opencv调用yolov3模型进行深度学习目标检测(Java版)
由于项目其他模块多用Scala/Java编写,与python交互不易。
将原多数用python/C++编写的目标检测程序,改写为Java。
建立目录,配置初始参数
类属性
static String pro_dir = "E:/yolov3/"; // 根路径
static float confThreshold = 0.3f; // 置信度阈值
static float nmsThreshold = 0.4f; // iou阈值
static int inpWidth = 416; // 修改输入图片的宽高
static int inpHeight = 416;
static List classes = new ArrayList(); // 存放类别的列表
主函数
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
System.loadLibrary(Core.NATIVE_LIBRARY_NAME);
// 配置 权重 图片路径 类别文件
String modelConfiguration = pro_dir + "yolov3.cfg"; // 模型配置文件
String modelWeights = pro_dir + "yolov3.weights"; // 模型权重文件
String image_path = "E:/pictures_test/pictureName.jpg"; // 图片路径,名字
String classesFile = pro_dir + "coco.names"; // 模型可识别类别的标签文件
// 进入识别图片的方法
detect_image(image_path, modelWeights, modelConfiguration, classesFile);
waitKey(0);
}
识别图片(detect_image)
读取可识别类别的标签文件,将所有类别存入List列表classses
coco.names的格式可能不同,读取时注意。
// 检测图片
public static void detect_image(String image_path, String modelWeights, String modelConfiguration, String classesFile) throws Exception {
// 读取classesFile路径的文件
InputStream in = new FileInputStream(classesFile);
int iAvail = in.available(); // 适用于本地一次读取多个字节时,返回得到的字节数。
byte[] bytes = new byte[iAvail];
in.read(bytes);
String allContent = new String(bytes); // 文件中的所有内容
String[] tempContent = allContent.trim().split("\n"); // allContent去除首尾空格,再按换行符分割。
System.out.println(tempContent.length);
// 遍历tempContent,添加到保存类别名的列表classes里。
for(int i=0; i加载网络配置与训练权重的文件,构建网络
Net net = Dnn.readNetFromDarknet(modelConfiguration, modelWeights);
net.setPreferableBackend(Dnn.DNN_BACKEND_OPENCV);
net.setPreferableTarget(Dnn.DNN_TARGET_OPENCL);
读入图片,配置宽高
Mat im = imread(image_path, Imgcodecs.IMREAD_COLOR); // 读入待检测的图片
// 当前是以窗体的形式查看检测后的图片,给窗体命名
final String kWinName = "Deep object detection in OpenCV";
namedWindow(kWinName, WINDOW_NORMAL);
// 将输入图片的宽高重新设置 (416, 416)
Mat frame = new Mat();
Size sz1 = new Size(im.cols(), im.rows());
Imgproc.resize(im, frame, sz1);
Mat resized = new Mat();
Size sz = new Size(inpWidth, inpHeight);
Imgproc.resize(im, resized, sz);
float scale = 1.0F / 255.0F; // 像素归一化
遍历得到Yolo输出层的名字
此处即原python代码
ln = [ln[i[0] - 1] for i in net.getUnconnectedOutLayers()
net.getUnconnectedOutLayers()得到的是MatOfInt类型,是未连接层的索引,toList(),转换为列表。
out:[[200, 267, 400]]
out.get(0):[200, 267, 400]
Yolo的输出层是未连接层的前一个元素,所以需要减一:i.get(a) - 1得到的也是索引值
ln.get(199) = “yolo_82”
ln.get(265) = “yolo_94”
ln.get(399) = “yolo_106”
Java:
List ln = net.getLayerNames(); // 获得YOLO各层的名字
List x = new ArrayList();
List> out = new ArrayList>(); // 存放的是列表
List temp = net.getUnconnectedOutLayers().toList(); // 获得未连接的输出层的索引列表
out.add(temp);
// out中存放的是一个List ,get(0)得到的就是list i 索引列表
List i = out.get(0);
System.out.println(i.size()); // 3
for(int a=0; a 将图像转换为标准输入格式
用需要检测的原始图像im构造一个blob图像,对原图像进行像素归一化 1/255.0,缩放尺寸(416,416),对应训练模型时的cfg文件交换了通道。
若原图像:BGR,且swapRB=true时,交换第一个通道和第三个通道的值,即变为 RGB
crop:调整大小后是否裁剪图像。
Mat blob = Dnn.blobFromImage(im, scale, sz, new Scalar(0), true, false);
进入检测方法
// 矩阵列表 [Mat[...], Mat[...], Mat[...]]
List outs = new ArrayList();
net.forward(outs, ln); // ln此时为输出层的名字列表,向前传播,将得到的检测结果传入outs
System.out.println(outs);
// 进入检测识别方法
postprocess_(im, outs);
// 检测结束后显示图片
imshow(kWinName, im); // 显示图片
waitKey(300000);
} // detect_image 方法结束
检测识别方法(postprocess_)
- 循环遍历outs中的每一个矩阵
- 过滤置信度小于阈值的检测结果
- 得到矩形框列表,类别序号列表,置信度列表,每一个都相互对应。
- 非极大值抑制
- 进入画框,添加文字标签方法
- 截取每张图片画出的每个矩形框,存为一个
List/存入本地路径
public static void postprocess_(Mat im, List outs) {
System.out.println("检测过程开始");
List boxes = new ArrayList(); // 矩形框列表
List classIds = new ArrayList(); // 类的序号列表
List confidences = new ArrayList(); // 置信度列表
// HashMap predicts_dict = new HashMap();
// 循环List
for (int i = 0; i < outs.size(); i++) {
Mat mat = outs.get(i);
// 循环每一个mat对象
// 按行循环
for (int j = 0; j < mat.rows(); j++) {
int probaility_index = 5; // [x,y,h,w,c,class1,class2] 所以是标号5
int size = (int) (mat.cols() * mat.channels());
float[] data = new float[size];
mat.get(j, 0, data);
float confidence = -1;
int classId = -1;
// 按列循环
for (int k = 0; k < mat.cols(); k++) {
// 相当于[5:] np.argmax(scores)
if (k >= probaility_index && confidence < data[k]) {
confidence = data[k]; // 最大值
classId = k - probaility_index; // 得到检测得的类别索引
}
}
// 过滤掉置信度较小的检测结果
if (confidence > 0.5) {
System.out.println("Result Object:" + j);
for (int k = 0; k < mat.cols(); k++) {
System.out.println(" " + k + ":" + data[k]);
}
System.out.println("");
float x = data[0]; // centerX 矩形中心点的X坐标
float y = data[1]; // centerY 矩形中心点的Y坐标
float width = data[2]; // 矩形框的宽
float height = data[3]; //矩形框的高
float xLeftBottom = (x - width / 2) * im.cols(); // 矩形左下角点的X坐标
float yLeftBottom = (y - height / 2) * im.rows(); // 矩形左下角点的Y坐标
float xRightTop = (x + width / 2) * im.cols(); // 矩形右上角点的X坐标
float yRightTop = (y + height / 2) * im.rows(); // 矩形右上角点的Y坐标
// boxes列表填值 Rect对象,参数是两个点
boxes.add(new Rect(new Point(xLeftBottom, yLeftBottom), new Point(xRightTop, yRightTop)));
confidences.add(confidence);
classIds.add(classId);
}
}
}
System.out.println(classIds);
System.out.println(confidences);
System.out.println(boxes.size());
System.out.println(boxes);
// 非极大值抑制
List indices = new ArrayList();
// 此处的非极大值抑制为自己重写的方法。
NMSBoxes(boxes, confidences, confThreshold, nmsThreshold, indices);
List cutImages = new ArrayList();
Mat cut;
int a = 0;
// indices : 最终剩下的按置信度由高到低的矩形框序号
if (indices.size() > 0) {
for (int b = 0; b < indices.size(); b++) {
a = a + 1;
Rect box = boxes.get(indices.get(b));
Point p1 = box.tl(); // 获得左 上角点
Point p2 = box.br(); // 获得右下角点
int classId = classIds.get(a - 1); // 得到类别序号
float confidence = confidences.get(a - 1); // 得到置信度值
// 进入画框框方法
drawPred_(classId, confidence, im, p1, p2);
// 将每个矩形框裁剪
cut = im.submat((int)p1.y, (int)p2.y, (int)p1.x, (int)p2.x);
cutImages.add(cut);
}
}
System.out.println(cutImages);
// 将裁剪后的图片存入本地路径(可省略)
String outputFilePath = "E:/pictures_output";
for (int i=0; i 非极大值抑制(NMSBoxes)
先创建一个静态类BBox
static class BBox{
public Rect getBox() {
return box;
}
public void setBox(Rect box) {
this.box = box;
}
public float getConfidence() {
return confidence;
}
public void setConfidence(float confidence) {
this.confidence = confidence;
}
public int getIndex() {
return index;
}
public void setIndex(int index) {
this.index = index;
}
Rect box = new Rect();
float confidence;
int index;
}
重写的非极大值抑制方法
public static void NMSBoxes(List boxes, List confidences, float confThreshold, float nmsThreshold, List indices){
// 新建一个List 存放BBox的对象
List bboxes = new ArrayList();
// 循环向bboxes里添加值:Rect(Point,Point) float confidence, int index
for(int i=0; i阈值,删除这个框,更改bboxes的长度
for (int j=i+1; j nmsThreshold){
bboxes.remove(j);
updated_size = bboxes.size();
}
}
}
}
获得交并比的方法
public static float getIouValue(Rect rect1, Rect rect2){
int xx1, yy1, xx2, yy2;
xx1 = Math.max(rect1.x, rect2.x);
yy1 = Math.max(rect1.y, rect2.y);
xx2 = Math.min(rect1.x + rect1.width - 1, rect2.x + rect2.width - 1);
yy2 = Math.min(rect1.y + rect1.height -1, rect2.y + rect2.height -1);
int insection_width, insection_height;
insection_width = Math.max(0, xx2 - xx1 + 1);
insection_height = Math.max(0, yy2 - yy1 + 1);
float insection_area, union_area, iou;
insection_area = insection_width * insection_height;
union_area = rect1.width * rect1.height + rect2.width * rect2.height - insection_area;
iou = insection_area / union_area;
return iou;
}
画矩形框,添加文字标签
public static void drawPred_(int classId, float confidence, Mat im, Point p1, Point p2){
String text;
double x = p1.x; // p1 的 x 坐标
double y = p1.y; // p1 的 y 坐标
// 下面加if语句只是为了区分人和其他类别的不同颜色,改成随机获取颜色也可以
if(classId == 0){
System.out.println("1");
rectangle(im, p1, p2, new Scalar(0, 0, 255), 3);
text = classes.get(classId) + ":" + confidence;
putText(im, text, new Point(x, y-5), FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.3, new Scalar(0, 255, 0), 1);
}else {
System.out.println("2");
rectangle(im, p1, p2, new Scalar(0, 255, 0), 3); // 画框
text = String.format("%s %f", classes.get(classId), confidence); // 标签内容
System.out.println(text);
// 把标签添加到矩形框左上
putText(im, text, new Point(x, y-5), FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, new Scalar(0, 0, 255), 1);
}
}
实现效果
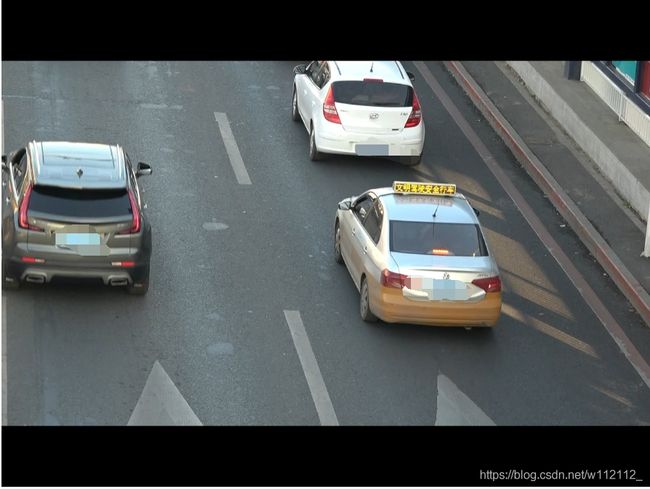

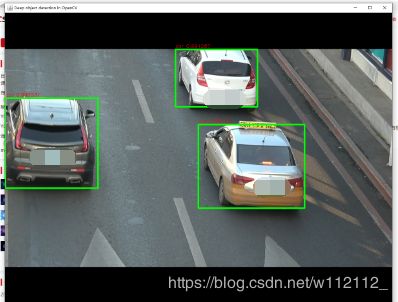



本文参考:
opencv调用yolov3模型进行目标检测,以实例进行代码详解:
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_32761549/article/details/90402438
OpenCV+yolov3实现目标检测(C++,Python):
https://blog.csdn.net/guyuealian/article/details/84098461#2.1%20C%2B%2B%E4%BB%A3%E7%A0%81
JAVA调用OPENCV中DNN.Darknet接口进行目标检测测试(代码备份):
https://blog.csdn.net/wjbwjbwjbwjb/article/details/78388248
c++版的NMS(非极大抑制)实现:
https://blog.csdn.net/avideointerfaces/article/details/88551325