OpenCV--直线拟合fitLine及求两直线对称轴
文章目录
- 直线拟合fitLine
- 求两直线对称轴
- 倾斜校正
- 附1 实验代码
直线拟合fitLine
void cv::fitLine(
cv::InputArray points, // 二维点的数组或vector
cv::OutputArray line, // 输出直线,Vec4f (2d)或Vec6f (3d)的vector
int distType, // 距离类型
double param, // 距离参数
double reps, // 径向的精度参数 表示直线到原点距离的精度,建议取 0.01。设为0,则自动选用最优值
double aeps // 角度精度参数 表示直线角度的精度,建议取 0.01
);
◆输出line:为一个四元素的容器,如Vec4f - (vx, vy, x0, y0)。(vx, vy) 是直线的方向向量,(x0, y0) 是直线上一点。
画出直线用cv::line(image, point1, point2, cv::Scalar(0, 255, 0), 2, 8, 0);需要输入直线上的两个点,
double cos_theta = line[0];
double sin_theta = line[1];
double x0 = line[2], y0 = line[3];
double k = sin_theta / cos_theta;
double b = y0 - k * x0;
//求出直线上另一点
double x = 0;
double y = k * x + b;
cv::line(image, Point(x0,y0), Point(x,y), cv::Scalar(255), 1);
◆参数param含义如下,为0时自动选择最优值
Numerical parameter ( C ) for some types of distances. If it is 0, an optimal value is chosen.
◆距离类型distType一共有六种,如下图,其中CV_DIST_L2就是最小二乘法
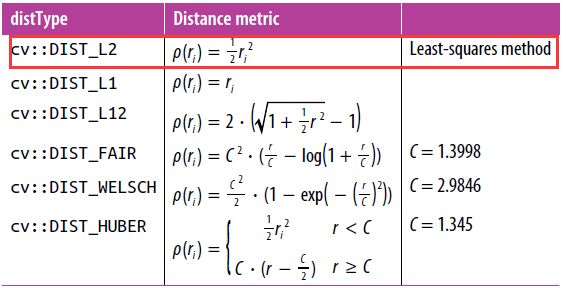
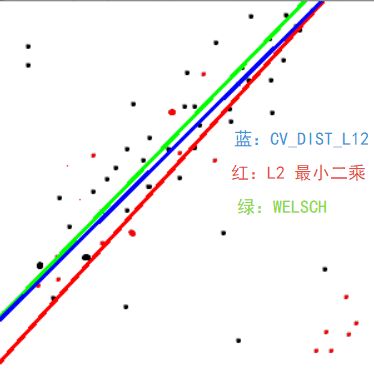
最小二乘法抗干扰能力不如其它5种方法,实验代码见附1
|
|
求两直线对称轴
由直线拟合得到两条Vec4f类型直线,求其对称轴
(1)求两直线交点
/*函数功能:求两条直线交点*/
/*输入:两条Vec4f类型直线
* Vec4f - (vx, vy, x0, y0)
* (vx, vy) 是直线的方向向量,(x0, y0) 是直线上一点*/
/*返回:Point2f类型的点*/
Point2f getCrossPoint(Vec4f LineA, Vec4f LineB)
{
double ka, kb;
ka = LineA[1]/LineA[0]; //求出LineA斜率
kb = LineB[1]/LineB[0];; //求出LineB斜率
Point2f crossPoint;
crossPoint.x = (ka*LineA[2] - LineA[3] - kb*LineB[2] + LineB[3]) / (ka - kb);
crossPoint.y = (ka*kb*(LineA[2] - LineB[2]) + ka*LineB[3] - kb*LineA[3]) / (ka - kb);
return crossPoint;
}
(2)对称轴斜率k2=(k0+k1)/2
(3)得到对称轴点斜式方程,令x=0代入,求得直线上另一点
double k_line2 =(k_line0+k_line1)/2;
Point p2_1(0, k_line2*(0 - crossPoint.x) + crossPoint.y); //x=0,求出直线上另一点
line(drawing, p2_1, crossPoint, Scalar(0, 0, 255), 3); //显示拟合出的直线
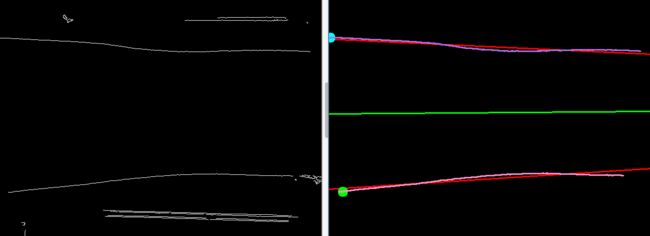
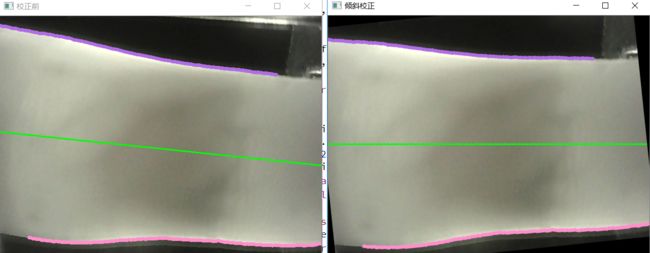
倾斜校正
Point2f center=Point2f(src.rows/2,src.cols/2);
Mat martix = getRotationMatrix2D(center, k_line2/CV_PI*180, 1);//得到仿射矩阵 k_line2/CV_PI*180 弧度转角度
warpAffine(src, dst, martix, drawing.size());
附1 实验代码
#include "opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp"
#include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp"
#include