)
at /root/mysql5.7.14/percona-server-5.7.14-7/sql/binlog.cc:9189
#4 0x000000000185700c in MYSQL_BIN_LOG::commit (this=0x2e02c80, thd=0x7fff58012930, all=false) at /root/mysql5.7.14/percona-server-5.7.14-7/sql/binlog.cc:8440可以说他是一个访问binlog cache和binlog stmt cache的统一的对外接口。
- binlog_trx_cache_data类和binlog_stmt_cache_data类:
他们都继承来自统一的父类binlog_cache_data。因为binlog_trx_cache_data要实现更多的功能,因为要支持事物,支持事物的回滚等功能,所以必须增加额外的功能呢但是。binlog_stmt_cache_data则不需要。
- binlog_cache_data类:
实现了主要成员包含:
- IO_CACHE cache_log:Cache to store data before copying it to the binary log.实际上所谓的binlog cache(binlog stmt cache)/max binlog cache(max stmt binlog cache)都是他实现的。
- Rows_log_event *m_pending:Pending binrows event. This event is the event where the rows are currently written.
- my_off_t saved_max_binlog_cache_size:参数max_binlog_cache_size/max_binlog_stmt_cache_size的大小。
- ulong *ptr_binlog_cache_use:状态binlog_cache_use/binlog_stmt_cache_use的值的指针。
- ulong *ptr_binlog_cache_disk_use:状态binlog_cache_disk_use/binlog_stmt_cache_disk_use的值的指针。
- IO_CACHE类:
实际上binlog event的写入binlog 或者 binlog临时文件都是由 IO_CACHE子系统实现的,本子系统实现了类似写缓存如果缓存不够写入物理文件的功能,从而降低了物理写入的次数,提升了性能。它封装了包含读缓存,写缓存以及物理文件等信息。如下:
- 读缓存 uchar *buffer;
- 写缓存 uchar *write_buffer;
- 物理文件描述符 File file;
其使用方式也分多种模式如:
- READ_CACHE模式
- WRITE_CACHE模式
- SEQ_READ_APPEND模式
当然IO_CACHE还用到其他地方,比如我们熟悉的filesort,进行内存和磁盘排序也是通过这个子系统作为存储方式完成的。栈帧参考结束附录,对于这个子系统更加详细的参考信息可以自行百度我发现有朋友写得很清楚,本文主要说明是binlog cache的使用方式而不是这个子系统。但是在涉及到源码部分的时候以binlog cache和binlog临时文件的写入为列子。
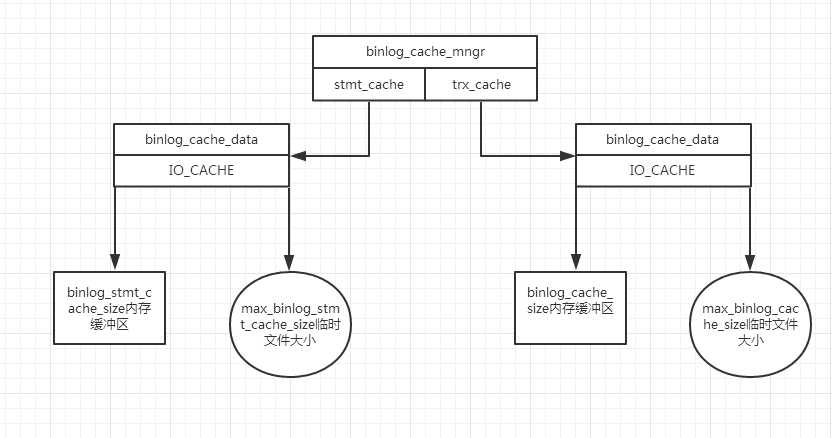
最后我们画一张这几个类的关系图,同时给出binlog cache(binlog stmt cache)和binlog临时文件(binlog stmt临时文件)的表示,如下:
这张图解释了他们的关系。
三、binlog_cache_size作用及其初始化
本节使用的binlog_cache_size大小为32678及默认值。
binlog_cache_size参数在官方文档的描述大概为如果开启了binlog功能,则在事物期间用于保存binlog event的缓存。如果经常使用大事物应该加大这个缓存,避免过多的磁盘使用,从Binlog_cache_use和Binlog_cache_disk_use可以看出是否使用了binlog cache或binlog 临时文件用于保存binlog event。
当然如我开头所说这部分是完全内存的。
实际上当我们的事物需要记录事物的binlog event的时候我们就会使用到binlog cache,其初始化栈帧如下:
#0 init_io_cache_ext (info=0x7fff58ca17c8, file=-1, cachesize=32768, type=WRITE_CACHE, seek_offset=0, use_async_io=0 '\000', cache_myflags=20, file_key=10)
at /root/mysql5.7.14/percona-server-5.7.14-7/mysys/mf_iocache.c:154
#1 0x00000000018c8b48 in init_io_cache (info=0x7fff58ca17c8, file=-1, cachesize=32768, type=WRITE_CACHE, seek_offset=0, use_async_io=0 '\000', cache_myflags=20)
at /root/mysql5.7.14/percona-server-5.7.14-7/mysys/mf_iocache.c:299
#2 0x00000000018c6b96 in open_cached_file (cache=0x7fff58ca17c8, dir=0x2fa1d70 "/root/mysql5.7.14/percona-server-5.7.14-7/mysql-test/var/tmp/mysqld.1",
prefix=0x2277d4e "ML", cache_size=32768, cache_myflags=16) at /root/mysql5.7.14/percona-server-5.7.14-7/mysys/mf_cache.c:60
#3 0x00000000018599b2 in THD::binlog_setup_trx_data (this=0x7fff58012930) at /root/mysql5.7.14/percona-server-5.7.14-7/sql/binlog.cc:9641
#4 0x0000000001859cb3 in binlog_start_trans_and_stmt (thd=0x7fff58012930, start_event=0x7ffff0359350) at /root/mysql5.7.14/percona-server-5.7.14-7/sql/binlog.cc:9742
#5 0x000000000185a0a6 in THD::binlog_write_table_map (this=0x7fff58012930, table=0x7fff58d98260, is_transactional=false, binlog_rows_query=false)
at /root/mysql5.7.14/percona-server-5.7.14-7/sql/binlog.cc:9835
#6 0x0000000000f7299f in write_locked_table_maps (thd=0x7fff58012930) at /root/mysql5.7.14/percona-server-5.7.14-7/sql/handler.cc:8019
#7 0x0000000000f72bf6 in binlog_log_row (table=0x7fff58d98260, before_record=0x7fff58d99120 "\375\001", after_record=0x0,
log_func=0xf77f7d )
at /root/mysql5.7.14/percona-server-5.7.14-7/sql/handler.cc:8089 我们可以在THD::binlog_setup_trx_data找到binlog_cache_size的作如下:
open_cached_file(&cache_mngr->trx_cache.cache_log, mysql_tmpdir,
LOG_PREFIX, binlog_cache_size, MYF(MY_WME)))大概解释一下部分参数的含义。
- &cache_mngr->trx_cache.cache_log 就是一个IO_CACHE实例。
- mysql_tmpdir 为参数tmpdir的定义目录。
- LOG_PREFIX 为如果使用临时文件临时文件的前缀,如果是binlog的临时磁盘文件则为"ML",如果是filesort的临时排序文件则为"MY"。
- cache_size 当然就是你参数binlog_cache_size设置的大小。
最终参数binlog_cache_size的值会通过init_io_cache函数传入到init_io_cache_ext中。我们关注一下以下几个传入到init_io_cache_ext的参数。
- file=-1:初始换缓存的情况下,不会非配实际的临时文件。索引用-1表示文件描述符
- cachesize=32768:binlog_cache_size设置的大小。
- type=WRITE_CACHE:IO_CACHE的使用模式。
下面是init_io_cache_ext函数关于binlog cache分配的重点代码部分:
info->file= file;(-1)
info->pos_in_file= seek_offset;(0)
info->pre_close = info->pre_read = info->post_read = 0;
info->arg = 0;
info->alloced_buffer = 0;
info->buffer=0;
info->seek_not_done= 0;
buffer_block= cachesize; //他们和binlog_cache_size参数指定相等(有对其操作)
if ((info->buffer= (uchar*) my_malloc(key_memory_IO_CACHE,
buffer_block, flags)) != 0)//为binlog cache分配实际的内存其大小就是binlog_cache_size指定的大小(有对其操作)
{
info->write_buffer=info->buffer;//write_buffer和buffer指向了同一片内存区域,及我们的binlog cache缓存区域
info->alloced_buffer=1;
}
info->read_length=info->buffer_length=cachesize; //此处将缓存的长度记录为binlog_cache_size指定的大小(有对其操作)
info->request_pos= info->read_pos= info->write_pos = info->buffer;//初始化各种位置为info->buffer指针指向的位置
if (type == WRITE_CACHE)
info->write_end= info->buffer+info->buffer_length- (seek_offset & (IO_SIZE-1));//将缓存的边界设置为(info->buffer指针指向位置+binlog_cache_size参数指定的大小)此后IO_CACHE对象已经分配了一块binlog_cache_size参数指定相等大小的内存,则使我们说的binlog cache已经初始化分配完成。
四、binlog临时文件的使用和分配方式
及当我们事物需要存储的binlog event已经不能在binlog cache中存下的时候,我们需要开启我们binlong临时文件来存储。其文件存放到tmpdir的定义的目录下,文件名为”ML”开头。但是这个文件不能用ls看到,因为使用了LINUX临时文件建立的方法,以避免其他进程使用这个文件而破坏这个文件的内容。也就是说,这个文件是mysqld进程内部专用的,在LINUX中MySQL使用mkstemp系统调用完成这个功能。对于这个文件可以使用lsof|grep delete看到最后我会给出一个例子。
分配栈帧如下:
#0 create_temp_file (to=0x7ffff0359040 "/root/mysql5.7.14/percona-server-5.7.14-7/mysql-test/var/tmp/mysqld.1/MLIdFGCH",
dir=0x7fff580167c0 "/root/mysql5.7.14/percona-server-5.7.14-7/mysql-test/var/tmp/mysqld.1", prefix=0x7fff58016830 "ML", mode=514, MyFlags=16)
at /root/mysql5.7.14/percona-server-5.7.14-7/mysys/mf_tempfile.c:141
#1 0x00000000018c693d in inline_mysql_file_create_temp (key=10, src_file=0x2296d78 "/root/mysql5.7.14/percona-server-5.7.14-7/mysys/mf_cache.c", src_line=80,
to=0x7ffff0359040 "/root/mysql5.7.14/percona-server-5.7.14-7/mysql-test/var/tmp/mysqld.1/MLIdFGCH",
dir=0x7fff580167c0 "/root/mysql5.7.14/percona-server-5.7.14-7/mysql-test/var/tmp/mysqld.1", pfx=0x7fff58016830 "ML", mode=514, myFlags=16)
at /root/mysql5.7.14/percona-server-5.7.14-7/include/mysql/psi/mysql_file.h:1048
#2 0x00000000018c6c87 in real_open_cached_file (cache=0x7fff58ca17c8) at /root/mysql5.7.14/percona-server-5.7.14-7/mysys/mf_cache.c:77
#3 0x00000000018cb4a9 in my_b_flush_io_cache (info=0x7fff58ca17c8, need_append_buffer_lock=0) at /root/mysql5.7.14/percona-server-5.7.14-7/mysys/mf_iocache.c:1528
#4 0x00000000018cad03 in _my_b_write (info=0x7fff58ca17c8, Buffer=0x7fff58de751a "", Count=186) at /root/mysql5.7.14/percona-server-5.7.14-7/mysys/mf_iocache.c:1330
#5 0x00000000018cb156 in my_b_safe_write (info=0x7fff58ca17c8, Buffer=0x7fff58de55e0 "\376\001", Count=8180)
at /root/mysql5.7.14/percona-server-5.7.14-7/mysys/mf_iocache.c:1437
#6 0x000000000180e7b2 in Log_event::wrapper_my_b_safe_write (this=0x7fff58972bb0, file=0x7fff58ca17c8, buf=0x7fff58de55e0 "\376\001", size=8180)
at /root/mysql5.7.14/percona-server-5.7.14-7/sql/log_event.cc:977
#7 0x000000000182b392 in Rows_log_event::write_data_body (this=0x7fff58972bb0, file=0x7fff58ca17c8)
at /root/mysql5.7.14/percona-server-5.7.14-7/sql/log_event.cc:11356
#8 0x0000000001835e63 in Log_event::write (this=0x7fff58972bb0, file=0x7fff58ca17c8) at /root/mysql5.7.14/percona-server-5.7.14-7/sql/log_event.h:825
#9 0x0000000001845899 in binlog_cache_data::write_event (this=0x7fff58ca17c0, thd=0x7fff58012930, ev=0x7fff58972bb0)
at /root/mysql5.7.14/percona-server-5.7.14-7/sql/binlog.cc:1120
#10 0x0000000001853625 in MYSQL_BIN_LOG::flush_and_set_pending_rows_event (this=0x2e02c80, thd=0x7fff58012930, event=0x7fff58954fd0, is_transactional=false)
at /root/mysql5.7.14/percona-server-5.7.14-7/sql/binlog.cc:7075当我们不断的写入binlog event的情况下,我们最终会将binlog cache写满(对于小事物肯定不会写满)。我们来梳理一下binlog 临时文件是怎么打开的,我们从my_b_safe_write函数开始:
注意这里实际对于IO_CACHE来讲是通用的方法我只是以binlog 临时文件建立的流程为例子,因为不同的模式走的逻辑不一样
- my_b_safe_write
这个函数在每次binlog event写入到binlog cache的时候都会调用。
在WRITE_CACHE的模式下会调用宏my_b_write,这是一个关键点宏的定义如下:
#define my_b_write(info,Buffer,Count) \
((info)->write_pos + (Count) <=(info)->write_end ?\
(memcpy((info)->write_pos, (Buffer), (size_t)(Count)),\
((info)->write_pos+=(Count)),0) : \
(*(info)->write_function)((info),(uchar *)(Buffer),(Count)))很简单如果binlog cache缓存当前写入的位置加上本次写入的总量大于了binlog cache的内存地址的边界则我们需要进行通过*(info)->write_function这个回调函数将binlog cache的内容写到磁盘了,这样才能腾出空间给新的binlog event存放。这里这个回调函数应该就是_my_b_write。
- _my_b_write
这个函数只会在binlog cache不够用的时候需要进行临时物理文件写入的时候调用。
大概逻辑如下:
rest_length= (size_t) (info->write_end - info->write_pos); //统计出此时binlog cache剩余的空间
memcpy(info->write_pos,Buffer,(size_t) rest_length); //写满这些剩余的空间
Buffer+=rest_length;//既然已经写了一部分那么待写入的数据应该减去写入的部分
Count-=rest_length;//写入的总量也应该的减去已经写入的部分
info->write_pos+=rest_length;//binlog cache的写入位置应该增加
if (my_b_flush_io_cache(info,1))//创建临时文件(如果没有创建的话)并且写入数据到临时文件
memcpy(info->write_pos,Buffer,(size_t) Count);//刷新完成后。binlog cache已经腾空可以继续使用了
info->write_pos+=Count;//简单的增加binlog cache指针的位置- my_b_flush_io_cache
这个函数主要负责了当binlog cache 写满后将binlog cache的数据全部写入到binlog 临时文件和清空binlog cache,当然最后会增加Binlog_cache_disk_use。
大概逻辑如下:
if (info->file == -1)//如果是第一次建立临时文件,这里的文件描述为-1,前面已经分析过了
{
if (real_open_cached_file(info))//打开临时文件返回文件描述符 !!!!!
length=(size_t) (info->write_pos - info->write_buffer)//统计本次写入临时文件数据的大小
pos_in_file=info->pos_in_file;
info->pos_in_file+=length;//将当前文件写入位置加上本次写入数据的大小及为下次文件写入的位置
if (mysql_file_write(info->file,info->write_buffer,length,info->myflags | MY_NABP))//将数据写入到临时文件中。
info->append_read_pos=info->write_pos=info->write_buffer; //此处将info->write_pos指针指向到binlog cache缓冲开始的位置及binlog cache缓冲全部释放
++info->disk_writes;//Binlog_cache_disk_use增加- create_temp_file
这个函数没什么说的就是调用mkstemp来完成临时文件的建立,我们关注一下输入两个参数即可
- to 临时文件的绝对路径
- dir 及临时文件所在的目录
- prefix 临时文件的前缀,这里是ML
注意对于filesort的临时文件也是通过这个函数建立,前缀为MY。
到这里我们的binlog cache内存空间已经分配,并且由于事物写入的binlog event大于了binlog cache设置的大小,binlog 临时文件已经分配并且进行了一次binlog cache数据写入到binlog 临时文件的操作。这就是整个流程。
五、max_binlog_cache_size设置过小的报错
报错如下:
(root@localhost)[06:19:12] [test ;]> insert into t1 select * from t1;
ERROR 1197 (HY000): Multi-statement transaction required more than 'max_binlog_cache_size' bytes of storage; increase this mysqld variable and try again当然报错也很清晰告诉你原因,但是在整个流程中到底是哪里抛错出来的呢?实际上就是函数_my_b_write中进行的判断。先来看看这个错误的错误码如下:
{ "ER_TRANS_CACHE_FULL", 1197, "Multi-statement transaction required more than \'max_binlog_cache_size\' bytes of storage; increase this mysqld variable and try again" },在函数_my_b_write中可以看到如下代码:
if (pos_in_file+info->buffer_length > info->end_of_file) //判断binlog临时文件的位置加上本次需要写盘的数据大于info->end_of_file的大小则抛错
{
errno=EFBIG;
set_my_errno(EFBIG);
return info->error = -1;
}而抛错的代码在MYSQL_BIN_LOG::check_write_error函数中如下:
if (is_transactional)
{
my_message(ER_TRANS_CACHE_FULL, ER(ER_TRANS_CACHE_FULL), MYF(MY_WME));
}其中info->end_of_file的大小正是来自于我们的参数max_binlog_cache_size,不再给出代码。
六、如何观察到binlog 临时文件的存在
前文已经说过可以使用lsof|grep delete来观察到这种文件,据我观察这个文件会以64k的倍数上涨如下:
[root@test ~]# lsof|grep delete|grep ML
mysqld 21414 root 77u REG 252,3 65536 1856092 /root/mysql5.7.14/percona-server-5.7.14-7/mysql-test/var/tmp/mysqld.1/MLUFzokf (deleted)
[root@test ~]# lsof|grep delete|grep ML
mysqld 21414 root 77u REG 252,3 131072 1856092 /root/mysql5.7.14/percona-server-5.7.14-7/mysql-test/var/tmp/mysqld.1/MLUFzokf (deleted)
[root@test ~]# lsof|grep delete|grep ML
mysqld 21414 root 77u REG 252,3 163840 1856092 /root/mysql5.7.14/percona-server-5.7.14-7/mysql-test/var/tmp/mysqld.1/MLUFzokf (deleted)
[root@test ~]# lsof|grep delete|grep ML
mysqld 21414 root 77u REG 252,3 229376 1856092 /root/mysql5.7.14/percona-server-5.7.14-7/mysql-test/var/tmp/mysqld.1/MLUFzokf (deleted)七、总结
写了这么多,这里需要总结一下参数的具体含义,以及注意点。
- binlog_cache_size:事物级别的参数,用于指定存储整个事物生成的binlog event的内存大小,对于大事物来讲很可能超过这个参数的设置,则需要开启binlog 临时文件用于存储。
- max_binlog_cache_size:事物级别的参数,用于指定当某个事物的binlog event超过了binlog_cache_size大小的设置开启binlog 临时文件的可用大小,如果事物的binlog event生成量超过了max_binlog_cache_size+binlog_cache_size设置的大小则会抛错:
ERROR 1197 (HY000): Multi-statement transaction required more than 'max_binlog_cache_size' bytes of storage; increase this mysqld variable and try again- 不管是binlog cache还是binlog 临时文件都是在事物没有提交之前用于存储binlog event的场所,一旦事物提交完成后,所有的binlog event都已经固化到binlog file,则它们可以释放和重用。
- binlog_stmt_cache_size/ max_binlog_stmt_cache_size:这一套参数和上面的两个参数含义差不多,但是针对的是非事物型的binlog event,显然对于innodb当道的今天大部分的event还是事物级别的,所以我没有过多研究,但是根据debug来看DDL语句返回的是非事物级别的,如下判断
断点 MYSQL_BIN_LOG::write_event函数,代码片段如下:
bool is_trans_cache= event_info->is_using_trans_cache();//DDL这里返回的false
binlog_cache_mngr *cache_mngr= thd_get_cache_mngr(thd);//得到cache_mngr指针地址,有了它不管是stmt缓存还是trx缓存都能找到如前文所述
binlog_cache_data *cache_data= cache_mngr->get_binlog_cache_data(is_trans_cache);//这里如果是非事物级别使用stmt缓存区八、备注信息
最后留下一些有用的接口信息:
- 事物提交临时文件被截断为0
这个接口实际上就是binlog_cache_mngr::flush->binlog_cache_data::flush->binlog_cache_data::reset->my_chsize - 事物提交binlog cache内存空间留用
这个接口可能是binlog_cache_mngr::flush->bMYSQL_BIN_LOG::write_cache->MYSQL_BIN_LOG::do_write_cache->reinit_io_cache - 断开连接整个IO CACHE全部释放掉
这个接口就是close_cached_file如下:
File file=cache->file;
cache->file= -1; /* Don't flush data */
(void) end_io_cache(cache);//释放整个IO_CACHE
if (file >= 0)
{
(void) mysql_file_close(file, MYF(0));//关闭临时文件
}