Leetcode刷题——树篇4
文章目录
- 4、树(简单篇4)
- 4.1、543. 二叉树的直径
- 4.2、112. 路径总和
- 4.3、671. 二叉树中第二小的节点
- 4.4、572. 另一个树的子树
- 4.5、501. 二叉搜索树中的众数
- 4.6、111. 二叉树的最小深度
- 4.7、687. 最长同值路径
4、树(简单篇4)
4.1、543. 二叉树的直径
给定一棵二叉树,你需要计算它的直径长度。一棵二叉树的直径长度是任意两个结点路径长度中的最大值。这条路径可能穿过也可能不穿过根结点。
示例 : 给定二叉树
1 / \ 2 3 / \ 4 5返回 3, 它的长度是路径 [4,2,1,3] 或者 [5,2,1,3]。
注意:两结点之间的路径长度是以它们之间边的数目表示。
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/diameter-of-binary-tree
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
思路解析:所谓的二叉树直径就是左子树最深结点的深度+右子树最深结点的深度,本质上就是求树的高度,在递归过程中,自底向上地求树的高度,需要先求出左子树高度和右子树高度,最大直径就是每次求得的左右子树高度之和的最大值。
题解代码(C++):
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int res = INT_MIN;
int getHight(TreeNode* root){
if(root==NULL) return 0;
int l = getHight(root->left);
int r = getHight(root->right);
this->res = this->res>l+r?this->res:l+r;
return max(l,r)+1;
}
int diameterOfBinaryTree(TreeNode* root) {
if(root==NULL) return 0;
getHight(root);
return this->res;
}
};
题解代码(Java):
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
int res = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
public int getHight(TreeNode root){
if(root==null) return 0;
int l = getHight(root.left);
int r = getHight(root.right);
this.res = this.res>l+r?this.res:l+r;
return Math.max(l,r)+1;
}
public int diameterOfBinaryTree(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null) return 0;
getHight(root);
return this.res;
}
}
题解代码(Python):
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution:
def __init__(self):
self.res = 0
def getHight(self,root:TreeNode)->int:
if root is None:
return 0
l = self.getHight(root.left)
r = self.getHight(root.right)
self.res = self.res if self.res>l+r else l+r
return max(l,r)+1
def diameterOfBinaryTree(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:
if root is None:
return 0
self.getHight(root)
return self.res
4.2、112. 路径总和
给定一个二叉树和一个目标和,判断该树中是否存在根节点到叶子节点的路径,这条路径上所有节点值相加等于目标和。
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例: 给定如下二叉树,以及目标和 sum = 22,
5 / \ 4 8 / / \ 11 13 4 / \ \ 7 2 1返回 true, 因为存在目标和为 22 的根节点到叶子节点的路径 5->4->11->2。
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/path-sum
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
思路解析:递归深度搜索求路径之和,如果找到路径则结束深度搜索。
题解代码(C++):
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool tag = false;
void dfs(TreeNode* root,int count,int &sum){
if(root==NULL || this->tag) return ;
count+=root->val;
if(root->left==NULL && root->right==NULL && count==sum){
this->tag=true;
return;
}
dfs(root->left,count,sum);
dfs(root->right,count,sum);
}
bool hasPathSum(TreeNode* root, int sum) {
this->tag = false;
dfs(root,0,sum);
return this->tag;
}
};
题解代码(Java):
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
boolean tag = false;
public void dfs(TreeNode root,int count,int sum){
if(root==null || this.tag) return;
count+=root.val;
if(root.left==null && root.right==null && count==sum){
this.tag=true;
return;
}
dfs(root.left,count,sum);
dfs(root.right,count,sum);
}
public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int sum) {
this.tag = false;
dfs(root,0,sum);
return this.tag;
}
}
题解代码(Python):
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution:
def __init__(self):
self.tag = False
def dfs(self,root:TreeNode,count:int,sum:int):
if root is None or self.tag:
return None
count += root.val
if root.left is None and root.right is None and count==sum:
self.tag = True
return None
self.dfs(root.left,count,sum)
self.dfs(root.right,count,sum)
def hasPathSum(self, root: TreeNode, sum: int) -> bool:
self.tag = False
self.dfs(root,0,sum)
return self.tag
4.3、671. 二叉树中第二小的节点
给定一个非空特殊的二叉树,每个节点都是正数,并且每个节点的子节点数量只能为 2 或 0。如果一个节点有两个子节点的话,那么这个节点的值不大于它的子节点的值。
给出这样的一个二叉树,你需要输出所有节点中的第二小的值。如果第二小的值不存在的话,输出 -1 。
示例 1:
输入:
2 / \ 2 5 / \ 5 7输出: 5 说明: 最小的值是 2 ,第二小的值是 5 。 示例 2:
输入:
2 / \ 2 2输出: -1 说明: 最小的值是 2, 但是不存在第二小的值。
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/second-minimum-node-in-a-binary-tree
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
思路解析:题目中说明了是特殊的非空二叉树。两个地方特殊:
- 每个节点的子节点数量只能为 2 或 0。
- 如果一个节点有两个子节点的话,那么这个节点的值不大于它的子节点的值。
这两个特殊条件限制了,根节点的值肯定是最小值,所以需要递归遍历找到比根节点值大的就行,如果找不到就返回-1。
题解代码(C++):
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool isFind = false;
int res = INT_MAX;
void dfs(TreeNode* root,int &m){
if(root==NULL) return;
if(root->val>m){
this->res = min(root->val,this->res);
this->isFind = true;
}
dfs(root->left,m);
dfs(root->right,m);
}
int findSecondMinimumValue(TreeNode* root) {
if(root==NULL) return -1;
dfs(root,root->val);
return this->isFind?this->res:-1;
}
};
题解代码(Java):
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
int res = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
boolean tag = false;
public void dfs(TreeNode root,int m){
if(root==null) return ;
if(root.val>m){
this.res = Math.min(this.res,root.val);
this.tag = true;
}
dfs(root.left,m);
dfs(root.right,m);
}
public int findSecondMinimumValue(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null) return -1;
dfs(root,root.val);
return this.tag?this.res:-1;
}
}
题解代码(Python):
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution:
def __init__(self):
self.res = pow(2,32)-1
self.tag = False
def dfs(self,root:TreeNode,m:int):
if root is None:
return None
if root.val>m:
self.res= min(root.val,self.res)
self.tag = True
self.dfs(root.left,m)
self.dfs(root.right,m)
def findSecondMinimumValue(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:
self.res = pow(2,32)-1
self.tag = False
if root is None:
return -1
self.dfs(root,root.val)
return self.res if self.tag else -1
4.4、572. 另一个树的子树
给定两个非空二叉树 s 和 t,检验 s 中是否包含和 t 具有相同结构和节点值的子树。s 的一个子树包括 s 的一个节点和这个节点的所有子孙。s 也可以看做它自身的一棵子树。
示例 1: 给定的树 s:
3 / \ 4 5 / \ 1 2给定的树 t:
4 / \ 1 2返回 true,因为 t 与 s 的一个子树拥有相同的结构和节点值。
示例 2: 给定的树 s:
3 / \ 4 5 / \ 1 2 / 0给定的树 t:
4 / \ 1 2返回 false。
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/subtree-of-another-tree
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
思路解析:实际上是判断树是否相同的问题,还要用到遍历,每个结点都可能是t树的根节点。
题解代码(C++):
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool isSame(TreeNode* s,TreeNode* t){
if(s==NULL && t==NULL) return true;
if(s!=NULL && t==NULL) return false;
if(s==NULL && t!=NULL) return false;
else return s->val==t->val && isSame(s->left,t->left) && isSame(s->right,t->right);
}
bool isSubtree(TreeNode* s, TreeNode* t) {
if(s==NULL) return false;
if(isSame(s,t)) return true;
else if(isSubtree(s->left,t)) return true;
else if(isSubtree(s->right,t)) return true;
else return false;
}
};
题解代码(Java):
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean isSame(TreeNode s,TreeNode t){
if(s==null && t==null) return true;
if(s!=null&&t==null) return false;
if(s==null&&t!=null) return false;
else return s.val==t.val &&isSame(s.left,t.left) && isSame(s.right,t.right);
}
public boolean isSubtree(TreeNode s, TreeNode t) {
if(s==null) return false;
if(isSame(s,t)) return true;
else if(isSubtree(s.left,t)) return true;
else if(isSubtree(s.right,t)) return true;
else return false;
}
}
题解代码(Python):
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution:
def isSame(self,s:TreeNode,t:TreeNode)->bool:
if s is None and t is None:
return True
if s is not None and t is None:
return False
if s is None and t is not None:
return False
else:
return s.val==t.val and self.isSame(s.left,t.left) and self.isSame(s.right,t.right)
def isSubtree(self, s: TreeNode, t: TreeNode) -> bool:
if s is None:
return False
if self.isSame(s,t):
return True
elif self.isSubtree(s.left,t):
return True
elif self.isSubtree(s.right,t):
return True
else:
return False
4.5、501. 二叉搜索树中的众数
给定一个有相同值的二叉搜索树(BST),找出 BST 中的所有众数(出现频率最高的元素)。
假定 BST 有如下定义:
结点左子树中所含结点的值小于等于当前结点的值 结点右子树中所含结点的值大于等于当前结点的值 左子树和右子树都是二叉搜索树 例如: 给定
BST [1,null,2,2],1 \ 2 / 2返回[2].
提示:如果众数超过1个,不需考虑输出顺序来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/find-mode-in-binary-search-tree
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
思路解析:中序遍历输出到数组,然后求取众数,缺点是使用更多的额外空间。优点是简单易实现。
也可以用map来统计数字出现的频度,然后取最大频度的数即可。
题解代码(C++):
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
map<int,int> mymap;
void dfs(TreeNode* root){
if(root==NULL) return;
dfs(root->left);
if(mymap.find(root->val)==mymap.end()) mymap[root->val] = 1;
else mymap[root->val] += 1;
dfs(root->right);
}
vector<int> findMode(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> res;
if(root==NULL) return res;
this->mymap.clear();
dfs(root);
int max = 0;
for(map<int,int>::iterator it=this->mymap.begin();it!=this->mymap.end();it++){
if(it->second>max) max = it->second;
}
for(map<int,int>::iterator it=this->mymap.begin();it!=this->mymap.end();it++){
if(it->second==max) res.push_back(it->first);
}
return res;
}
};
题解代码(Java):
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
HashMap<Integer,Integer> mymap;
public void dfs(TreeNode root){
if(root==null) return ;
dfs(root.left);
if(this.mymap.get(root.val)!=null) mymap.put(root.val,mymap.get(root.val)+1);
else mymap.put(root.val,1);
dfs(root.right);
}
public int[] findMode(TreeNode root) {
ArrayList<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
if(root!=null){
this.mymap = new HashMap<>();
dfs(root);
int max = 0;
for(int k:this.mymap.keySet()){
if(this.mymap.get(k)>max) max = this.mymap.get(k);
}
for(int k:this.mymap.keySet()){
if(this.mymap.get(k)==max) res.add(k);
}
}
int[] a = new int[res.size()];
for(int i=0;i<res.size();i++) a[i] = res.get(i);
return a;
}
}
题解代码(Python):
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution:
def __init__(self):
self.frq = {}
def dfs(self,root:TreeNode):
if root is None:
return None
self.dfs(root.left)
if self.frq.get(root.val) is None:
self.frq[root.val] = 1
else:
self.frq[root.val]+=1
self.dfs(root.right)
def findMode(self, root: TreeNode) -> List[int]:
if root is None:
return None
self.frq = {}
self.dfs(root)
res = []
m = 0
for k,v in self.frq.items():
if v > m:
m=v
for k,v in self.frq.items():
if v==m:
res.append(k)
return res
4.6、111. 二叉树的最小深度
给定一个二叉树,找出其最小深度。
最小深度是从根节点到最近叶子节点的最短路径上的节点数量。
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例:
给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],
3 / \ 9 20 / \ 15 7返回它的最小深度 2.
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/minimum-depth-of-binary-tree
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
思路解析:在遍历的过程中,遇到叶子节点就计算深度,比较一下最小深度即可。
题解代码(C++):
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int res = INT_MAX;
void dfs(TreeNode* root,int d){
if(root==NULL) return;
if(root->left==NULL && root->right ==NULL){
this->res = this->res>d?d:this->res;
return ;
}
dfs(root->left,d+1);
dfs(root->right,d+1);
}
int minDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if(root==NULL) return 0;
this->res=INT_MAX;
dfs(root,1);
return this->res;
}
};
题解代码(Java):
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
int res = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
public void dfs(TreeNode root,int d){
if(root==null) return;
if(root.left==null&root.right==null){
this.res = this.res>d?d:this.res;
}
dfs(root.left,d+1);
dfs(root.right,d+1);
}
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null) return 0;
this.res = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
dfs(root,1);
return this.res;
}
}
题解代码(Python):
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution:
def __init__(self):
self.res = pow(2,32)-1
def dfs(self,root:TreeNode,d: int):
if root is None:
return None
if root.left is None and root.right is None:
self.res = d if self.res>d else self.res
self.dfs(root.left,d+1)
self.dfs(root.right,d+1)
def minDepth(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:
if root is None:
return 0
self.res = pow(2,32)-1
self.dfs(root,1)
return self.res
4.7、687. 最长同值路径
给定一个二叉树,找到最长的路径,这个路径中的每个节点具有相同值。 这条路径可以经过也可以不经过根节点。
注意:两个节点之间的路径长度由它们之间的边数表示。
示例 1:
输入:5 / \ 4 5 / \ \ 1 1 5输出:2
示例 2:
输入:1 / \ 4 5 / \ \ 4 4 5输出: 2
注意: 给定的二叉树不超过10000个结点。 树的高度不超过1000。来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/longest-univalue-path
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
思路解析:
题目中的最长路径是这个情况:
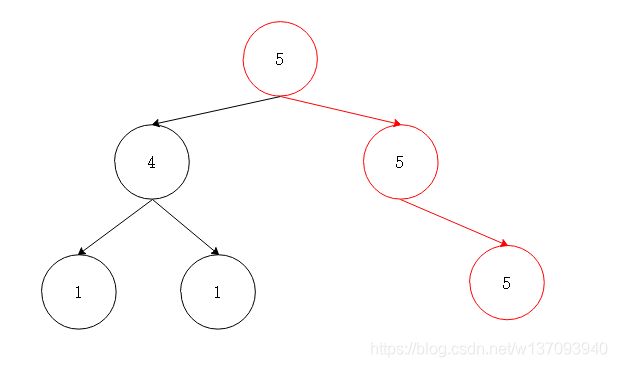

在后序遍历中,自底向上遍历每一个结点,对于某一个结点来说,看以该节点为根节点的子树,如果该节点的值与左右孩子的值相等,那么可以连通,如果不等,就不能连通成为路径。
简单框架:
int dfs(TreeNode* root){
if(root==NULL) return 0;//空结点就返回0
int l = dfs(root->left);
int r = dfs(root->right);
//root结点和左右孩子 值的比较,如果相等,则加入路径,不等就路径长度为0
l = (root->left != NULL && root->val == root->left->val)?l+1:0;
r = (root->right != NULL && root->val == root->right->val) ?r+1:0;
return max(l,r);//选取最长的路径
}
题解代码(C++):
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int res;
int dfs(TreeNode* root){
if(root==NULL) return 0;
int l = dfs(root->left);
int r = dfs(root->right);
if(root->left!=NULL && root->val == root->left->val) l++;
else l=0;
if(root->right!=NULL && root->val == root->right->val) r++;
else r=0;
this->res = max(this->res,l+r);
return max(l,r);
}
int longestUnivaluePath(TreeNode* root) {
if(root==NULL) return 0;
this->res = 0;
dfs(root);
return this->res;
}
};
题解代码(Java):
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
int res;
public int dfs(TreeNode root){
if(root==null) return 0;
int l = dfs(root.left);
int r = dfs(root.right);
l = (root.left!=null && root.left.val ==root.val)?l+1:0;
r = (root.right!=null && root.right.val == root.val)? r+1:0;
this.res = Math.max(this.res,l+r);
return Math.max(l,r);
}
public int longestUnivaluePath(TreeNode root) {
this.res = 0;
dfs(root);
return this.res;
}
}
题解代码(Python):
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution:
def __init__(self):
self.res = 0
def dfs(self,root:TreeNode)->int:
if root is None:
return 0
l = self.dfs(root.left)
r = self.dfs(root.right)
l = l+1 if root.left is not None and root.left.val == root.val else 0
r = r+1 if root.right is not None and root.right.val ==root.val else 0
self.res = max(self.res,l+r)
return max(l,r)
def longestUnivaluePath(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:
self.res =0
self.dfs(root)
return self.res