《 Netty权威指南 NIO 中级篇 编解码 》
《Netty NIO 中级篇 编解码》
- 编解码技术简介
- Java序列化的缺点
- 主流的编解码框架
- MessagePak编解码
- Google Protobuf编解码
- Netty的Protobuf的图书订阅服务/客户端实例
- JBoss Marshalling编解码
编解码技术简介
在基于Netty的NIO网络开发中我们重点关注网络传输,当进行远程跨进程服务调用时,需要把传输的java对象编码为字节数组或者ByteBuffer对象,当远程服务读取到ByteBuffer对象或者字节数组时,需要将其解码为发送时的java对象,这就是java对象编解码技术。java序列化仅仅是java编解码技术中的一种,由于序列化存在种种缺陷,通常不会选择java序列化作为远程跨节点调用的编解码框架,因此衍生出多种编解码技术与框架。
Java序列化的缺点
java序列化通过实现Serializable接口来实现,序列化的两个目的:网络传输和对象的持久化,主要的缺点有:
- 无法跨语言,由于java序列化技术是java语言内部的私有协议,对于序列化后的字节数组,其他语言无法反序列化。当我们需要跨进程服务调用,与异构语言类似C++进行交互时,java序列化就难以胜任。
- 序列化后的码流太大,由于java序列化后的码流会偏大,在网络传输时更加占宽带,导致系统吞吐量降低。
- 序列化性能太低
JDK序列化机制与通用二进制编码码流大小比较
用于测试序列化码流大小和序列化性能的对象UserInfo:实现Serializable接口,并生成了一个默认的序列号serialVersionUID = 1L,说明Userinfo对象可以通过JDK默认的序列化机制进行序列化与反序列化。codeC()方法使用基于ByteBuffer的通用二进制编码技术对UserInfo对象进行编码,结果仍然是byte数组。
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
public class UserInfo implements Serializable {
/**
* 默认的序列号
*/
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private String userName;
private int userID;
public UserInfo buildUserName(String userName) {
this.userName = userName;
return this;
}
public UserInfo buildUserID(int userID) {
this.userID = userID;
return this;
}
public final String getUserName() {
return userName;
}
public final void setUserName(String userName) {
this.userName = userName;
}
public final int getUserID() {
return userID;
}
public final void setUserID(int userID) {
this.userID = userID;
}
public byte[] codeC() {
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
byte[] value = this.userName.getBytes();
buffer.putInt(value.length);
buffer.put(value);
buffer.putInt(this.userID);
buffer.flip();
value = null;
byte[] result = new byte[buffer.remaining()];
buffer.get(result);
return result;
}
}
测试码流大小:通用二进制编码技术与传统的jdk序列化流对比,由此可以看出JDK序列化得到的二进制数组是二进制编码技术的5.29倍。
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
public class TestUserInfo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
UserInfo info = new UserInfo();
info.buildUserID(100).buildUserName("Welcome to Netty");
ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream os = new ObjectOutputStream(bos);
os.writeObject(info);
os.flush();
os.close();
byte[] b = bos.toByteArray();
System.out.println("The jdk serializable length is : " + b.length);
bos.close();
System.out.println("-------------------------------------");
System.out.println("The byte array serializable length is : " + info.codeC().length);
}
}
运行结果:

JDK序列化机制与通用二进制编码性能比较
在上诉的Userinfo中新增方法:
public byte[] codeC(ByteBuffer buffer) {
buffer.clear();
byte[] value = this.userName.getBytes();
buffer.putInt(value.length);
buffer.put(value);
buffer.putInt(this.userID);
buffer.flip();
value = null;
byte[] result = new byte[buffer.remaining()];
buffer.get(result);
return result;
}
同时创建一个性能测试版本的UserInfo测试程序:PerformTestUserInfo
public class PerformTestUserInfo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
UserInfo info = new UserInfo();
info.buildUserID(100).buildUserName("Welcome to Netty");
int loop = 1000000;
ByteArrayOutputStream bos = null;
ObjectOutputStream os = null;
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < loop; i++) {
bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
os = new ObjectOutputStream(bos);
os.writeObject(info);
os.flush();
os.close();
byte[] b = bos.toByteArray();
bos.close();
}
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("The jdk serializable cost time is : " + (endTime - startTime) + " ms");
System.out.println("-------------------------------------");
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < loop; i++) {
byte[] b = info.codeC(buffer);
}
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("The byte array serializable cost time is : " + (endTime - startTime) + " ms");
}
}
运行结果:更让人惊讶是java序列化性能也只有二进制的6.17%。
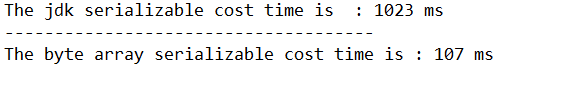
主流的编解码框架
当前业界主流的编解码框架有:1)MessagePack高效的二进制序列化框架;2)Google 的Protobuf;3)Facebook的Thrift;4)JBoss Marshalliing
我们评价一个编解码框架的优势时,往往会考虑以下几个因素:
- 能否支持跨语言,支持的语言是否种类丰富
- 编码后的码流大小
- 编解码的性能
- 使用者手工开发的工作量与难度
并且高性能的通信协议数据存储不使用XML,经管XML 可读性和可扩展性非常好,也非常适合数据结构,但是XML的解析时间开销和XML为了可读性和牺牲空间开销非常大。
Google的Protobuf
Google的Protobuf全称Google Protocol Buffers,数据结构以.proto文件描述特点:
- 文本化的数据结构描述语言,可以实现语言和平台无关,特别适合异构系统间的集成
- 高效的编解码性能
- 扩展性好,方便后序的管理和维护
- 通过标识字段的顺序可以实现协议的前向兼容
Facebooke的Thrift
Thrift在不同语言之间通信,可以作为高性能的通信中间件使用。
- 支持数据对象序列化和多种类型的RPC服务
- 支持三种经典的编解码方式(通用二进制编解码、压缩二进制编解码、优化的可选字段压缩编解码)
- 通过标识字段的顺序可以实现协议的前向兼容
- Thift适用于静态的数据交换,需要先确定它的数据结构,当数据结构发生变化时,必须重新编辑IDL文件,生成代码与编译,这一点与其他IDL工具相比可以视为是Thrift的弱项。
JBoss Marshalling
JBoss Marshallig 是java对象序列化API包,修正了JDK自带的序列化包的很多问题,单同时跟java.io.Serializable接口兼容,相比传统的java序列化机制,优点在于:
- 可插拔的类解析器,通过一个接口即可实现定制
- 可插拔的对象替换技术,不需要通过继承的方式
- 可插拔的预定义类缓存表,可以减小序列化的字节数组长度
- 无需实现java.io.Serializable接口也可实现java序列化,使用简单,通常应用在JBoss内部,使用范围有限
MessagePak编解码
MessagePack是一个高效的二进制序列化框架,像JSON一样支持不同语言间的数据交换,速度更快,序列化之后的码流更小。项目中需要将msgpack-0.6.12.jar、javassist-3.20.0-GA.jar 都添加至构建路径中。
MessagePack特点:其支持的语言有: Java、Python、Ruby、Haskell、C#、OCaml、Lua、Go、C、C++等。
- 编解码高效,性能高
- 序列化后的码流小
- 支持跨语言
Maven引用的方式:
<dependencies>
...
<dependency>
<groupId>org.msgpack</groupId>
<artifactId>msgpack</artifactId>
<version>${msgpack.version}</version>
</dependency>
...
</dependencies>
在我们使用Netty开发基于网络的应用程序的时候,需要实现一些符合自己应用的codec,在Netty中也提供了很多种编解码的实现,在实现自定义编解码器的时候,我们只需要继承相关接口后,重写部分方法就可以实现decode和encode。
MessagePack是一个类似Json的序列化技术,据官方说它比json更小更快。在这个例子中,在客户端中,MsgPackEncode在继承MessageToByteEncoder后重写了encode()方法,把Student对象编码为byte数组;在服务器端MsgPackDecode在继承MessageToMessageDecoder后重写了decode()方法,把byte数组解码成List。
一个编解码的demo可以对MessagePack进行编解码例子:
TimeClient:
public class EchoClient {
private final String host;
private final int port;
private final int sendNum;
private EchoClient(String host, int port, int sendNum){
this.host = host;
this.port = port;
this.sendNum = sendNum;
}
public void run(){
//NioEventLoopGroup是一个线程组,它包含了一组NIO线程
EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
//客户端辅助启动类
Bootstrap b = new Bootstrap();
//设置线程组
b.group(group)
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)//设置Channel
.option(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, true)//设置TCP的参数
.option(ChannelOption.CONNECT_TIMEOUT_MILLIS, 3000)
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {//匿名内部类设置handler
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
//解决拆包、粘包读写问题
//在解码器之前增加LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder,用于处理半包消息,这样接受到的永远是整包消息
//个人觉得和分隔符的意义差不多
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast("frameDecode",
new LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder(65535, 0, 2,0,2));
//解码
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast("msgpack decoder", new MsgpackDecoder());
//在编码器之前增加2个消息的消息长度字段
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast("frameEncode", new LengthFieldPrepender(2));
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast("msgpack encoder", new MsgpackEncoder());
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new EchoClientHandler(sendNum));
}
});
//异步连接客户端,同步阻塞直到连接成功
ChannelFuture f = b.connect(host, port).sync();
//阻塞,等待客户端链路关闭后main函数才退出
f.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
group.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String host = "127.0.0.1";
int port = 30000;
new EchoClient(host, port, 10).run();
}
}
EchoClientHandler:
public class EchoClientHandler extends ChannelHandlerAdapter {
private final int sendNum;
public EchoClientHandler(int sendNum){
this.sendNum = sendNum;
}
/**
* 连接服务端成功后开始发送消息
* @param ctx
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
UserInfo [] userInfos = userInfo();
for (UserInfo userInfo: userInfos) {
ctx.writeAndFlush(userInfo);
}
// ctx.writeAndFlush(userInfos[0]);
}
private UserInfo [] userInfo(){
UserInfo [] userInfos = new UserInfo[sendNum];
for (int i = 0; i < sendNum; i++){
UserInfo userInfo = new UserInfo();
userInfo.setAge(i);
userInfo.setName("ABCDEF------->" + i);
userInfos[i] = userInfo;
}
return userInfos;
}
/**
* 读取客户端的返回消息
*/
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
System.out.println("Client receive the msgpack messag:" + msg);
}
@Override
public void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
ctx.flush();
}
/**
* 发生异常时关闭ctx
*/
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
//super.exceptionCaught(ctx, cause);
ctx.close();
}
}
服务端代码: TimeServer:
public class EchoServer {
public void bind(int port){
//NioEventLoopGroup是一个线程组,它包含了一组NIO线程,
// 这里的两个线程组一个是用于服务端接受客户端的连接,
// 另一个用于SocketChannel的网络读写
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
//netty用于启动NIO服务端的辅助启动类
ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap();
//设置线程组
b.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)//设置channel
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 100)//设置channel的TCP参数
.option(ChannelOption.CONNECT_TIMEOUT_MILLIS, 3000)
.childHandler(new ChildChannelHandler());//绑定IO事件处理类
//绑定监听端口,调用同步阻塞方法等待绑定完成
ChannelFuture f = b.bind(port).sync();
//阻塞,等待服务端链路关闭后main函数才退出
f.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
//优雅退出,释放跟shutdownGracefully相关联的所有资源
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
private class ChildChannelHandler extends ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>{
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel serverSocket) throws Exception {
serverSocket.pipeline().addLast("frameDecode",
new LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder(65535, 0, 2,0,2));
serverSocket.pipeline().addLast("msgpack decoder", new MsgpackDecoder());
serverSocket.pipeline().addLast("frameEncode", new LengthFieldPrepender(2));
serverSocket.pipeline().addLast("msgpack encoder", new MsgpackEncoder());
serverSocket.pipeline().addLast(new EchoServerHandler());
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int port = 30000;
new EchoServer().bind(port);
}
}
EchoServerHandler:
public class EchoServerHandler extends ChannelHandlerAdapter {
/**
* 当异常发生时
*/
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
//super.exceptionCaught(ctx, cause);
ctx.close();
}
/**
* 读取缓冲区里面的数据,处理并返回
*/
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
List<UserInfo> userInfo = (List<UserInfo>) msg;
System.out.println("server receive message from client =" + userInfo);
ctx.writeAndFlush(userInfo);
}
}
其中服务端和客户端都有的Student类、MsgPackEncode、MsgPackDecode为: Student:
MsgpackDecoder:注意:最后服务端decode后的对象是一个List< Object >,你直接用对象去接收,会报异常org.msgpack.type.ArrayValueImpl cannot be cast to com.nettyserver.Student
public class MsgpackDecoder extends MessageToMessageDecoder<ByteBuf> {
@Override
protected void decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf msg, List<Object> out) throws Exception {
//首先获取需要解码的byte数组
final byte [] array;
final int length = msg.readableBytes();
array = new byte[length];
msg.getBytes(msg.readerIndex(), array, 0, length);
//mp的read方法将其反序列化为object对象
MessagePack mp = new MessagePack();
mp.register(UserInfo.class);
out.add(mp.read(array));
}
}
MsgpackEncoder:
public class MsgpackEncoder extends MessageToByteEncoder<Object> {
@Override
protected void encode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg, ByteBuf out) throws Exception {
MessagePack mp = new MessagePack();
byte [] raw = mp.write(msg);
out.writeBytes(raw);
}
}
UserInfo:要传输的javabean一定要加上注解@message,否则会报错
@Message
public class UserInfo{
private String name;
private int age;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "UserInfo{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
Google Protobuf编解码
protobuf 是一个灵活、高效、结构化的数据序列化框架。相比XML等传统序列化工具,它更小、更快、更简单,Protobuf支持数据结构化一次编译可以到处使用,甚至是跨语言使用,通过代码生成工具可以自动生成不同语言版本的源代码,甚至可以在不同的版本数据结构进程中进行数据传递,实现数据结构的前向兼容。
下载安装
下载Protobuf的Windows版本,https://github.com/protocolbuffers/protobuf/releases/tag/v2.5.0 中下载protoc-2.5.0-win32.zip,解压后的目录如下:将bin路径配置至环境变量中。

在命令行窗口中输入protoc有:

ProtoBuf的使用
| 接下来就可以对写的文件进行编译生成.java文件。在这里千万要注意的是, 一:proto文件编写语法与java不同,比如,java字符串类型为String,赋值是加双引号的,而proto不认识,它的声明词是小写的string,其赋值是不需要加双引号的;二:需要注意proto3也不同于proto2,采用proto3必须要写出其版本号syntax = “proto3”; |
我们以图书订购流程为例,定义SubscribeReq.proto和SubscribeResp.proto,数据定义格式如下:
SubscribeResp.proto 其中message相当于是class,subReqId、respCode、desc后面的赋值相当于是赋键值,不可相同。
option java_package="Chapter8";
option java_outer_classname="SubscribeRespProto";
message SubscribeResp{
required int32 subReqId = 1;
required int32 respCode = 2;
required string desc = 3;
}
SubscribeReq.proto
option java_package="Chapter8";
option java_outer_classname="SubscribeReqProto";
message SubscribeReq{
required int32 subReqId = 1;
required string userName = 2;
required string productName = 3;
repeated string address = 4;
}
通过protoc.exe命令生成java代码,命令行如图所示:
运行后:在当前目录下新增两个java文件

将生成的的POJO代码SubscribeReqProto.java和SubscribeRespProto.java复制到对应的java项目中:代码还缺少protobuf-java-2.5.jar包,需要下载添加至工程中,注意如果前面的编译版本跟导入的jar包不相同,会出错。

到此,我们已经完成对google protobuf 开发环境搭建工作,我们接下来通过一个简单的Demo 来了解Protobuf 类库使用:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* Created by vixuan-008 on 2015/6/24.
*/
public class TestSubscribeReq {
public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception{
SubscribeReqProto.SubscribeReq req=createSubscribeReq();
System.out.println("Before encode:"+req.toString());
SubscribeReqProto.SubscribeReq result=decode(encode(req));
System.out.println("decode cotent is:"+result.toString());
}
private static byte[] encode(SubscribeReqProto.SubscribeReq req){
return req.toByteArray();
}
private static SubscribeReqProto.SubscribeReq decode(byte[] body) throws Exception{
return SubscribeReqProto.SubscribeReq.parseFrom(body);
}
private static SubscribeReqProto.SubscribeReq createSubscribeReq(){
SubscribeReqProto.SubscribeReq.Builder builder= SubscribeReqProto.SubscribeReq.newBuilder();
builder.setSubReqId(1);
builder.setUserName("MrRight");
builder.setProductName("Netty Book");
List<String> address=new ArrayList<String>();
address.add("杭州");
address.add("浙江");
address.add("大学");
builder.addAllAddress(address);
return builder.build();
}
}
运行结果:

代码分析:
首先我们看如何创建SubscribeReqProto.SubscribeReq的实例,通过SubscribeReqProto.SubscribeReq的静态方法newBuilder创建SubscribeReqProto.SubscribeReq的Builder实例。
SubscribeReqProto.SubscribeReq.Builder builder= SubscribeReqProto.SubscribeReq.newBuilder();
通过Builder构造器对SubscribeReq的属性进行相关设置,对于集合类型,通过addAllXXX()方法可以将集合对象添加到对象属性当中。
builder.setSubReqId(1);
builder.setUserName("MrRight");
builder.setProductName("Netty Book");
List address=new ArrayList();
address.add("杭州");
address.add("浙江");
address.add("大学");
builder.addAllAddress(address);
编码通过调用SubscribeReqProto.SubscribeReq实例的toByteArray方法,即可将SubscribeReq对象编码为byte数组,使用非常方便。解码通过调用SubscribeReqProto.SubscribeReq的静态方法parseFrom将二进制数组解码为原始数据对象。
private static byte[] encode(SubscribeReqProto.SubscribeReq req){
return req.toByteArray();
}
private static SubscribeReqProto.SubscribeReq decode(byte[] body) throws Exception{
return SubscribeReqProto.SubscribeReq.parseFrom(body);
}
Netty的Protobuf的图书订阅服务/客户端实例
SubRespProServer.java源代码(Handler 存在问题可能需要修改):
其中:向ChannelPipeline添加ProtobufVarint32FrameDecoder,主要是用于半包处理,随后继续添加ProtobufDecoder解码器,参数是com.google.protobuf.MessageLite,实际上就是告诉ProtobufDecoder需要解码的目标类是什么。
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new ProtobufVarint32FrameDecoder());
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new ProtobufDecoder(SubscribeReqProto.SubscribeReq.getDefaultInstance()));
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new ProtobufVarint32LengthFieldPrepender());
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new ProtobufEncoder());
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new SubRespProHandler());
}
import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelOption;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.codec.protobuf.ProtobufDecoder;
import io.netty.handler.codec.protobuf.ProtobufEncoder;
import io.netty.handler.codec.protobuf.ProtobufVarint32FrameDecoder;
import io.netty.handler.codec.protobuf.ProtobufVarint32LengthFieldPrepender;
import io.netty.handler.logging.LogLevel;
import io.netty.handler.logging.LoggingHandler;
public class SubRespProServer {
public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception{
int port=15444;
new SubRespProServer().bind(port);
}
public void bind(int port)throws Exception{
//配置服务端的NIO线程池
EventLoopGroup bossGroup=new NioEventLoopGroup();
EventLoopGroup workGroup=new NioEventLoopGroup();
try{
ServerBootstrap b=new ServerBootstrap();
b.group(bossGroup, workGroup);
b.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class);
b.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 100);
b.handler(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.INFO));
b.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new ProtobufVarint32FrameDecoder());
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new ProtobufDecoder(SubscribeReqProto.SubscribeReq.getDefaultInstance()));
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new ProtobufVarint32LengthFieldPrepender());
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new ProtobufEncoder());
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new SubRespProHandler());
}
});
//绑定端口,等待同步成功
ChannelFuture f=b.bind(port).sync();
//等待服务端关闭监听端口
f.channel().closeFuture().sync();
}finally {
//释放线程池资源
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
SubRespProHandler :由于ProtobufDecoder已经对消息进行了自动解码,因此接收到的订阅请求消息可以直接使用,对用户名校验,校验通过后构造应答消息返回给客户端,由于使用了ProtobufEncoder,所以不需要对SubscribeRespProto.SubscribeResp进行手工编码。
import Chapter8.SubscribeReqProto;
import Chapter8.SubscribeRespProto;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerAdapter;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
public class SubRespProHandler extends ChannelHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
ctx.close();
}
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
super.channelActive(ctx);
}
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
SubscribeReqProto.SubscribeReq req=(SubscribeReqProto.SubscribeReq)msg;
System.out.println("server receiver client message is:"+req.toString());
ctx.writeAndFlush(resp(req.getSubReqId()));
}
private SubscribeRespProto.SubscribeResp resp(int subReqId)throws Exception{
SubscribeRespProto.SubscribeResp.Builder resp= SubscribeRespProto.SubscribeResp.newBuilder();
resp.setSubReqId(subReqId);
resp.setRespCode(0);
resp.setDesc("Netty Book order succeed 3 day later,sent to the designated adderss");
return resp.build();
}
@Override
public void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
super.channelReadComplete(ctx);
}
}
开发支持Protobuf 的Netty 客户端:
import Chapter8.SubscribeRespProto;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelOption;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.codec.protobuf.ProtobufDecoder;
import io.netty.handler.codec.protobuf.ProtobufEncoder;
import io.netty.handler.codec.protobuf.ProtobufVarint32FrameDecoder;
import io.netty.handler.codec.protobuf.ProtobufVarint32LengthFieldPrepender;
import io.netty.handler.codec.serialization.ClassResolvers;
import io.netty.handler.codec.serialization.ObjectDecoder;
import io.netty.handler.codec.serialization.ObjectEncoder;
/**
* Created by vixuan-008 on 2015/6/24.
*/
public class SubReqProClient {
public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception{
int port=15444;
new SubReqProClient().bind(port, "127.0.0.1");
}
public void bind(int port,String host)throws Exception{
//配置客户端NIO线程池
EventLoopGroup workGroup=new NioEventLoopGroup();
try{
io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap b=new io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap();
b.group(workGroup);
b.channel(NioSocketChannel.class);
b.option(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY,true);
b.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new ProtobufVarint32FrameDecoder());
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new ProtobufDecoder(SubscribeRespProto.SubscribeResp.getDefaultInstance()));
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new ProtobufVarint32LengthFieldPrepender());
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new ProtobufEncoder());
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new SubReqProHandler());
}
});
//发起异步连接操作
ChannelFuture f=b.connect(host,port).sync();
//等待客户端链路关闭
f.channel().closeFuture().sync();
}finally {
//释放NIO 线程组
workGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
SubReqProHandler :
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerAdapter;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import Chapter8.SubscribeReqProto;
public class SubReqProHandler extends ChannelHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
ctx.close();
}
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
ctx.write(subReq(i));
}
ctx.flush();
}
private SubscribeReqProto.SubscribeReq subReq(int i){
SubscribeReqProto.SubscribeReq.Builder req=SubscribeReqProto.SubscribeReq.newBuilder();
req.setProductName("Netty Book");
req.setUserName("zhouzhigang");
req.setSubReqId(i);
List<String> address=new ArrayList<String>();
address.add("china");
address.add("usa");
address.add("france");
req.addAllAddress(address);
return req.build();
}
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
System.out.println("Receiver server message is:"+msg);
}
@Override
public void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
ctx.flush();
}
}
运行结果:


Protobuf 使用注意事项:
ProtobufDecoder仅仅负责解码,它不支持读半包。因此,在ProtobufDecode前面,一定要有能够处理读半包的解码器,有三种方式可以选择:
- 使用Netty提供的ProtobufVarint32FrameDecoder,它可以处理半包消息;
- 集成Netty提供的通用半包解码器LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder;
- 继承ByteMessageDecoder类,自己处理半包消息。
如果你只使用ProtobufDecoder解码器而忽视对半包消息处理,程序是不能正常运行的。
JBoss Marshalling编解码
JbossMarshalling是一个java对象序列化包,对JDK默认的序列化框架进行了优化,但又保持跟java.io.Serializable接口的兼容,同时增加了一些可调的参数和附加的特性,这些参数和特性可通过工厂类进行配置。
使用Marshalling传输信息,需要有以下两个包,可以在官网下载jboss-marshalling-1.3.0.CR9.jar、jboss-marshalling-serial-1.3.0.CR9.jar,并添加至构建路径中。
编写要作为传输的Javabean,Student类一定要继承Serializable接口,才能实现序列化:
import java.io.Serializable;
public class Student implements Serializable{
String name;
String classs;
int age;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student [name=" + name + ", classs=" + classs + ", age=" + age + "]";
}
public Student(String name, String classs, int age) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.classs = classs;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getClasss() {
return classs;
}
public void setClasss(String classs) {
this.classs = classs;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
编写客户端:通过MarshallingCodeFactory获得MarshallingDecoder和MarshallingEncoder,并将这两个编解码器添加到channelpipeline中。
import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelOption;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel;
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
new Client().connect("127.0.0.1", 8888);
}
public void connect(String host, int port) throws Exception {
EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
Bootstrap b = new Bootstrap();
b.group(group).channel(NioSocketChannel.class);
b.option(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, true);
b.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(MarshallingCodeCFactory.buildMarshallingDecoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast(MarshallingCodeCFactory.buildMarshallingEncoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ClientChannelHandler());
}
});
ChannelFuture f = b.connect(host, port);
f.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
group.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
MarshallingCodeFactory的代码如下:MarshallingCodeCFactory 工厂类创建了MarshallingDecoder 解码器,编码器。
import org.jboss.marshalling.MarshallerFactory;
import org.jboss.marshalling.Marshalling;
import org.jboss.marshalling.MarshallingConfiguration;
import io.netty.handler.codec.marshalling.DefaultMarshallerProvider;
import io.netty.handler.codec.marshalling.DefaultUnmarshallerProvider;
import io.netty.handler.codec.marshalling.MarshallerProvider;
import io.netty.handler.codec.marshalling.MarshallingDecoder;
import io.netty.handler.codec.marshalling.MarshallingEncoder;
import io.netty.handler.codec.marshalling.UnmarshallerProvider;
public class MarshallingCodeCFactory {
public static MarshallingDecoder buildMarshallingDecoder() {
final MarshallerFactory factory = Marshalling.getProvidedMarshallerFactory("serial");
final MarshallingConfiguration configuration = new MarshallingConfiguration();
configuration.setVersion(5);
UnmarshallerProvider provider = new DefaultUnmarshallerProvider(factory, configuration);
MarshallingDecoder decoder = new MarshallingDecoder(provider, 1024);
return decoder;
}
public static MarshallingEncoder buildMarshallingEncoder() {
final MarshallerFactory factory = Marshalling.getProvidedMarshallerFactory("serial");
final MarshallingConfiguration configuration = new MarshallingConfiguration();
configuration.setVersion(5);
MarshallerProvider provider = new DefaultMarshallerProvider(factory, configuration);
MarshallingEncoder encoder = new MarshallingEncoder(provider);
return encoder;
}
}
ClientChannelHandler的代码如下:客户端与服务端连通后,客户端直接将Student对象写入channelpipeline中
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerAdapter;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
public class ClientChannelHandler extends ChannelHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
Student s = new Student("MrRight", "浙江", 12);
ctx.writeAndFlush(s);
}
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
}
}
服务端代码:MarshallingCodeCFactory工厂类创建了MarshallingDecoder解码器,并将其加入到ChannelPipeline。
import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelOption;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
public class Server {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
new Server().bind(8888);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void bind(final int port) throws Exception {
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
EventLoopGroup workGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap();
b.option(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, true);
b.group(bossGroup, workGroup).channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(MarshallingCodeCFactory.buildMarshallingDecoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast(MarshallingCodeCFactory.buildMarshallingEncoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ServerChannelHandler());
}
});
ChannelFuture f = b.bind(port).sync();
System.out.println("服务端已启动");
f.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
ServerChannelHandler的代码如下:
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerAdapter;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
public class ServerChannelHandler extends ChannelHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
System.out.println("active");
}
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
System.out.println(msg);
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
cause.printStackTrace();
}
}
运行结果:

通过使用Netty的Marshalling编解码器,我们可以轻松的开发使用JBoss Marshalling序列化的客户端和服务器程度,方便对接JBoss的内部模块,同时有利于对已有使用Jboss Marshalling框架做通信协议的模块桥接与重用。

