系统服务管理者:ServiceManager进程
概述
framework/native/cmds/servicemanager/
- service_manager.c
- binder.c
kernel/drivers/ (不同Linux分支路径略有不同)
- staging/android/binder.c
- android/binder.c
service_manager进程是由是由init进程,通过解析init.rc文件来启动的进程。
service_manager是Binder IPC通信过程中的守护进程,本身也是一个Binder服务,但并没有采用libbinder中的多线程模型来与Binder驱动通信,而是自行编写了binder.c直接和Binder驱动来通信,并且只有一个循环binder_loop来进行读取和处理事务,这样的好处是简单而高效。
service_manager本身工作相对简单,其功能:查询和注册服务。 对于Binder IPC通信过程中,其实更多的情形是BpBinder和BBinder之间的通信,比如ActivityManagerProxy和ActivityManagerService之间的通信等。
系统服务的启动与注册
######1. 如下图所示,该图概要描述了系统启动时的整个过程:
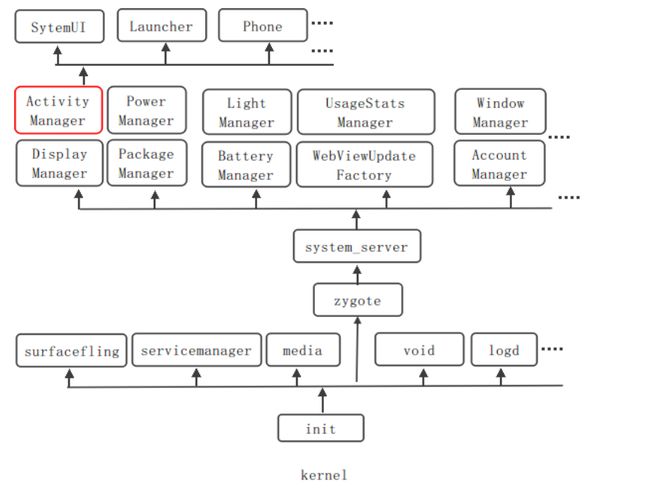
1)系统启动时,会先启动kernel模块
2) kenel模块中会启动init进程,而init进程会解析init.rc文件并启动一系列native服务。
3) Zygote进程预加载和初始化一些核心类库,便于之后的应用进程的代码共享。
4) Zygote启动(fork)系统服务进程system_server
5) System_Server进程中会发布一系列的系统服务,而AMS就是其中之一,并在之后的生命周期中运行在system_server的进程中。
6) AMS启动(fork)出一系列的应用进程。
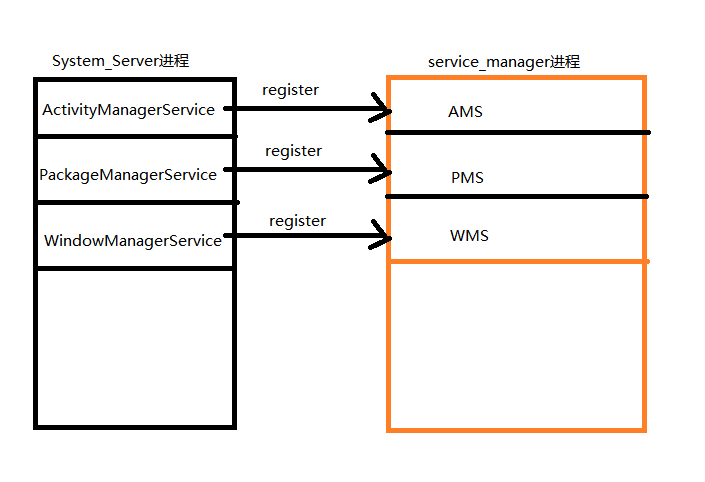
######2. System_Server进程中会启动的一系列的系统服务注册到service_manager进程中
system_server进程启动的一系列系统服务,如:AMS,PMS,WMS等,这些由system_server进程启动的服务都以线程的形式,运行在system_server进程中。
在服务被启动之后,就会通过ServiceManager#addService(String name, IBinder service)方法,注册到service_manager进程当中。
如AMS(ActivityManagerService)服务的启动和注册如下:
在SystemServer#startBootstrapServices()方法中:
private void startBootstrapServices() {
..........
// Activity manager runs the show.
traceBeginAndSlog("StartActivityManager");
mActivityManagerService = mSystemServiceManager.startService(
ActivityManagerService.Lifecycle.class).getService();
mActivityManagerService.setSystemServiceManager(mSystemServiceManager);
mActivityManagerService.setInstaller(installer);
traceEnd();
......................
// Set up the Application instance for the system process and get started.
traceBeginAndSlog("SetSystemProcess");
mActivityManagerService.setSystemProcess();
traceEnd();
.....................................
}
// ActivityManagerService的setSystemProcess方法
public void setSystemProcess() {
try {
// 这里把启动的AMS服务注册到了service_manager进程当中,
// 这里的IPC操作就是system_server进程与service_manager进程的通信
ServiceManager.addService(Context.ACTIVITY_SERVICE, this, true);
ServiceManager.addService(ProcessStats.SERVICE_NAME, mProcessStats);
ServiceManager.addService("meminfo", new MemBinder(this));
ServiceManager.addService("gfxinfo", new GraphicsBinder(this));
ServiceManager.addService("dbinfo", new DbBinder(this));
if (MONITOR_CPU_USAGE) {
ServiceManager.addService("cpuinfo", new CpuBinder(this));
}
ServiceManager.addService("permission", new PermissionController(this));
ServiceManager.addService("processinfo", new ProcessInfoService(this));
ApplicationInfo info = mContext.getPackageManager().getApplicationInfo(
"android", STOCK_PM_FLAGS | MATCH_SYSTEM_ONLY);
mSystemThread.installSystemApplicationInfo(info, getClass().getClassLoader());
synchronized (this) {
ProcessRecord app = newProcessRecordLocked(info, info.processName, false, 0);
app.persistent = true;
app.pid = MY_PID;
app.maxAdj = ProcessList.SYSTEM_ADJ;
app.makeActive(mSystemThread.getApplicationThread(), mProcessStats);
synchronized (mPidsSelfLocked) {
mPidsSelfLocked.put(app.pid, app);
}
updateLruProcessLocked(app, false, null);
updateOomAdjLocked();
}
} catch (PackageManager.NameNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to find android system package", e);
}
}
其它的系统服务也都是这样由system_server进程启动,然后通过ServiceManager#addService注册到service_manager进程的,这里就不一一分析了。
ServiceManager的理解:
ServiceManager.java是service_manager进程在java层的表现,提供查询和注册服务的功能。
该类是隐藏起来的,只能系统调用。为了更加方便的调用各个系统服务,Android又提供了各个服务的封装类,如ActivityManager,InputMethodManager,WindowManager等。
这些类实现了服务类的部分方法,但内部的具体实现还是通过对应的服务类对象来完成的,服务类的对象通过ServiceManager#getService
方法获取。
应用App获取系统服务
在App启动加载ContextImpl类的时候,各种服务就会在静态代码块中被注册到一个Map集合当中,当应用需要用到相关服务的时候,通过Context#getSystemService方法就可以得到相关服务的对象。
- 静态代码块注册服务到Map集合中
ContextImpl#getSystemService方法中我可以知道,服务都保存在SystemServiceRegistry类中:
final class SystemServiceRegistry {
// Service registry information.
// This information is never changed once static initialization has completed.
private static final HashMap<Class<?>, String> SYSTEM_SERVICE_NAMES =
new HashMap<Class<?>, String>();
// 服务生产者集合
private static final HashMap<String, ServiceFetcher<?>> SYSTEM_SERVICE_FETCHERS =
new HashMap<String, ServiceFetcher<?>>();
// 静态代码块,注册服务到Map集合当中
static {
...........................
registerService(Context.ACTIVITY_SERVICE, ActivityManager.class,
new CachedServiceFetcher<ActivityManager>() {
@Override
public ActivityManager createService(ContextImpl ctx) {
return new ActivityManager(ctx.getOuterContext(), ctx.mMainThread.getHandler());
}});
registerService(Context.ALARM_SERVICE, AlarmManager.class,
new CachedServiceFetcher<AlarmManager>() {
@Override
public AlarmManager createService(ContextImpl ctx) throws ServiceNotFoundException {
IBinder b = ServiceManager.getServiceOrThrow(Context.ALARM_SERVICE);
IAlarmManager service = IAlarmManager.Stub.asInterface(b);
return new AlarmManager(service, ctx);
}});
..........................
}
/**
* Statically registers a system service with the context.
* This method must be called during static initialization only.
*/
private static <T> void registerService(String serviceName, Class<T> serviceClass,
ServiceFetcher<T> serviceFetcher) {
SYSTEM_SERVICE_NAMES.put(serviceClass, serviceName);
SYSTEM_SERVICE_FETCHERS.put(serviceName, serviceFetcher);
}
}
- Context获取系统服务:
// ContextImpl的getSystemService方法
@Override
public Object getSystemService(String name) {
return SystemServiceRegistry.getSystemService(this, name);
}
/**SystemServiceRegistry 类的getSystemService方法,根据服务名称,在Map集合当中找到该服务
* 的提供者,并获取服务对象。
* Gets a system service from a given context.
*/
public static Object getSystemService(ContextImpl ctx, String name) {
ServiceFetcher<?> fetcher = SYSTEM_SERVICE_FETCHERS.get(name);
return fetcher != null ? fetcher.getService(ctx) : null;
}
这样我们就获取到了想要的系统服务了,如:输入法服务。
ServiceManager源码分析
public final class ServiceManager {
private static final String TAG = "ServiceManager";
// service_manager进程访问的Binder对象
private static IServiceManager sServiceManager;
// 服务对象缓存集合,访问过的对象缓存起来,避免重复去service_manager进程获取
private static HashMap<String, IBinder> sCache = new HashMap<String, IBinder>();
private static IServiceManager getIServiceManager() {
if (sServiceManager != null) {
return sServiceManager;//
}
// 如果 service_manager进程访问的Binder对象为空,则创建一个。
// Find the service manager
sServiceManager = ServiceManagerNative
.asInterface(Binder.allowBlocking(BinderInternal.getContextObject()));
return sServiceManager;
}
/**
* Returns a reference to a service with the given name.
*
* @param name the name of the service to get
* @return a reference to the service, or null if the service doesn't exist
*/
public static IBinder getService(String name) {
try {
// 首先从缓存列表中查找服务
IBinder service = sCache.get(name);
if (service != null) {
return service;
} else {
// 如果缓存列表中没有找到对应的服务,则去service_manager进程中查找
return Binder.allowBlocking(getIServiceManager().getService(name));
}
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "error in getService", e);
}
return null;
}
/**
* Returns a reference to a service with the given name, or throws
* {@link NullPointerException} if none is found.
*
* @hide
*/
public static IBinder getServiceOrThrow(String name) throws ServiceNotFoundException {
final IBinder binder = getService(name);
if (binder != null) {
return binder;
} else {
throw new ServiceNotFoundException(name);
}
}
/**
* Place a new @a service called @a name into the service
* manager.
*
* @param name the name of the new service
* @param service the service object
*/
public static void addService(String name, IBinder service) {
try {
// 把服务注册到service_manager进程中,便于统一管理
getIServiceManager().addService(name, service, false);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "error in addService", e);
}
}
/**
* Place a new @a service called @a name into the service
* manager.
*
* @param name the name of the new service
* @param service the service object
* @param allowIsolated set to true to allow isolated sandboxed processes
* to access this service
*/
public static void addService(String name, IBinder service, boolean allowIsolated) {
try {
getIServiceManager().addService(name, service, allowIsolated);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "error in addService", e);
}
}
/**
* Retrieve an existing service called @a name from the
* service manager. Non-blocking.
*/
public static IBinder checkService(String name) {
try {
IBinder service = sCache.get(name);
if (service != null) {
return service;
} else {
return Binder.allowBlocking(getIServiceManager().checkService(name));
}
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "error in checkService", e);
return null;
}
}
/**
* Return a list of all currently running services.
* @return an array of all currently running services, or null in
* case of an exception
*/
public static String[] listServices() {
try {
// 获取在service_manager进程中注册的服务列表
return getIServiceManager().listServices();
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "error in listServices", e);
return null;
}
}
/**
* This is only intended to be called when the process is first being brought
* up and bound by the activity manager. There is only one thread in the process
* at that time, so no locking is done.
*
* @param cache the cache of service references
* @hide
*/
public static void initServiceCache(Map<String, IBinder> cache) {
if (sCache.size() != 0) {
throw new IllegalStateException("setServiceCache may only be called once");
}
sCache.putAll(cache);
}
/**
* Exception thrown when no service published for given name. This might be
* thrown early during boot before certain services have published
* themselves.
*
* @hide
*/
public static class ServiceNotFoundException extends Exception {
public ServiceNotFoundException(String name) {
super("No service published for: " + name);
}
}
}