SpringBoot的RabbitMQ消息队列: 六、第五模式"Topics"
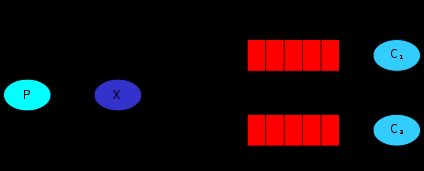
Topics模式,官方的解释是Receiving messages based on a pattern (topics),它的结构是
消费者各自监控自己的队列;交换机通过一种模式策略确定生产者的消息放入那个队列。
1、建立工程, 通过http://start.spring.io,建立Topic工程
2、下载、解压,导入eclipse
3、修改pom.xml,以便于热部署
4、增加日志文件logback.xml
5、修改application.properties
#服务器配置
spring.application.name=rabbitmq-topic
server.port=9080
#rabbitmq连接参数
spring.rabbitmq.host=localhost
spring.rabbitmq.port=5672
spring.rabbitmq.username=test
spring.rabbitmq.password=123456 package com.example;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Binding;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.BindingBuilder;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.TopicExchange;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class TopicRabbitConfig {
final static String message = "topic.message";
final static String messages = "topic.messages";
@Bean
public Queue queueMessage() {
return new Queue(TopicRabbitConfig.message);
}
@Bean
public Queue queueMessages() {
return new Queue(TopicRabbitConfig.messages);
}
@Bean
TopicExchange exchange() {
return new TopicExchange("exchange");
}
@Bean
Binding bindingExchangeMessage(Queue queueMessage, TopicExchange exchange) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(queueMessage).to(exchange).with("topic.message");
}
@Bean
Binding bindingExchangeMessages(Queue queueMessages, TopicExchange exchange) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(queueMessages).to(exchange).with("topic.#");
}
}package com.example;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.AmqpTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class TopicSender {
protected static Logger logger=LoggerFactory.getLogger(TopicSender.class);
@Autowired
private AmqpTemplate rabbitTemplate;
public void send1() {
String context = "hi, i am message 1";
logger.debug("Sender : " + context);
this.rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("exchange", "topic.message", context);
}
public void send2() {
String context = "hi, i am messages 2";
logger.debug("Sender : " + context);
this.rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("exchange", "topic.messages", context);
}
}package com.example;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitHandler;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@RabbitListener(queues = "topic.message")
public class TopicReceiver {
protected static Logger logger=LoggerFactory.getLogger(TopicReceiver.class);
@RabbitHandler
public void process(String message) {
logger.debug("Topic Receiver1 : " + message);
}
}package com.example;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitHandler;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@RabbitListener(queues = "topic.messages")
public class TopicReceiver2 {
protected static Logger logger=LoggerFactory.getLogger(TopicReceiver2.class);
@RabbitHandler
public void process(String message) {
logger.debug("Topic Receiver2 : " + message);
}
}package com.example;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class TopicController {
@Autowired
private TopicSender topicSender;
@RequestMapping("/send1")
public String send1() {
topicSender.send1();
return "send1 ok";
}
@RequestMapping("/send2")
public String send2() {
topicSender.send2();
return "send2 ok";
}
}12、在浏览器中分别输入http://localhost:9080/send1 ,http://localhost:9080/send2,查看控制台输出
http://localhost:9080/send1,控制台的输出,两个接收器都收到消息
http://localhost:9080/send2,控制台的输出,第二个接收器收到消息
13、小结
A、在配置文件中,定义了一个TopicExchange,然后对两个队列,分别配置了绑定规则。(变更绑定规则测试时,先停止命令行的spring-boot,再删除rabbitmq management中的队列)。
B、发送器,发送send1会匹配到topic.#和topic.message 两个Receiver都可以收到消息,发送send2只有topic.#可以匹配所有只有Receiver2监听到消息。
发送器在发送消息时,使用的方法是需要传入一个特定的交换机的。
C、接收器,依然各自监控自己的队列;