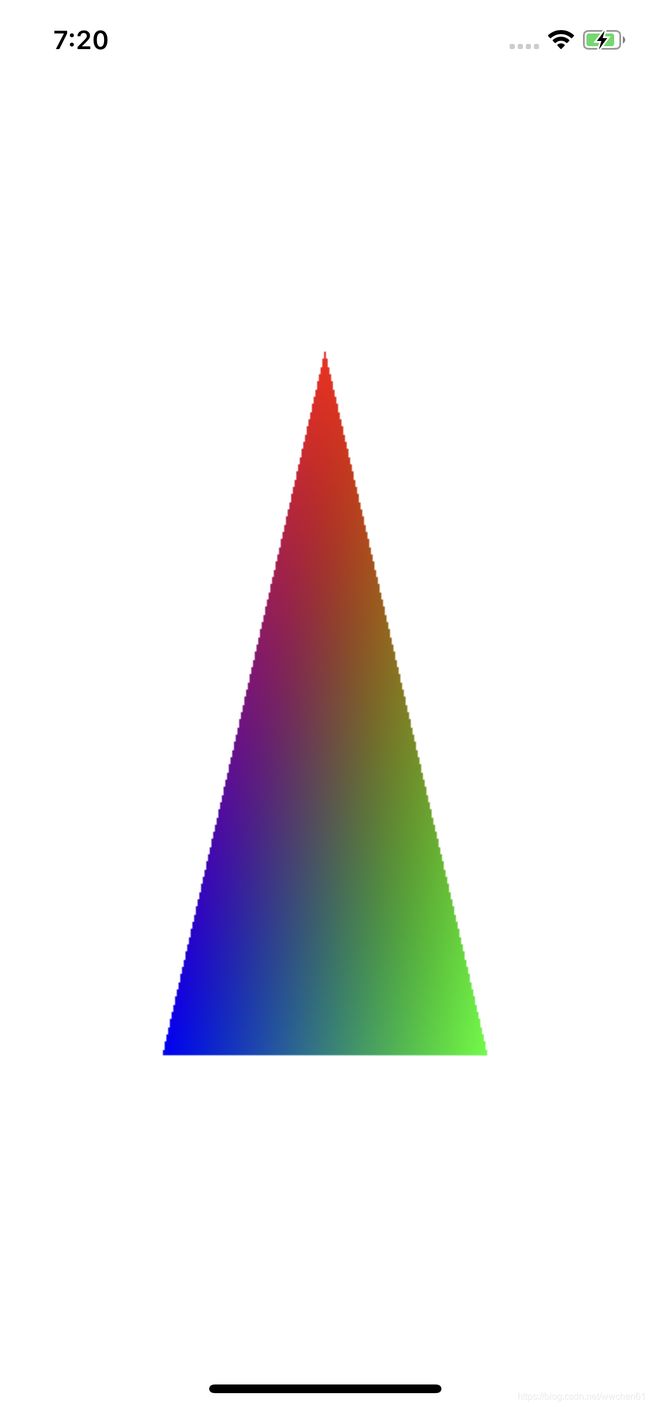Metal学习:用Metal画一个三角形
Metal基本概念
Metal是Apple提出的新一代的Graphics API架构,用来代替OpenGL。从2014年Metal提出开始,到2019年Apple正式废弃OpenGL/OpenGL ES的支持,Metal发展是非常快的,基本上以后在ios/Mac的开发中,metal是底层图形开发的唯一的选择。
基于以下的原因,OpenGL需要被Metal替代:
- OpenGL是25年前的标准,而现代的GPU设计和25年前已经非常的不同了
- OpenGL没有考虑多线程支持,它的执行像一个巨大的状态机,每次执行都必须查询这个状态机的所有状态,使得它的效率不高
- OpenGL没有异步支持,CPU和GPU之间交互是非常耗时的操作
Metal具有的特性:
- 低的CPU负载,Metal把运算放到GPU中来执行,降低CPU的负载
- 多线程支持
- 分支预测技术支持,避免像OpenGL那样,分支对性能影响非常大
- 资源和同步控制,GPU和CPU可以互相交互
在学习Metal之前,有些基本的概念需要先了解一下:
- 渲染管道
渲染管道是指一个一堆原始数据,经过各种变化处理,最终在屏幕上显示的过程,这个过程是在GPU中执行的。比如OpenGL的执行过程如下所示
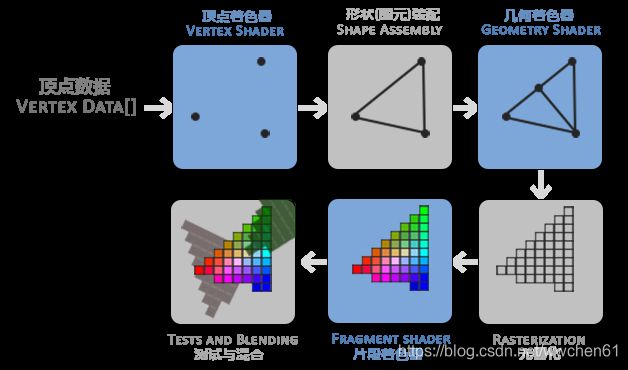
- Vertex Shader
顶点着色器是顶点数据的处理阶段,接受从CPU来的顶点数据,有可能还附带一些顶点的属性数据,输出则是经过各种变换以后的顶点数据。可以简单理解为输入是真实世界的3D点坐标,然后在vertex shader中经过在各种空间坐标系下的转换(model,view,perspective),最终变化为屏幕上的2D坐标,可以输出渲染管道的后续部分处理。 - Primitive Assembly
这是图元装配阶段,从顶点处理得到的是一个个单独的点,这时候我们需要对这些点进行重新的组合,使得他们成为一个个的图元(点,线,三角形),这样后面才能以这个形状来进行处理。 - Geometry Shader
几何着色器可以对图元装配产生的图元,通过产生新的顶点来构造出新的图元,比如上图中是产生了另外一个三角形。(一般这个阶段很少需要变动) - Rasterization
光栅化阶段是将图元真正映射到屏幕上,对应屏幕上的像素,生成给片段着色器需要的片段。一般是一个像素组成一个片段,但是也有可能几个像素组成一个片段。视图以外的所有像素会进行裁剪,以提高渲染效率 - Fragment Shader
片段着色器是决定每个像素的颜色,也是所有的后处理,光照,阴影等效果产生的地方。片段着色器产生的结果一般还要经过深度测试(决定这个像素是否被其他物体遮挡)和混合测试(和预先设置的模板进行操作),才最终显示到屏幕上来。
- Shaders
可以看到图形渲染管道非常复杂,但是一般我们只要关心顶点着色器和片段着色器就可以了,这也是可编程管道要求我们必须实现的。也就是我们可以自己定义图形渲染管道中的顶点和片段两个处理阶段,通过GPU的程序来实现,我们称之为着色器(shaders)。可以简单理解着色器就是可以在GPU上执行的小程序,遵循专门的着色器语言规范,在OpenGL中是GLSL(OpenGL Shading language),在Metal中是“Metal shading language”。 - Uniform
Uniform表示CPU向GPU发送数据的一种方式,它是全局性的,也就是在一次渲染过程中,当你将Uniform数据传送到GPU,它会被所有的着色器程序在任意阶段访问。Uniform设置后,就会一直保存他的数据,直到它被重置或者更新。
Metal对象
Device和CommandQueue
不同于OpenGL,在Metal中基本上所有组件都是基于对象的。比如GPU抽象为一个MTLDevice的对象,从MTLDevice可以创建command queue,texture,buffer和pipeline等渲染对象。
id device = MTLCreateSystemDefaultDevice();
从Device可以创建Queue,它是用来执行命令的(command buffer),一般在初始化的时候创建一个Queue即可
id commnadQueue = [device newCommandQueue];
Textures,Buffers, Pipelines
Textures, Buffers和Pipelines我们统一把他们称之为渲染对象,他们都是从device对象中创建。
创建TextureObject首先需要有Texture Descriptor来描述这个对象,具体包括这个Texture的type,size,format和存储模式等信息。其中存储模式可以决定这个texture是否和CPU进行共享。
MTLTextureDescriptor *textureDescriptor = [MTLTextureDescriptor new];
textureDescriptor.pixelFormat = MTLPixelFormatBGRA8Unorm;
textureDescriptor.width = 512;
textureDescriptor.height = 512;
textureDescriptor.storageMode = MTLStorageModeShared;
id texture = [device newTextureWithDescriptor:textureDescriptor];
可以上传数据到Texture,如下所示:
NSUInteger bytesPerRow = 4 * image.width;
MTLRegion region = {
{0, 0, 0},
{512, 512, 1}
};
[texture replaceRegion:region mipmapLevel:0 withBytes:imageData bytesPerRow:bytesPerRow];
Metal中所有的数据都是buffer,例如顶点,索引和uniform。创建buffer和更新数据如下所示
id buffer = [device newBufferWithLength:bufferDataByteSize options:MTLResourceStorageModeShared];
struct MyUniforms *uniforms = (struct MyUniforms*)buffer.content;
uniforms->modelViewProjection = modelViewProjection;
uniforms->sunPosition = sunPosition;
需要注意的是buffer是采用自动对齐的机制,例如虽然一个float是占用4个字节,但是float3和float4一样,都是占用16字节。
Pipeline对象由device创建,代表的是渲染的具体过程。和Texture一样,他也需要一个MTLRenderPipelineDescriptor的对象来描述。主要是包括vertex和fragment的shader程序,以及渲染的pixelFormat。
id defaultLibrary = [device newDefaultLibrary];
id vertexFunction = [defaultLibrary newFunctionWithName:@"vertexShader"];
id fragmentFunction = [defaultLibrary newFunctionWithName:@"fragmentShader"];
MTLRenderPipelineDescriptor *pipelineStateDescriptor = [MTLRenderPipelineDescriptor new];
pipelineStateDescriptor.vertexFunction = vertexFunction;
pipelineStateDescriptor.fragmentFunction = fragmentFunction;
pipelineStateDescriptor.colorAttachement[0].pixelFormt = MTLPixelFormatRGBA8Unorm;
id pipelineState;
pipelineState = [device newRenderPipelineStateWithDescriptor:pipelineStateDescriptor error:nil];
渲染过程
上面提到的对象都是全局的对象,是运行过程中长期存在的,需要在初始化阶段就分配好。当进入渲染阶段,
我们通过Command Buffer和Command Encoder两个对象来进行提交渲染任务。
Command Buffer通过Command Queue产生,它主要控制任务的提交, 一次帧渲染可以有多个command buffer,同时这些command buffer可以在不同的线程中产生,每个command buffer可以注册一个任务完成的回调。
id commandBuffer = [commandQueue commandBuffer];
//Encode Commands
[commandBuffer addCompletedHander:^(id commandBuffer){
//GPU is done with my buffer
}]
[commandBuffer commit]
Command Encoder负责具体的渲染过程,它是从Command Buffer分配出来的,需要通过一个MTLRenderPassDescritor来描述。
MTLRenderPassDescriptor *desc = [MTLRenderPassDescriptor new];
desc.colorAttachment[0].texture = myColorTexture;
desc.colorAttachment[0].loadAction = MTLLoadActionClear;
desc.colorAttachment[0].clearColor = MTLClearColorMake(1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f);
desc.colorAttachment[0].storeAction = MTLStoreActionStore;
id encoder = [commandBuffer renderCommandEncoderWithDescriptor:desc];
[encoder setPipelineState:myPipeline];
[encoder setVertexBuffer:myVertexData offset:0 atIndex:0];
[encoder setVertexBuffer:myUniforms offset:0 atIndex:1];
[encoder setFragmentBuffer:myUniforms offset:0 atIndex:1];
[encoder setFragmentTexture:myTexture atIndex:0];
[encoder drawPrimitives:MTLPrimitiveTypeTriangle vertexStart:0 vertexCount:numVertices];
[encoder endEncoding];
用Metal画一个三角形
创建iOS项目
首选打开XCode创建一个Single View Application,并且使用Object-C作为编程语言。
在ViewController.h中包含以下头文件
#import
#import
CAMetalLayer提供一个可以给Metal来进行渲染的纹理,我们后面需要使用这个类型的layer来进行渲染
初始化
对于需要长期存在的对象,我们在interface中声明为全局的类对象,在ViewController.m中,声明如下的对象
id mtlDevice;
id mtlCommandQueue;
id renderPipelineState;
id vertexBuffer;
CAMetalLayer *metalLayer;
id frameDrawable;
CADisplayLink *displayLink;
然后在viewDidLoad方法中,初始化这些对象
mtlDevice = MTLCreateSystemDefaultDevice();
mtlCommandQueue = [mtlDevice newCommandQueue];
id mtlLibrary = [mtlDevice newDefaultLibrary];
id vertexProgram = [mtlLibrary newFunctionWithName:@"vertexShader"];
id fragmentProgram = [mtlLibrary newFunctionWithName:@"fragmentShader"];
MTLRenderPipelineDescriptor *mtlRenderPipelineDescriptor = [[MTLRenderPipelineDescriptor alloc] init];
[mtlRenderPipelineDescriptor setVertexFunction:vertexProgram];
[mtlRenderPipelineDescriptor setFragmentFunction:fragmentProgram];
mtlRenderPipelineDescriptor.colorAttachments[0].pixelFormat = MTLPixelFormatBGRA8Unorm;
renderPipelineState = [mtlDevice newRenderPipelineStateWithDescriptor:mtlRenderPipelineDescriptor error:nil];
static float vertices[] = {
0.0, 0.5, 0.0, 1.0,
0.5, -0.5, 0.0, 1.0,
-0.5, -0.5, 0.0, 1.0
};
vertexBuffer = [mtlDevice newBufferWithBytes:vertices length:sizeof(vertices) options:MTLResourceOptionCPUCacheModeDefault];
metalLayer = [CAMetalLayer layer];
metalLayer.device = mtlDevice;
metalLayer.pixelFormat = MTLPixelFormatBGRA8Unorm;
metalLayer.frame = self.view.bounds;
[self.view.layer addSublayer:metalLayer];
displayLink = [CADisplayLink displayLinkWithTarget:self selector:@selector(renderScene)];
[displayLink addToRunLoop:[NSRunLoop currentRunLoop] forMode:NSDefaultRunLoopMode];
其中displayLink是一个计时器,它会周期性的触发函数renderScene,我们在这个函数中进行每一帧的渲染,也就是画一个三角形。
Render Pass
在函数renderScene中,做如下的操作
frameDrawable = [metalLayer nextDrawable];
id mtlCommandBuffer = [mtlCommandQueue commandBuffer];
MTLRenderPassDescriptor *mtlRenderPassDescriptor = [MTLRenderPassDescriptor renderPassDescriptor];
mtlRenderPassDescriptor.colorAttachments[0].texture = frameDrawable.texture;
mtlRenderPassDescriptor.colorAttachments[0].loadAction = MTLLoadActionClear;
mtlRenderPassDescriptor.colorAttachments[0].clearColor = MTLClearColorMake(1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0);
mtlRenderPassDescriptor.colorAttachments[0].storeAction = MTLStoreActionStore;
id renderEncoder = [mtlCommandBuffer renderCommandEncoderWithDescriptor:mtlRenderPassDescriptor];
[renderEncoder setRenderPipelineState:renderPipelineState];
[renderEncoder setVertexBuffer:vertexBuffer offset:0 atIndex:0];
[renderEncoder drawPrimitives:MTLPrimitiveTypeTriangle vertexStart:0 vertexCount:3];
[renderEncoder endEncoding];
[mtlCommandBuffer presentDrawable:frameDrawable];
[mtlCommandBuffer commit];
Metal Library
新建一个metal文件,File->New->File,选择类型为Metal File。添加如下代码
vertex float4 vertexShader(device float4* vertices [[buffer(0)]],
uint vid [[vertex_id]]) {
return vertices[vid];
}
fragment float4 fragmentShader(float4 in [[stage_in]]) {
return float4(1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0);
}
运行程序,屏幕上显示出三角形。
顶点添加颜色
上面画的三角形是一个全部是红色的三角形,我们可以利用传递给顶点的数据带上一个颜色信息,然后给三角形画上指定的颜色。
在metal中,不论是attribute还是uniform都是MTLBuffer,首先我们申明一个MTLBuffer的 colorBuffer;
id colorBuffer;
然后给这个MTLBuffer填充颜色数据,每一个顶点分别填充红绿蓝三个颜色,
static float colors[] = {
1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0,
0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 1.0,
0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 1.0
};
colorBuffer = [mtlDevice newBufferWithBytes:colors length:sizeof(colors) options:MTLResourceOptionCPUCacheModeDefault];
在renderpass中,将这个colorBuffer传递到顶点着色器,注意它的index是1,这个就是在着色器中对应的索引值
[renderEncoder setVertexBuffer:colorBuffer offset:0 atIndex:1];
相应的metal文件修改如下:
struct VertexOut {
float4 position [[position]];
float4 color;
};
vertex VertexOut vertexShader(device float4* position [[buffer(0)]],
constant float4* color[[buffer(1)]],
uint vid [[vertex_id]]) {
VertexOut vert;
vert.position = position[vid];
vert.color = color[vid];
return vert;
}
fragment float4 fragmentShader(VertexOut in [[stage_in]]) {
return in.color;
}
这样我们就得到一个彩色的三角形,因为顶点着色器的数据在经过光栅化后,它的顶点坐标和相应的颜色值都会进行线性插值处理,所以看到的是彩色的三角形。