Android应用程序之数据存储(一)
可以将应用程序的数据以数据库、文件或者选项文件(preference)的形式存放到内部或可移除的存储介质中。你也可以添加数据备份服务,让用户可以存储或恢复应用程序或系统数据。
Android为你永久保存应用程序数据提供了几种选择。你选择哪种解决方案取决于你的特定的需求,例如是否这些数据应该是你的应用程序私有的,或者其他应用程序或用户可以访问的,你的数据需要多大的空间。
你可以选择的数据存储选项包括以下几类:
- 共享选项文件(Shared Preferences)
以键值对的方式存储私有的基本数据。 - 内部存储(Internal Storage)
在设备内存中存储私有数据 - 外部设备(External Storage)
在共享的外部存储设备中存储公共数据 - SQLite数据库(SQLite Database)
在私有数据库中存储结构化的数据 - 网络连接(Network Connection)
使用你自己的网络服务器将数据存储在网上
Android提供了一种方式让你可以将自己的私有数据暴露给其他应用程序,使用内容提供者(Content Provider)。内容提供者是一个可选的组件,它将为你的应用程序数据暴露读写访问,同时遵循你想要保留的任何限制。
使用共享选项文件
SharedPreferences类提供了一个通用的框架,允许你来保存和取回永久保存的基本数据类型的键值对。你可以使用SharedPreferences存储任何基本数据:boolean, float, int, long和string。
为了给你的应用程序获得SharedPreferences对象,使用下面两个方法之一:
- getSharedPreferences() - 如果你需要多个选项文件并且这些文件通过名称区分的话,使用这个方法。这个方法的第一个参数就是选项文件的名称。第二个参数为模式,可以是
MODE_PRIVATE,MODE_WORLD_READABLE和MODE_WORLD_WRITABLE之一。也可以是MODE_MULTI_PROCESS支持多进程修改同一个文件,在Android 2.3或更低版本的Android,该选项总是打开的,在后来的版本中都默认关闭了。 - getPreferences() - 如果你的活动只需要一个选项文件,那么使用这个方法。因为这将是你的活动的唯一的选项文件,你不需要为其指定名称。
为了写入值:
1. 调用edit()获得SharedPreferences.Editor;
2. 使用putBoolean(), putString()方法添加值;
3. 使用commit()方法提交新值。
使用SharedPreferences的getBoolean()和getString()等方法读出值。
下面是分别使用getSharedPreferences()和getPreferences()的两个例子。
package lemon.learnandroid;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.content.SharedPreferences;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class SharedPreferencesOption extends Activity
{
public static final String PREFS_NAME = "MyPrefFile";
/** Called when the activity is first created. */
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)
{
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
//取回选项文件
SharedPreferences setting = getSharedPreferences(PREFS_NAME, MODE_PRIVATE);
boolean silent = setting.getBoolean("silentMode", false);
if (silent)
Toast.makeText(SharedPreferencesOption.this,
"silentModel为真", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
else
Toast.makeText(SharedPreferencesOption.this,
"silendModel为假", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
public void onPause()
{
super.onPause();
SharedPreferences setting = getSharedPreferences(PREFS_NAME, MODE_PRIVATE);
//需要Editor对象来处理选项改变
SharedPreferences.Editor editor = setting.edit();
editor.putBoolean("silentMode", true);
//提交变动
editor.commit();
}
}package lemon.learnandroid;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.content.SharedPreferences;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class SingleSharedPreferences extends Activity
{
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)
{
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
TextView tvShow = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.textview_show);
SharedPreferences setting = getPreferences(MODE_PRIVATE);
boolean silent = setting.getBoolean("silentMode", false);
if (silent)
tvShow.setText("silentMode : true");
else
tvShow.setText("silentMode : false");
}
@Override
public void onPause()
{
super.onPause();
SharedPreferences setting = getPreferences(MODE_PRIVATE);
SharedPreferences.Editor editor = setting.edit();
editor.putBoolean("silentMode", true);
editor.commit();
}
}使用内部存储(Internal Storage)
你可以在设备的内部存储中直接保存文件。默认情况下,保存到内部存储的文件对你的应用程序来说是私有的,其他的应用程序不能访问它们(用户也不能)。当用户卸载你的应用程序时,这些文件将被移除。
为了在内部存储中创建和写文件:
1. 使用文件的名称和操作模式,调用openFileOutput()。这个方法会返回一个FileOutputStream。
2. 使用write()方法写入文件.
3. 使用close()方法关闭文件流。
例如:
package lemon.learnandroid;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.widget.TextView;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.File;
public class InternalStorage extends Activity
{
public static final String FILENAME = "hello_file";
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)
{
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
TextView tvShow = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.textview_show);
String message = FILENAME;
File tempFile = new File(getFilesDir() +"/"+ FILENAME);
if (tempFile.exists())
{
try{
FileInputStream fis = openFileInput(FILENAME);
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int hasRead = 0;
while((hasRead = fis.read(buffer)) > 0)
{
message = message + ": " + new String(buffer, 0, hasRead);
}
fis.close();
}catch(IOException e)
{
System.out.println(e);
message += e;
}
}
tvShow.setText(message);
}
@Override
public void onPause()
{
super.onPause();
try{
FileOutputStream fos = openFileOutput(FILENAME, InternalStorage.MODE_PRIVATE);
String message = "OnPause: Hello World";
fos.write(message.getBytes());
fos.close();
}catch(IOException e)
{
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}MODE_PRIVATE模式会创建文件(或者替换同名的文件),并且这个文件对你的应用程序来说是私有的。其他可用的模式包括:MODE_APPEND,MODE_WORLD_READABLE和MODE_WORLD_WRITABLE。
为了从内部存储中读出文件:
1. 调用openFileInput()并传入要读的文件名称。这个方法返回一个FileInputStream。
2. 使用read()方法从文件中读出字节。
3. 使用close()方法关闭文件流。
小技巧:如果你想要在编译时在你的应用程序保存一个静态文件,将文件保存在res/law/目录下。你可以使用openRawResource(),传入R.raw.资源ID来打开它。这个方法将返回一个输入流,你可以使用它来读文件,但你不能写入原始文件。
保存缓存文件(Cache files)
如果你想要缓存某些数据,而不是永久地存储它,你应该使用getCacheDir()方法打开一个File,这个File代表你的应用程序存储临时缓存文件的内部目录。
当设备内部存储空间不足时,Android会删除这些缓存文件来回收空间。然而,你不应该依赖于系统去为你清理这些文件。你应该总是自己维护缓存文件,使其占用的空间保持在一个合理的限度,例如1MB.当用户卸载你的应用程序时,这些文件会被移除。
其他有用的方法
- getFilesDir()
获得保存你的内部文件的文件系统目录的绝对路径。 - getDir()
为你的内部存储空间创建(或打开一个存在的)目录。 - deleteFile()
删除保存在内部存储空间中的文件。 - fileList()
返回当前你的应用程序保存的文件数组。
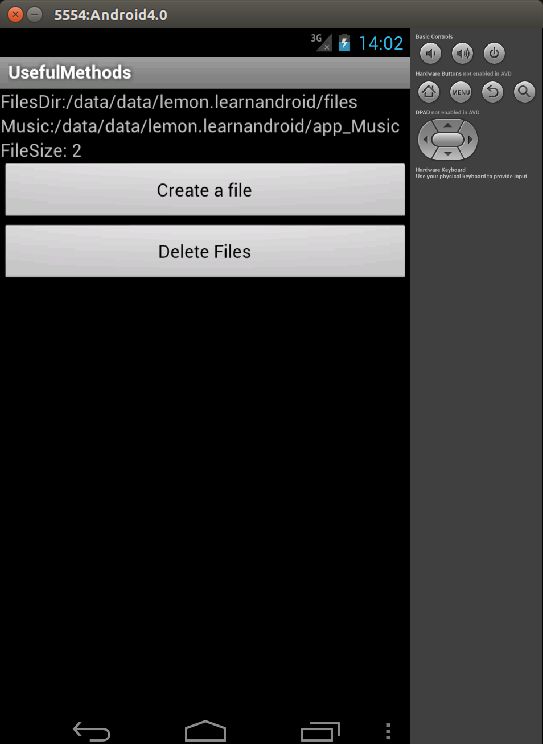
package lemon.learnandroid;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.widget.TextView;
import android.view.View;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class UsefulMethods extends Activity
{
private static int index = 1;
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)
{
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.layout_usefulmethods);
String filesDir = getFilesDir().getAbsolutePath();
TextView tvFilesDir = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.tv_filedir);
tvFilesDir.setText(tvFilesDir.getText() + filesDir);
String musicDir = getDir("Music", UsefulMethods.MODE_PRIVATE).getAbsolutePath();
TextView tvMusicDir = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.tv_musicdir);
tvMusicDir.setText(tvMusicDir.getText() + musicDir);
updateSize();
}
public void onCreateAFile(View v)
{
try{
FileOutputStream fos = openFileOutput("File" + index,
UsefulMethods.MODE_PRIVATE);
index++;
fos.close();
}catch(IOException e)
{
System.out.println(e);
}
updateSize();
}
public void updateSize()
{
int size = fileList().length;
TextView tvFileSize = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.tv_filesize);
tvFileSize.setText("FileSize: " + size);
}
public void onDeleteFiles(View v)
{
for(String file : fileList())
{
deleteFile(file);
}
updateSize();
}
}layout_usefulmethods.xml
<LinearLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<TextView android:id="@+id/tv_filedir"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:text="FilesDir:"/>
<TextView android:id="@+id/tv_musicdir"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:text="Music:"/>
<TextView android:id="@+id/tv_filesize"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:text="FileSize: 0"/>
<Button android:id="@+id/btn_createFile"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:text="Create a file"
android:onClick="onCreateAFile"/>
<Button android:id="@+id/btn_deletefile"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:text="Delete Files"
android:onClick="onDeleteFiles"/>
LinearLayout>原文
- android-sdk-linux/docs/guide/topics/data/data-storage.html#filesExternal