java本地方法 hashcode是怎样生成的?hashcode与地址有关系吗?
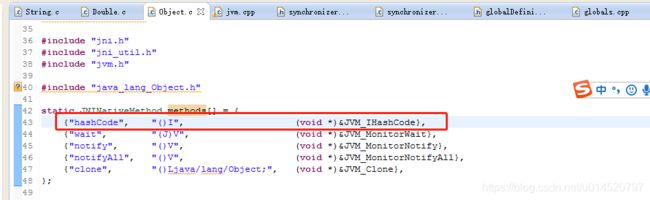
1、java Obeject类中的hashcode函数
/**
返回一个对象的散列码,这个方法有利于哈希表,例如HashMap
Returns a hash code value for the object. This method is supported for the benefit of hash tables such as those provided by java.util.HashMap.
*/
public native int hashCode();2、hashcode方法和equals 方法都是Obeject类中的方法,当不重写equals 方法时,比较的是 两个对象是否完全相等。
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
return (this == obj);
}我们知道hashcode方法和equals 方法是配套使用的,当我们重写equals 方法时我们需要重写hashcode方法。为什么?因为java中有这样的规范。规范如下
摘自Object规范 (JavaSE6):
- 在应用程序的执行期间,只要对象的equals方法的比较操作所用到的信息没有被修改,那么对这同一个对象调用多次,hashCode方法都必须始终如一地返回同一个整数。在同一个程序多次执行过程中,每次执行所返回的整数可以不一致;
- 如果两个对象根据equals方法比较是相等的,那么调用者两个对象的hashCode方法必须返回同一个整数;
- 如果两个对象根据equals方法比较是不相等的,那么调用者两个对象的hashCode方法不一定返回不同整数。给不相等的对象产生截然不同的整数结果,有可能提高散列表(hash table)的性能;
3、tostring方法也与hashcode方法有关,不重写时返回的是hashcode的16进制表达形式
public String toString() {
return getClass().getName() + "@" + Integer.toHexString(hashCode());
}
4、hashcode是本地方法,具体实现是用c++写的,我们可以下载openjdk源码阅读。
下载地址:https://download.csdn.net/download/u014520797/12454866
官网地址:http://openjdk.java.net/
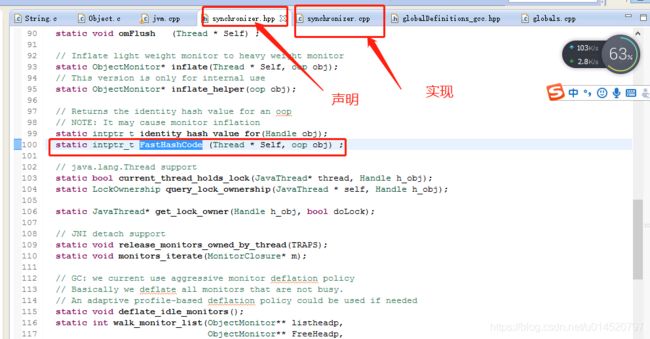
5、用c++版本的eclipse来看看 源码
声明在synchronizer.hpp 实现在这里synchronizer.cpp。
主要函数有两个get_next_hash和FastHashCode,FastHashCode函数里会调用get_next_hash函数,get_next_hash函数中有6种产生hashcode的方式,由于hashCode默认值是5(可在虚拟机启动时配置 -XX:hashCode, java8以前默认值是0,java8以后是5),所以默认是最后一种产生方式。
static inline intptr_t get_next_hash(Thread * Self, oop obj) {
intptr_t value = 0 ;
if (hashCode == 0) {//随机数生成
// This form uses an unguarded global Park-Miller RNG,
// so it's possible for two threads to race and generate the same RNG.
// On MP system we'll have lots of RW access to a global, so the
// mechanism induces lots of coherency traffic.
value = os::random() ;
} else
if (hashCode == 1) {//这与第5个方式类似,都调用了cast_from_oop函数,只不过此处又增加了位偏移和addrBits ^ (addrBits >> 5) ^ GVars.stwRandom计算
// This variation has the property of being stable (idempotent)
// between STW operations. This can be useful in some of the 1-0
// synchronization schemes.
intptr_t addrBits = cast_from_oop(obj) >> 3 ;
value = addrBits ^ (addrBits >> 5) ^ GVars.stwRandom ;
} else
if (hashCode == 2) {//灵敏度测试,不知道干嘛的
value = 1 ; // for sensitivity testing
} else
if (hashCode == 3) {//自增序列
value = ++GVars.hcSequence ;
} else
if (hashCode == 4) {//
value = cast_from_oop(obj) ;
} else {//Marsaglia's 异或-位移方案
// Marsaglia's xor-shift scheme with thread-specific state
// This is probably the best overall implementation -- we'll
// likely make this the default in future releases.
unsigned t = Self->_hashStateX ;
t ^= (t << 11) ;
Self->_hashStateX = Self->_hashStateY ;
Self->_hashStateY = Self->_hashStateZ ;
Self->_hashStateZ = Self->_hashStateW ;
unsigned v = Self->_hashStateW ;
v = (v ^ (v >> 19)) ^ (t ^ (t >> 8)) ;
Self->_hashStateW = v ;
value = v ;
}
value &= markOopDesc::hash_mask;
if (value == 0) value = 0xBAD ;
assert (value != markOopDesc::no_hash, "invariant") ;
TEVENT (hashCode: GENERATE) ;
return value;
}
简单点:
0 - 使用Park-Miller伪随机数生成器(跟地址无关)
1 - 使用地址与一个随机数做异或(地址是输入因素的一部分)
2 - 总是返回常量1作为所有对象的identity hash code(跟地址无关)
3 - 使用全局的递增序列(跟地址无关)
4 - 使用对象地址的“当前”地址来作为它的identity hash code(就是当前地址)
5 - 使用线程局部状态来实现Marsaglia's 异或-位移随机数生成(跟地址无关)
intptr_t ObjectSynchronizer::FastHashCode (Thread * Self, oop obj) {
if (UseBiasedLocking) {
// NOTE: many places throughout the JVM do not expect a safepoint
// to be taken here, in particular most operations on perm gen
// objects. However, we only ever bias Java instances and all of
// the call sites of identity_hash that might revoke biases have
// been checked to make sure they can handle a safepoint. The
// added check of the bias pattern is to avoid useless calls to
// thread-local storage.
if (obj->mark()->has_bias_pattern()) {
// Box and unbox the raw reference just in case we cause a STW safepoint.
Handle hobj (Self, obj) ;
// Relaxing assertion for bug 6320749.
assert (Universe::verify_in_progress() ||
!SafepointSynchronize::is_at_safepoint(),
"biases should not be seen by VM thread here");
BiasedLocking::revoke_and_rebias(hobj, false, JavaThread::current());
obj = hobj() ;
assert(!obj->mark()->has_bias_pattern(), "biases should be revoked by now");
}
}
// hashCode() is a heap mutator ...
// Relaxing assertion for bug 6320749.
assert (Universe::verify_in_progress() ||
!SafepointSynchronize::is_at_safepoint(), "invariant") ;
assert (Universe::verify_in_progress() ||
Self->is_Java_thread() , "invariant") ;
assert (Universe::verify_in_progress() ||
((JavaThread *)Self)->thread_state() != _thread_blocked, "invariant") ;
ObjectMonitor* monitor = NULL;
markOop temp, test;
intptr_t hash;
markOop mark = ReadStableMark (obj);
// object should remain ineligible for biased locking
assert (!mark->has_bias_pattern(), "invariant") ;
if (mark->is_neutral()) {
hash = mark->hash(); // this is a normal header
if (hash) { // if it has hash, just return it
return hash;
}
hash = get_next_hash(Self, obj); // allocate a new hash code
temp = mark->copy_set_hash(hash); // merge the hash code into header
// use (machine word version) atomic operation to install the hash
test = (markOop) Atomic::cmpxchg_ptr(temp, obj->mark_addr(), mark);
if (test == mark) {
return hash;
}
// If atomic operation failed, we must inflate the header
// into heavy weight monitor. We could add more code here
// for fast path, but it does not worth the complexity.
} else if (mark->has_monitor()) {
monitor = mark->monitor();
temp = monitor->header();
assert (temp->is_neutral(), "invariant") ;
hash = temp->hash();
if (hash) {
return hash;
}
// Skip to the following code to reduce code size
} else if (Self->is_lock_owned((address)mark->locker())) {
temp = mark->displaced_mark_helper(); // this is a lightweight monitor owned
assert (temp->is_neutral(), "invariant") ;
hash = temp->hash(); // by current thread, check if the displaced
if (hash) { // header contains hash code
return hash;
}
// WARNING:
// The displaced header is strictly immutable.
// It can NOT be changed in ANY cases. So we have
// to inflate the header into heavyweight monitor
// even the current thread owns the lock. The reason
// is the BasicLock (stack slot) will be asynchronously
// read by other threads during the inflate() function.
// Any change to stack may not propagate to other threads
// correctly.
}
// Inflate the monitor to set hash code
monitor = ObjectSynchronizer::inflate(Self, obj);
// Load displaced header and check it has hash code
mark = monitor->header();
assert (mark->is_neutral(), "invariant") ;
hash = mark->hash();
if (hash == 0) {
hash = get_next_hash(Self, obj);
temp = mark->copy_set_hash(hash); // merge hash code into header
assert (temp->is_neutral(), "invariant") ;
test = (markOop) Atomic::cmpxchg_ptr(temp, monitor, mark);
if (test != mark) {
// The only update to the header in the monitor (outside GC)
// is install the hash code. If someone add new usage of
// displaced header, please update this code
hash = test->hash();
assert (test->is_neutral(), "invariant") ;
assert (hash != 0, "Trivial unexpected object/monitor header usage.");
}
}
// We finally get the hash
return hash;
}
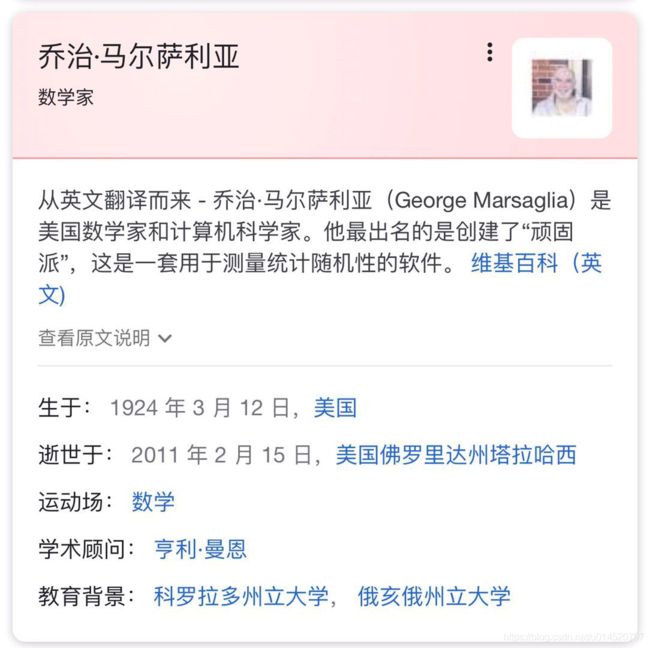
6、Marsaglia's 异或-位移方案是什么?https://www.docin.com/p-1787859407.html
弗罗里达州立大学一位叫做乔治.马尔萨莉亚(George Marsaglia)的数学家发表了一篇使用位移以及亦或运算生成随机数的方法。
7、总结:常规情况下,hashcode与地址无关。
解读c++源码请看这里https://www.zhihu.com/question/29976202
参考资料:https://www.docin.com/p-1787859407.html
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/28270828
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_30566111/article/details/97126305
http://www.voidcn.com/search/nsepkc
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/33915892