Python中使用pyqtgraph绘图库实时绘制计算机CPU使用率等数据曲线
一、项目需求
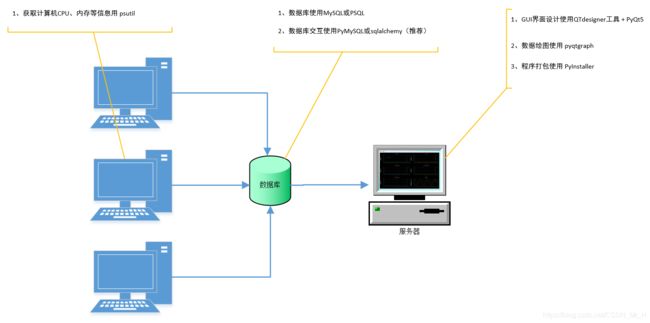
- 获取约30台电脑的CPU使用率、CPU温度、系统盘容量、系统盘使用率、总硬盘使用率、内存使用率、GPU使用率等数据
- 将1中数据集中用图表的形式集中展示出来
二、设计思路
- 采用C/S架构(客户端/服务器),客户端负责收集数据并汇总数据到数据库,服务器负责读取数据
- 使用QTdesigner工具制作GUI界面配合PyQt5使用数据做图展示
- 使用PyInstaller打包发布
三、代码实现
这里主要记录用收集的数据进行绘图并展示的部分
官方demo效果图及代码
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Various methods of drawing scrolling plots.
"""
# import initExample ## Add path to library (just for examples; you do not need this)
import pyqtgraph as pg
from pyqtgraph.Qt import QtCore, QtGui
import numpy as np
win = pg.GraphicsLayoutWidget(show=True)
win.setWindowTitle('pyqtgraph example: Scrolling Plots')
# 1) Simplest approach -- update data in the array such that plot appears to scroll
# In these examples, the array size is fixed.
p1 = win.addPlot()
p2 = win.addPlot()
data1 = np.random.normal(size=300)
curve1 = p1.plot(data1)
curve2 = p2.plot(data1)
ptr1 = 0
def update1():
global data1, ptr1
data1[:-1] = data1[1:] # shift data in the array one sample left
# (see also: np.roll)
data1[-1] = np.random.normal()
curve1.setData(data1)
ptr1 += 1
curve2.setData(data1)
curve2.setPos(ptr1, 0)
# 2) Allow data to accumulate. In these examples, the array doubles in length
# whenever it is full.
win.nextRow()
p3 = win.addPlot()
p4 = win.addPlot()
# Use automatic downsampling and clipping to reduce the drawing load
p3.setDownsampling(mode='peak')
p4.setDownsampling(mode='peak')
p3.setClipToView(True)
p4.setClipToView(True)
p3.setRange(xRange=[-100, 0])
p3.setLimits(xMax=0)
curve3 = p3.plot()
curve4 = p4.plot()
data3 = np.empty(100)
ptr3 = 0
def update2():
global data3, ptr3
data3[ptr3] = np.random.normal()
ptr3 += 1
if ptr3 >= data3.shape[0]:
tmp = data3
data3 = np.empty(data3.shape[0] * 2)
data3[:tmp.shape[0]] = tmp
curve3.setData(data3[:ptr3])
curve3.setPos(-ptr3, 0)
curve4.setData(data3[:ptr3])
# 3) Plot in chunks, adding one new plot curve for every 100 samples
chunkSize = 100
# Remove chunks after we have 10
maxChunks = 10
startTime = pg.ptime.time()
win.nextRow()
p5 = win.addPlot(colspan=2)
p5.setLabel('bottom', 'Time', 's')
p5.setXRange(-10, 0)
curves = []
data5 = np.empty((chunkSize + 1, 2))
ptr5 = 0
def update3():
global p5, data5, ptr5, curves
now = pg.ptime.time()
for c in curves:
c.setPos(-(now - startTime), 0)
i = ptr5 % chunkSize
if i == 0:
curve = p5.plot()
curves.append(curve)
last = data5[-1]
data5 = np.empty((chunkSize + 1, 2))
data5[0] = last
while len(curves) > maxChunks:
c = curves.pop(0)
p5.removeItem(c)
else:
curve = curves[-1]
data5[i + 1, 0] = now - startTime
data5[i + 1, 1] = np.random.normal()
curve.setData(x=data5[:i + 2, 0], y=data5[:i + 2, 1])
ptr5 += 1
# update all plots
def update():
update1()
update2()
update3()
timer = pg.QtCore.QTimer()
timer.timeout.connect(update)
timer.start(50)
## Start Qt event loop unless running in interactive mode or using pyside.
if __name__ == '__main__':
import sys
if (sys.flags.interactive != 1) or not hasattr(QtCore, 'PYQT_VERSION'):
QtGui.QApplication.instance().exec_()
自己实现的效果图及代码
main.py
# !/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# author:dell
import sys
import numpy as np
import pyqtgraph as pg
from PyQt5 import QtWidgets
from random import randint, random
from MyGUI.demo_kyd.kyd import Ui_MainWindow
from SQLutil.common import model1, model2, model3, model4
# https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43417472/article/details/89356461
# https://zmister.com/archives/187.html
# https://zmister.com/archives/793.html
class MyGraphWindow(QtWidgets.QMainWindow, Ui_MainWindow):
def __init__(self):
super(MyGraphWindow, self).__init__()
self.setupUi(self) # 初始化窗口
self.p1, self.p2, self.p3, self.p4, self.p5, self.p6 = self.set_graph_ui() # 设置绘图窗口
# self.pushButton.clicked.connect(self.plot_sin_cos) # 点击按键开始绘图
self.n = 0 # 用于函数执行计次
# TODO 绘制十字光标
self.vLine = pg.InfiniteLine(angle=90, movable=False) # 创建一个垂直线条
self.hLine = pg.InfiniteLine(angle=0, movable=False) # 创建一个水平线条
self.vb = self.p6.vb
# 将mouseMoved方法连接到self.p6这个图形部件的信号事件上,使得鼠标移动时可以实时响应
self.proxy = pg.SignalProxy(self.p6.scene().sigMouseMoved, rateLimit=60, slot=self.mouseMoved)
def set_graph_ui(self):
pg.setConfigOptions(antialias=True) # pg全局变量设置函数,antialias=True开启曲线抗锯齿
win = pg.GraphicsLayoutWidget(show=True) # 创建pg layout,可实现数据界面布局自动管理
# pg绘图窗口可以作为一个widget添加到GUI中的graph_layout,当然也可以添加到Qt其他所有的容器中
self.verticalLayout.addWidget(win)
p1 = win.addPlot(title="教师机") # 添加第一个绘图窗口
p1.setLabel('left', text='CPU使用率', color='#ffffff', units='%') # 设置y轴说明信息
p1.setLabel('bottom', text='time', units='') # x轴设置函数
p1.showGrid(x=True, y=True) # 栅格设置函数
p1.setLogMode(x=False, y=False) # False代表线性坐标轴,True代表对数坐标轴
p1.addLegend() # 可选择是否添加legend 标识
# win.nextRow() # layout换行,采用垂直排列,不添加此行则默认水平排列
p2 = win.addPlot(title="仪表机")
p2.setLabel('left', text='内存使用率', color='#ffffff', units='%')
p2.setLabel('bottom', text='time', units='')
p2.showGrid(x=True, y=True)
p2.setLogMode(x=False, y=False)
# p2.addLegend()
win.nextRow()
p3 = win.addPlot(title="主场景计算机") # 添加第一个绘图窗口
p3.setLabel('left', text='GPU使用率', color='#ffffff', units='%') # 设置y轴说明信息
p3.setLabel('bottom', text='time', units='') # x轴设置函数
p3.showGrid(x=True, y=True) # 栅格设置函数
p3.setLogMode(x=False, y=False) # False代表线性坐标轴,True代表对数坐标轴
p4 = win.addPlot(title="左右视景计算机") # 添加第一个绘图窗口
p4.setLabel('left', text='CPU使用率', color='#ffffff', units='%') # 设置y轴说明信息
p4.setLabel('bottom', text='time', units='') # x轴设置函数
p4.showGrid(x=True, y=True) # 栅格设置函数
p4.setLogMode(x=False, y=False) # False代表线性坐标轴,True代表对数坐标轴
win.nextRow()
p5 = win.addPlot(title="摄像计算机") # 添加第一个绘图窗口
p5.setLabel('left', text='CPU使用率', color='#ffffff', units='%') # 设置y轴说明信息
p5.setLabel('bottom', text='time', units='') # x轴设置函数
p5.showGrid(x=True, y=True) # 栅格设置函数
p5.setLogMode(x=False, y=False) # False代表线性坐标轴,True代表对数坐标轴
p6 = win.addPlot(title="计算机6") # 添加第一个绘图窗口
p6.setLabel('left', text='其他数据曲线(示例)', color='#ffffff', units='%') # 设置y轴说明信息
p6.setLabel('bottom', text='time', units='') # x轴设置函数
p6.showGrid(x=True, y=True) # 栅格设置函数
p6.setLogMode(x=False, y=False) # False代表线性坐标轴,True代表对数坐标轴
# p6.addLegend()
# self.label = pg.LabelItem(justify='right') # 创建一个文本项
# win.addItem(self.label) # TODO 这里的 LabelItem 好像只能在 win 中显示
# p6.addItem(self.label) # 在图形部件中添加文本项
return p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6
def plot_sin_cos(self):
"""获取数据,更新数据并实时作图"""
self.n += 1 # 从第二次执行开始就要更新数据了
if self.n <= 1:
self.data1 = [0] * 200
self.data2 = [0] * 200
self.data3 = [0] * 200
self.data4 = [0] * 200
self.data5 = [0] * 200
self.data6 = [0] * 200
self.p1.plot(self.data1, pen=(0, 255, 0), name="Red curve")
self.p2.plot(self.data2, pen=(0, 255, 0), name="Red curve")
self.p3.plot(self.data3, pen=(0, 255, 0), name="Red curve")
self.p4.plot(self.data4, pen=(0, 255, 0), name="Red curve")
self.p5.plot(self.data5, pen=(0, 255, 0), name="Red curve")
self.p6.plot(self.data6, pen=(0, 255, 0), name="Red curve")
# self.p6.setXRange(-200, 0)
t = np.linspace(0, 20, 200)
self.y_sin = np.sin(t) # x的每个元素的正弦。如果x是标量,则这是标量。 # https://vimsky.com/examples/usage/python-numpy.sin.html
self.y_cos = np.cos(t)
self.p6.plot(self.y_sin, pen=(255, 0, 0), name="Red curve", clear=True)
self.p6.plot(self.y_cos, pen=(0, 255, 0), name="Green curve", )
# self.y_cos = [random() for i in range(0, 200)]
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------测试--------↓
# self.p2.plot(self.y_sin, pen=(255, 0, 0), name="Red curve")
# self.p2.plot(self.y_cos, pen=(0, 255, 0), name="Green curve")
# self.y_cos = [randint(1, 50) for i in range(0, 200)]
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------测试--------↑
else:
self.temp_data1 = self.data1[1::] # 截取第二位至最后一位
self.temp_data1.append(model2.cpu_usage) # 新增数据,更新列表状态
self.data1 = self.temp_data1
self.p1.plot(self.data1, pen=(0, 255, 0), name="Red curve", clear=True) # TODO clear=True 会把之前的图像清除
self.temp_data2 = self.data2[1::] # 截取第二位至最后一位
self.temp_data2.append(model2.get_memory_info("m_Usage")) # 新增数据,更新列表状态
self.data2 = self.temp_data2
self.p2.plot(self.data2, pen=(255, 255, 0), name="Red curve", clear=True)
self.temp_data3 = self.data3[1::] # 截取第二位至最后一位
self.temp_data3.append(model2.get_gpu_info("gpu_Usage")) # 新增数据,更新列表状态
self.data3 = self.temp_data3
self.p3.plot(self.data3, pen=(0, 255, 255), name="Red curve", clear=True)
self.temp_data4 = self.data4[1::] # 截取第二位至最后一位
self.temp_data4.append(model2.cpu_usage) # 新增数据,更新列表状态
self.data4 = self.temp_data4
self.p4.plot(self.data4, pen=(0, 255, 0), name="Red curve", clear=True)
self.temp_data5 = self.data5[1::] # 截取第二位至最后一位
self.temp_data5.append(model2.cpu_usage) # 新增数据,更新列表状态
self.data5 = self.temp_data5
self.p5.plot(self.data5, pen=(0, 255, 0), name="Red curve", clear=True)
self.y_sin_one = self.y_sin[0] # 取出第一位
self.c_y_sin = self.y_sin[1::] # 截取第二位至最后一位
self.y_sin = np.append(self.c_y_sin, self.y_sin_one) # 新增数据,更新列表状态
self.y_cos_one = self.y_cos[0] # 取出第一位
self.c_y_cos = self.y_cos[1::] # 截取第二位至最后一位
self.y_cos = np.append(self.c_y_cos, self.y_cos_one)
self.p6.plot(self.y_sin, pen=(255, 0, 0), name="Red curve", clear=True)
self.p6.plot(self.y_cos, pen=(0, 255, 0), name="Green curve", )
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------测试--------↓
# TODO clear=True 会把之前的图像清除
# self.temp_data1 = self.data1[1::] # 截取第二位至最后一位
# self.temp_data1.append(model2.cpu_usage) # 新增数据,更新列表状态
# self.data1 = self.temp_data1
# self.p1.plot(self.data1, pen=(0, 255, 0), name="Red curve", clear=True)
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------测试--------↑
pass
def mouseMoved(self, evt):
"""指定区域中移动鼠标,会触发此函数"""
pos = evt[0] ## using signal proxy turns original arguments into a tuple 使用信号代理将原始参数转换为元组,获取事件的鼠标位置
if self.p6.sceneBoundingRect().contains(pos): # 如果鼠标位置在绘图部件中
mousePoint = self.vb.mapSceneToView(pos) # 转换鼠标坐标
index = int(mousePoint.x()) # 鼠标所处的X轴坐标
if index > 0 and index < len(self.data1):
# self.label.setText(
# "x=%0.1f, y1=%0.1f, y2=%0.1f" % (
# mousePoint.x(), self.data1[index], self.data2[index]))
# self.p6_txt = "x=%0.1f, y1=%0.1f, y2=%0.1f" % (
# mousePoint.x(), self.y_sin[index], self.y_cos[index])
self.p6_txt = "x=%0.1f, y1=%0.1f, y2=%0.1f" % (
mousePoint.x(), self.y_sin[index], self.y_cos[index])
self.p6.setLabel('bottom', text='{}'.format(self.p6_txt)) # TODO 设置底部说明信息
# self.label.setPos(mousePoint.x(), mousePoint.y()) # 设置label的位置
# 设置垂直线条和水平线条的位置组成十字光标
self.vLine.setPos(mousePoint.x())
self.hLine.setPos(mousePoint.y())
# TODO 将十字光标,加入到图6中
self.p6.addItem(self.vLine, ignoreBounds=True) # 在图形部件中添加垂直线条
self.p6.addItem(self.hLine, ignoreBounds=True) # 在图形部件中添加水平线条
else:
self.p6.setLabel('bottom', text='time', units='', ) # 设置底部说明信息
# self.p6.setLabel('bottom', text="time", units='',) # 设置底部说明信息
pass
if __name__ == '__main__':
app = QtWidgets.QApplication(sys.argv)
myWin = MyGraphWindow()
myWin.show()
timer = pg.QtCore.QTimer() # 定时器 https://www.cnblogs.com/hhh5460/p/4280612.html
timer.timeout.connect(myWin.plot_sin_cos)
timer.start(500)
sys.exit(app.exec_())
kyd.py
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# Form implementation generated from reading ui file 'zzkyd.ui'
#
# Created by: PyQt5 UI code generator 5.15.0
#
# WARNING: Any manual changes made to this file will be lost when pyuic5 is
# run again. Do not edit this file unless you know what you are doing.
from PyQt5 import QtCore, QtGui, QtWidgets
class Ui_MainWindow(object):
def setupUi(self, MainWindow):
MainWindow.setObjectName("MainWindow")
MainWindow.resize(1000, 750)
self.centralwidget = QtWidgets.QWidget(MainWindow)
self.centralwidget.setObjectName("centralwidget")
self.gridLayout = QtWidgets.QGridLayout(self.centralwidget)
self.gridLayout.setObjectName("gridLayout")
self.verticalLayout = QtWidgets.QVBoxLayout()
self.verticalLayout.setObjectName("verticalLayout")
self.gridLayout.addLayout(self.verticalLayout, 0, 0, 1, 1)
MainWindow.setCentralWidget(self.centralwidget)
self.menubar = QtWidgets.QMenuBar(MainWindow)
self.menubar.setGeometry(QtCore.QRect(0, 0, 1000, 23))
self.menubar.setObjectName("menubar")
self.menu_1 = QtWidgets.QMenu(self.menubar)
self.menu_1.setObjectName("menu_1")
self.menu_2 = QtWidgets.QMenu(self.menubar)
self.menu_2.setObjectName("menu_2")
MainWindow.setMenuBar(self.menubar)
self.statusbar = QtWidgets.QStatusBar(MainWindow)
self.statusbar.setObjectName("statusbar")
MainWindow.setStatusBar(self.statusbar)
self.action_1_1 = QtWidgets.QAction(MainWindow)
self.action_1_1.setObjectName("action_1_1")
self.action_2_1 = QtWidgets.QAction(MainWindow)
self.action_2_1.setObjectName("action_2_1")
self.menu_1.addAction(self.action_1_1)
self.menu_2.addAction(self.action_2_1)
self.menubar.addAction(self.menu_1.menuAction())
self.menubar.addAction(self.menu_2.menuAction())
self.retranslateUi(MainWindow)
QtCore.QMetaObject.connectSlotsByName(MainWindow)
def retranslateUi(self, MainWindow):
_translate = QtCore.QCoreApplication.translate
MainWindow.setWindowTitle(_translate("MainWindow", "计算机监测系统"))
self.menu_1.setTitle(_translate("MainWindow", "菜单1"))
self.menu_2.setTitle(_translate("MainWindow", "菜单2"))
self.action_1_1.setText(_translate("MainWindow", "菜单1-1"))
self.action_2_1.setText(_translate("MainWindow", "菜单2-1"))
common.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import time
from datetime import date
from sqlalchemy.orm import sessionmaker
from sqlalchemy.ext.declarative import declarative_base
from sqlalchemy import Column, String, create_engine, Integer, VARCHAR, DateTime, DATETIME, DATE, Date, text
Computer_Info_Dict = {
"computer1": "10.0.40.223",
"computer2": "10.0.40.42",
"computer3": "10.0.40.194",
"computer4": "10.0.40.223",
"computer5": "10.0.40.223",
"computer6": "10.0.40.42",
}
# Computer_Info_Dict = {
# "tb_10_0_120_178": "10.0.120.178",
# "tb_10_0_120_177": "10.0.120.177",
# "tb_10_0_120_179": "10.0.120.179",
# "tb_10_0_120_180": "10.0.120.180",
# "tb_10_0_120_175": "10.0.120.175",
# }
def make_model(TableName):
"""sqlalchemy 动态创建表对象"""
Base = declarative_base() # 创建对象的基类(生成一个SQLORM基类)
class table_model(Base):
__tablename__ = TableName
# 表的结构
id = Column(Integer, primary_key=True)
ip = Column(VARCHAR(20))
cpu = Column(VARCHAR(20))
# cpu_t = Column(VARCHAR(20))
disk = Column(VARCHAR(20))
memory = Column(VARCHAR(20))
gpu = Column(VARCHAR(20))
date = Column(DATE)
event = Column(VARCHAR(20))
return table_model
class QueryModel():
"""数据表查询对象"""
def __init__(self, TableObj):
# 初始化数据库链接
engine = create_engine('postgresql+psycopg2://postgres:[email protected]:5432/zzkyd', echo=True)
# 创建DBSession类型
DBSession = sessionmaker(bind=engine)
self.session = DBSession()
self.TabModel = self.session.query(TableObj)
self.table_name = TableObj.__tablename__
self.tab_obj = TableObj
self.ip = Computer_Info_Dict.get(self.table_name, None)
# 初始化获取基础硬件信息
self.CPU_Name = -1
self.C_Disk_Size = -1
self.Memory_Size = -1
self.GPU_Size = -1
self.cpu_usage
self.get_memory_info()
self.get_disk_info()
self.get_gpu_info()
@property
def query_all(self):
"""查询所有数据"""
return self.TabModel.filter().all()
@property
def query_last(self):
"""查询最后一条数据"""
# [(285, '10.0.40.42', 'Intel(R) Core(TM) i7-6700 CPU @ 3.40GHz,2', '100.0,73.4,1155.1,186.1,16.1', '16,11,31.8', '6144.0,686.8,11.2', datetime.datetime(2020, 7, 24, 10, 26, 9, 179375), None)]
# TODO 方法一,使用原生SQL语句
# sql = """select * from {} order by id desc limit 1;""".format(self.table_name)
# return self.session.execute(text(sql)).fetchall()
# TODO 方法二,使用ORM对象关系映射
result = self.TabModel.order_by(self.tab_obj.date.desc()).first() # 按日期查询取最后一条数据
if result:
return result
else:
return None
@property
def cpu_usage(self):
"""实时获取cpu使用率,初始化调用此函数可获得self.CPU_Name信息"""
last_data_obj = self.query_last
if not last_data_obj:
return 0
CPU_INFO_str = last_data_obj.cpu # Intel(R) Core(TM) i7-6700 CPU @ 3.40GHz,2
CPU_INFO_li = CPU_INFO_str.split(",") # ['Intel(R) Core(TM) i7-6700 CPU @ 3.40GHz', '2']
self.CPU_Name = CPU_INFO_li[0]
CPU_Usage = int(CPU_INFO_li[1]) # 2 Int 型
return CPU_Usage
def get_disk_info(self, type=None):
"""获取硬盘信息"""
last_data_obj = self.query_last
if not last_data_obj:
return 0
C_Disk_INFO_str = last_data_obj.disk # 100.0,73.4,1155.1,186.1,16.1
C_Disk_INFO_li = C_Disk_INFO_str.split(",") # ['100.0', '73.4', '1155.1', '186.1', '16.1']
self.C_Disk_Size = C_Disk_INFO_li[0] # 100.0 系统盘总容量
C_Usage = float(C_Disk_INFO_li[1]) # 系统盘使用率
total_Size = float(C_Disk_INFO_li[2]) # 硬盘总容量
total_Used = float(C_Disk_INFO_li[3]) # 硬盘已使用
total_Usage = float(C_Disk_INFO_li[4]) # 硬盘使用率
if type == "C_Size":
return self.C_Disk_Size
elif type == "C_Usage":
return C_Usage
elif type == "total_Size":
return total_Size
elif type == "total_Used":
return total_Used
elif type == "total_Usage":
return total_Usage
def get_memory_info(self, type=None):
"""获取内存信息"""
last_data_obj = self.query_last
if not last_data_obj:
return 0
memory_INFO_str = last_data_obj.memory
memory_INFO_li = memory_INFO_str.split(",")
self.Memory_Size = float(memory_INFO_li[0]) # 内存总量
m_Can_Use = float(memory_INFO_li[1]) # 内存可用量
m_Usage = float(memory_INFO_li[2]) # 内存使用率
if type == "m_Size":
return self.Memory_Size
elif type == "m_Can_Use":
return m_Can_Use
elif type == "m_Usage":
return m_Usage
def get_gpu_info(self, type=None):
"""获取GPU信息"""
last_data_obj = self.query_last
if not last_data_obj:
return 0
gpu_INFO_str = last_data_obj.gpu
gpu_INFO_li = gpu_INFO_str.split(",")
self.GPU_Size = float(gpu_INFO_li[0]) # GPU总量
gpu_Used = float(gpu_INFO_li[1]) # GPU已使用
gpu_Usage = float(gpu_INFO_li[2]) # GPU使用率
if type == "gpu_Size":
return self.GPU_Size
elif type == "gpu_Used":
return gpu_Used
elif type == "gpu_Usage":
return gpu_Usage
def query_some(self, num=100):
"""查询固定数量的条目信息,默认查询最近100条数据"""
# TODO 注意,这里是按日期倒序排列的
result = self.TabModel.order_by(self.tab_obj.date.desc()).limit(num).all()
return result
def query_with_date(self):
"""根据日期查询 TODO 后期根据按日期查询需求决定"""
timestring = "2020-07-24 16:14:06.132375"
# timestring = "2020-07-24 0:0:0"
# TODO 方法一,使用原生SQL语句
# sql = """select * from {} where date > \'{}\';""".format(self.table_name, timestring)
# return self.session.execute(text(sql)).fetchall()
# TODO 方法二,使用ORM对象关系映射
result = self.TabModel.filter(self.tab_obj.date > """\'{}\'""".format(timestring)).all()
return result
@property
def test(self):
# sql = """select * from {};""".format(self.table_name)
# result = self.session.execute(text(sql)).fetchall()
# self.TabModel.order_by(self.tab_obj.date.desc()).first() # TODO 按日期获取最后一条数据
result = self.TabModel.order_by(self.tab_obj.date.desc()).first()
return result
model1 = QueryModel(make_model("computer1"))
model2 = QueryModel(make_model("computer2"))
model3 = QueryModel(make_model("computer3"))
model4 = QueryModel(make_model("computer4"))
model5 = QueryModel(make_model("computer5"))
model6 = QueryModel(make_model("computer6"))
if __name__ == '__main__':
# # 初始化数据库链接
# engine = create_engine('postgresql+psycopg2://postgres:[email protected]:5432/zzkyd', echo=True)
# # 创建DBSession类型
# DBSession = sessionmaker(bind=engine)
# session = DBSession()
# Computer = make_model("computer2")
# comp = session.query(Computer).filter().all()
#
# for i in comp:
# print("id", i.id)
# print("ip", i.ip)
# # print("cpu", type(i.cpu))
# print("cpu", i.cpu)
# print("cpu_t", i.cpu_t)
# print("disk", i.disk)
# print("memory", i.memory)
# print("date", i.date)
# # print("date", i.date.today().year)
# print("event", i.event)
#
# print('-' * 100 + '\n')
table1 = make_model("computer2")
m = QueryModel(table1)
# m.query_some()
m.query_with_date()
四、相关资源
- python模块之psutil详解
- 廖雪峰的官方网站–常用模块psutil
- python中使用psutil和matplotlib绘制监控cpu消耗图
- psutil 官方github
- PyQt5的PyQtGraph实践系列2:绘制股票十字光标K线图
- pyqtgraph数据可视化3:使用PyQtGraph绘制精美折线图——以上证指数为例
- Python GUI教程(十三):在GUI中使用pyqtgraph绘图库
- PyQt5 教程
- PyQt5的PyQtGraph实践系列3之实时数据更新绘制图形
- PyQt5图形界面编程(知乎专栏)
- Qt Designer常用部件介绍
- 使用sqlalchemy ORM创建表及数据的插入
- sqlAlchemy基本使用
- Python SQLAlchemy基本操作和常用技巧(包含大量实例,非常好)
- SQLAlchemy基本使用