Android KeyEvent分发机制
Android KeyEvent分发机制
简介
KeyEvent的分发机制和TouchEvent的分发机制略有不同,KeyEvent向下分发的事件没有被消费,并且KeyCode为KEYCODE_DPAD_LEFT,KEYCODE_DPAD_RIGHT,KEYCODE_DPAD_UP,KEYCODE_DPAD_DOWN,那么会按方向查找下一个控件并获取焦点。
触摸事件分发机制传送门: Android触摸事件分发机制源码分析
分发机制分析
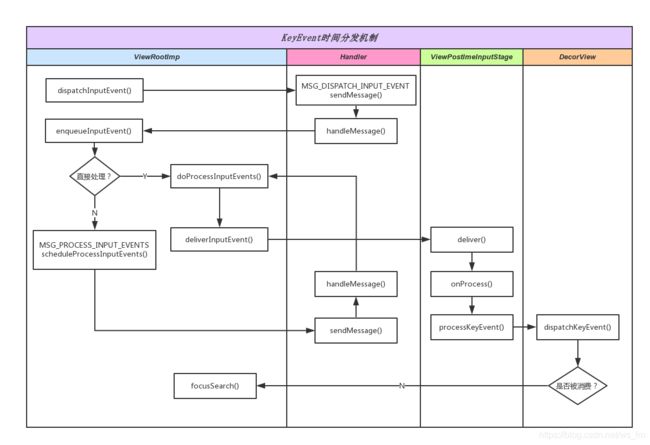
先放上整体流程图,稍后再详细解释:
ViewRootImpl是所有View的顶层容器,所以从ViewRootImpl着手。ViewRootImpl的dispatchInputEvent()方法,向消息队列发出MSG_DISPATCH_INPUT_EVENT消息,Handler处理消息并调用ViewRootImpl的enqueueInputEvent()方法,将QueuedInputEvent插入到未处理KeyEvent队列的尾部。
enqueueInputEvent()方法具体实现:
void enqueueInputEvent(InputEvent event,InputEventReceiver receiver, int flags, boolean processImmediately) {
adjustInputEventForCompatibility(event);
QueuedInputEvent q = obtainQueuedInputEvent(event, receiver, flags);
QueuedInputEvent last = mPendingInputEventTail;
if (last == null) {
mPendingInputEventHead = q;
mPendingInputEventTail = q;
} else {
last.mNext = q;
mPendingInputEventTail = q;
}
mPendingInputEventCount += 1;
Trace.traceCounter(Trace.TRACE_TAG_INPUT, mPendingInputEventQueueLengthCounterName,mPendingInputEventCount);
if (processImmediately) {
doProcessInputEvents();
} else {
scheduleProcessInputEvents();
}
}
keyEvent插入未处理事件队列后,接下来要处理这些事件了。有两种处理方式,直接处理和向Handler发送异步消息处理。这里只分析直接处理的情况。
doProcessInputEvents()方法遍历未处理事件队列逐个处理:
void doProcessInputEvents() {
// Deliver all pending input events in the queue.
while (mPendingInputEventHead != null) {
QueuedInputEvent q = mPendingInputEventHead;
mPendingInputEventHead = q.mNext;
if (mPendingInputEventHead == null) {
mPendingInputEventTail = null;
}
q.mNext = null;
mPendingInputEventCount -= 1;
Trace.traceCounter(Trace.TRACE_TAG_INPUT, mPendingInputEventQueueLengthCounterName,
mPendingInputEventCount);
long eventTime = q.mEvent.getEventTimeNano();
long oldestEventTime = eventTime;
if (q.mEvent instanceof MotionEvent) {
MotionEvent me = (MotionEvent)q.mEvent;
if (me.getHistorySize() > 0) {
oldestEventTime = me.getHistoricalEventTimeNano(0);
}
}
mChoreographer.mFrameInfo.updateInputEventTime(eventTime, oldestEventTime);
deliverInputEvent(q);
}
// We are done processing all input events that we can process right now
// so we can clear the pending flag immediately.
if (mProcessInputEventsScheduled) {
mProcessInputEventsScheduled = false;
mHandler.removeMessages(MSG_PROCESS_INPUT_EVENTS);
}
}
QueuedInputEvent交给deliverInputEvent()方法来处理:
private void deliverInputEvent(QueuedInputEvent q) {
Trace.asyncTraceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW,"deliverInputEvent",
q.mEvent.getSequenceNumber());
if (mInputEventConsistencyVerifier != null) {
mInputEventConsistencyVerifier.onInputEvent(q.mEvent, 0);
}
InputStage stage;
if (q.shouldSendToSynthesizer()) {
stage = mSyntheticInputStage;
} else {
stage = q.shouldSkipIme() ? mFirstPostImeInputStage : mFirstInputStage;
}
if (stage != null) {
stage.deliver(q);
} else {
finishInputEvent(q);
}
}
重头戏来了,这里出现了个InputStage对象stage,它是什么,从哪来?在ViewRootImpl的setView()方法中初始化InputStage对象:
public void setView(View view, WindowManager.LayoutParams attrs, View panelParentView) {
// Set up the input pipeline.
CharSequence counterSuffix = attrs.getTitle();
mSyntheticInputStage = new SyntheticInputStage();
InputStage viewPostImeStage = new ViewPostImeInputStage(mSyntheticInputStage);
InputStage nativePostImeStage = new NativePostImeInputStage(viewPostImeStage,"aq:native-post-ime:" + counterSuffix);
InputStage earlyPostImeStage = new EarlyPostImeInputStage(nativePostImeStage);
InputStage imeStage = new ImeInputStage(earlyPostImeStage,
"aq:ime:" + counterSuffix);
InputStage viewPreImeStage = new ViewPreImeInputStage(imeStage);
InputStage nativePreImeStage = new NativePreImeInputStage(viewPreImeStage,
"aq:native-pre-ime:" + counterSuffix);
mFirstInputStage = nativePreImeStage;
mFirstPostImeInputStage = earlyPostImeStage;
}
InPuStage实际上是个管道,也就是责任链模式,事件在前一个InputStage未处理完会继续向下传递。KeyEvent的处理单元是ViewPostImeInputStage。
InputStage的deliver()方法会调用onProcess()方法,这个是InputStage子类具体处理KeyEvent的方法。看看ViewPostImeInputStage的onProcess()方法实现:
protected int onProcess(QueuedInputEvent q) {
if (q.mEvent instanceof KeyEvent) {
return processKeyEvent(q);
} else {
final int source = q.mEvent.getSource();
if ((source & InputDevice.SOURCE_CLASS_POINTER) != 0) {
return processPointerEvent(q);
} else if ((source & InputDevice.SOURCE_CLASS_TRACKBALL) != 0) {
return processTrackballEvent(q);
} else {
return processGenericMotionEvent(q);
}
}
}
可以看到里面调用了processKeyEvent()方法:
private int processKeyEvent(QueuedInputEvent q) {
final KeyEvent event = (KeyEvent)q.mEvent;
// Deliver the key to the view hierarchy.
if (mView.dispatchKeyEvent(event)) {
return FINISH_HANDLED;
}
if (shouldDropInputEvent(q)) {
return FINISH_NOT_HANDLED;
}
// If the Control modifier is held, try to interpret the key as a shortcut.
if (event.getAction() == KeyEvent.ACTION_DOWN
&& event.isCtrlPressed()
&& event.getRepeatCount() == 0
&& !KeyEvent.isModifierKey(event.getKeyCode())) {
if (mView.dispatchKeyShortcutEvent(event)) {
return FINISH_HANDLED;
}
if (shouldDropInputEvent(q)) {
return FINISH_NOT_HANDLED;
}
}
// Apply the fallback event policy.
if (mFallbackEventHandler.dispatchKeyEvent(event)) {
return FINISH_HANDLED;
}
if (shouldDropInputEvent(q)) {
return FINISH_NOT_HANDLED;
}
// Handle automatic focus changes.
if (event.getAction() == KeyEvent.ACTION_DOWN) {
int direction = 0;
switch (event.getKeyCode()) {
case KeyEvent.KEYCODE_DPAD_LEFT:
if (event.hasNoModifiers()) {
direction = View.FOCUS_LEFT;
}
break;
case KeyEvent.KEYCODE_DPAD_RIGHT:
if (event.hasNoModifiers()) {
direction = View.FOCUS_RIGHT;
}
break;
case KeyEvent.KEYCODE_DPAD_UP:
if (event.hasNoModifiers()) {
direction = View.FOCUS_UP;
}
break;
case KeyEvent.KEYCODE_DPAD_DOWN:
if (event.hasNoModifiers()) {
direction = View.FOCUS_DOWN;
}
break;
case KeyEvent.KEYCODE_TAB:
if (event.hasNoModifiers()) {
direction = View.FOCUS_FORWARD;
} else if (event.hasModifiers(KeyEvent.META_SHIFT_ON)) {
direction = View.FOCUS_BACKWARD;
}
break;
}
if (direction != 0) {
View focused = mView.findFocus();
if (focused != null) {
View v = focused.focusSearch(direction); if (v != null && v != focused) {
// do the math the get the interesting rect
// of previous focused into the coord system of
// newly focused view
focused.getFocusedRect(mTempRect);
if (mView instanceof ViewGroup) {
((ViewGroup) mView).offsetDescendantRectToMyCoords(focused, mTempRect);
((ViewGroup) mView).offsetRectIntoDescendantCoords(v, mTempRect);
}
if (v.requestFocus(direction,mTempRect)) {
playSoundEffect(SoundEffectConstants
.getContantForFocusDirection(direction));
return FINISH_HANDLED;
}
}
// Give the focused view a last chance to handle the dpad key.
if (mView.dispatchUnhandledMove(focused, direction)) {
return FINISH_HANDLED;
}
} else {
// find the best view to give focus to in this non-touch-mode with no-focus
View v = focusSearch(null, direction);
if (v != null && v.requestFocus(direction)) {
return FINISH_HANDLED;
}
}
}
}
return FORWARD;
}
看到调用了DecorView的dispatchKeyEvent()方法开始向View传递KeyEvent事件,如果事件未被消费,并且KeyCode为KEYCODE_DPAD_LEFT,KEYCODE_DPAD_RIGHT,KEYCODE_DPAD_UP,KEYCODE_DPAD_DOWN,那么会按方向查找下一个控件并获取焦点。这部分内容下一节节介绍。
focusSearch流程分析
processKeyEvent()在调用DecorView的dispatchKeyEvent()返回false后,先确定方向,并且根据当前是否有已获取焦点控件用不同的方式进行查找。
focusSearch()方法的大致流程:
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-67AmDGeV-1586764136973)(https://www.github.com/wslaimin/blog/raw/master/pics/focusSearch.png)]
- 当前focused!=null的情况
当前focused!=null时,调用View的focusSearch()方法,寻找下一个获取焦点控件,代码如下:
public View focusSearch(@FocusRealDirection int direction) {
if (mParent != null) {
return mParent.focusSearch(this, direction);
} else {
return null;
}
}
实际上是调用了ViewGroup的focusSearch()方法:
public View focusSearch(View focused, int direction) {
if (isRootNamespace()) {
// root namespace means we should consider ourselves the top of the
// tree for focus searching; otherwise we could be focus searching
// into other tabs. see LocalActivityManager and TabHost for more info
return FocusFinder.getInstance().findNextFocus(this, focused, direction);
} else if (mParent != null) {
return mParent.focusSearch(focused, direction);
}
return null;
}
可以看到这个寻找过程是不断的调用上层容器的focusSearch()方法,直到DecorView才真正调用FocusFinder的findNextFocus()方法寻找下一个获取焦点控件。findNextFocus()方法后面再分析。
- 当focused==null的情况
当前focused==null时,ViewRootImpl调用focusSearch()方法,focusSearch()方法中调用了FocusFinder的findNextFocus()方法。接下来中点介绍findNextFocus()方法。
findNextFocus()方法实现:
public final View findNextFocus(ViewGroup root, View focused, int direction) {
return findNextFocus(root, focused, null, direction);
}
调用了重载方法findNextFocus():
private View findNextFocus(ViewGroup root, View focused, Rect focusedRect, int direction) {
View next = null;
if (focused != null) {
next = findNextUserSpecifiedFocus(root, focused, direction);
}
if (next != null) {
return next;
}
ArrayList<View> focusables = mTempList;
try {
focusables.clear();
root.addFocusables(focusables, direction);
if (!focusables.isEmpty()) {
next = findNextFocus(root, focused, focusedRect, direction, focusables);
}
} finally {
focusables.clear();
}
return next;
}
addFocusables()方法返回root下所有能获取焦点的控件,然后继续调用重载方法findNextFocus():
private View findNextFocus(ViewGroup root, View focused, Rect focusedRect,int direction, ArrayList<View> focusables) {
if (focused != null) {
if (focusedRect == null) {
focusedRect = mFocusedRect;
}
// fill in interesting rect from focused
focused.getFocusedRect(focusedRect);
root.offsetDescendantRectToMyCoords(focused, focusedRect);
} else {
if (focusedRect == null) {
focusedRect = mFocusedRect;
// make up a rect at top left or bottom right of root
switch (direction) {
case View.FOCUS_RIGHT:
case View.FOCUS_DOWN:
setFocusTopLeft(root, focusedRect);
break;
case View.FOCUS_FORWARD:
if (root.isLayoutRtl()) {
setFocusBottomRight(root, focusedRect);
} else {
setFocusTopLeft(root, focusedRect);
}
break;
case View.FOCUS_LEFT:
case View.FOCUS_UP:
setFocusBottomRight(root, focusedRect);
break;
case View.FOCUS_BACKWARD:
if (root.isLayoutRtl()) {
setFocusTopLeft(root, focusedRect);
} else {
setFocusBottomRight(root, focusedRect);
break;
}
}
}
}
switch (direction) {
case View.FOCUS_FORWARD:
case View.FOCUS_BACKWARD:
return findNextFocusInRelativeDirection(focusables, root, focused, focusedRect,direction);
case View.FOCUS_UP:
case View.FOCUS_DOWN:
case View.FOCUS_LEFT:
case View.FOCUS_RIGHT:
return findNextFocusInAbsoluteDirection(focusables, root, focused,focusedRect, direction);
default:
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unknown direction: " + direction);
}
}
由于focusedRect==null,先根据焦点移动方向确定focusedRect,然后调用findNextFocusInAbsoluteDirection()方法:
View findNextFocusInAbsoluteDirection(ArrayList<View> focusables, ViewGroup root, View focused,Rect focusedRect, int direction) {
// initialize the best candidate to something impossible
// (so the first plausible view will become the best choice)
mBestCandidateRect.set(focusedRect);
switch(direction) {
case View.FOCUS_LEFT:
mBestCandidateRect.offset(focusedRect.width() + 1, 0);
break;
case View.FOCUS_RIGHT:
mBestCandidateRect.offset(-(focusedRect.width() + 1), 0);
break;
case View.FOCUS_UP:
mBestCandidateRect.offset(0, focusedRect.height() + 1);
break;
case View.FOCUS_DOWN:
mBestCandidateRect.offset(0, -(focusedRect.height() + 1));
}
View closest = null;
int numFocusables = focusables.size();
for (int i = 0; i < numFocusables; i++) {
View focusable = focusables.get(i);
// only interested in other non-root views
if (focusable == focused || focusable == root) continue;
// get focus bounds of other view in same coordinate system
focusable.getFocusedRect(mOtherRect);
root.offsetDescendantRectToMyCoords(focusable, mOtherRect);
if (isBetterCandidate(direction, focusedRect, mOtherRect, mBestCandidateRect)) {
mBestCandidateRect.set(mOtherRect);
closest = focusable;
}
}
return closest;
}
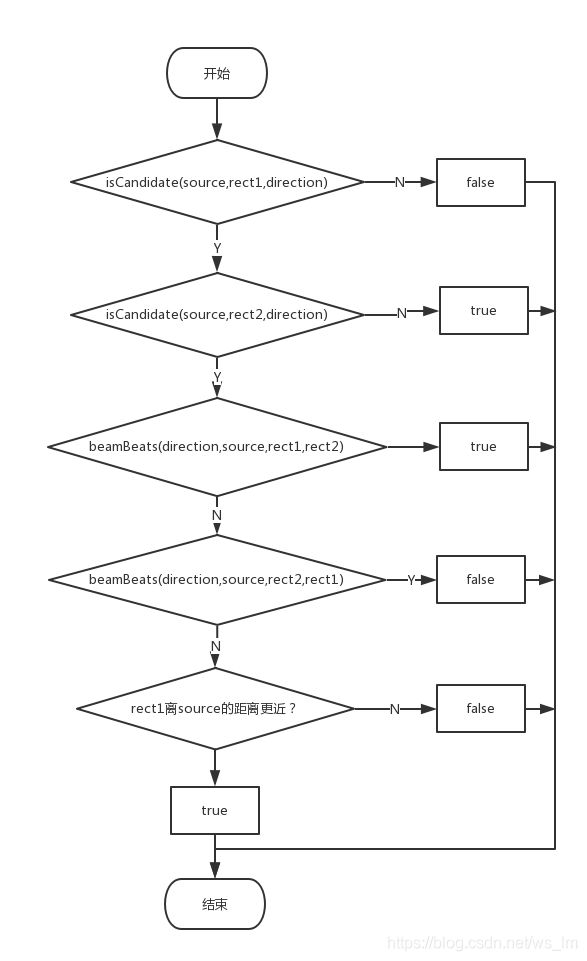
focusable存储所有可获取焦点控件,遍历focusable,root.offsetDescendantRectToMyCoords()方法把控件置于root的坐标系中,然后通过isBetterCandidate()方法选出最优控件。
isCandidate()方法判断是否在source对应的方向上
beamBeats()方法判断rect1是否优于rect2,比较从三个维度展开:
- 是否有重叠
- rect1有重叠,rect2无重叠,再从rect2是否完全在source的对应方向上。比如direction为FOCUS_LEFT,rect2.right<=source.left表示rect2完全在source左边
- 离source在direction方向上的距离