压缩与解压1---字符串的压缩与解压
1.引言
最近在做项目中,平台提供一个http服务给其他系统调用,然后我接收到其他系统的json格式的报文后去解析,然后用拿到的数据去调用corba服务,我再把corba的返回值封装完成json字符串返回给外部系统。遇到一个接口去调用corba服务,然后corba返回的数据经过封装后字符串的长度达到7M左右,导致http客户端无法正常的接收完所有的数据。你可能会说这个接口设计的不合理,为什么不增加查询条件把查询条件范围缩小一点?但是,这个不是本节要讨论的内容,主要是因为corba服务已经发布用了很久且不在此次项目改造范围之内,再者这个corba服务已经上线用了N久,轻易的改变可能会导致未知的错误。签于此,我想到可以把json格式的字符串给压缩,然后客户端再解压。(一是字符串的压缩比例比较的高,二是字符串的压缩和解压实现起来也比较简单)。虽然,最后没有用到字符串的压缩和解压的方式,而是修改客户端(1.http客户端进一步精确查询条件 2.读取返回数据流采用循环读取的方式)来解决此问题,我还是把字符串的压缩和解压做一下简单的记录。
2.关于压缩与解压
压缩算法有多种,我说知道和接触有java I/O自带的zip和gzip两种方式。
本节主要来简单介绍一下在系统交互之间遇到大容量的字符串数据交互时,采用一端压缩,另一端再解压的方式来发送和接收数据。
关于此次的压缩和解压用到的主要就是GZIPOutputStream和GZIPInputStream类,此类的相关介绍在JDK中有详细的介绍,这里就不再累述了。
3.代码如下:
解压:
完整代码的如下:
最近在做项目中,平台提供一个http服务给其他系统调用,然后我接收到其他系统的json格式的报文后去解析,然后用拿到的数据去调用corba服务,我再把corba的返回值封装完成json字符串返回给外部系统。遇到一个接口去调用corba服务,然后corba返回的数据经过封装后字符串的长度达到7M左右,导致http客户端无法正常的接收完所有的数据。你可能会说这个接口设计的不合理,为什么不增加查询条件把查询条件范围缩小一点?但是,这个不是本节要讨论的内容,主要是因为corba服务已经发布用了很久且不在此次项目改造范围之内,再者这个corba服务已经上线用了N久,轻易的改变可能会导致未知的错误。签于此,我想到可以把json格式的字符串给压缩,然后客户端再解压。(一是字符串的压缩比例比较的高,二是字符串的压缩和解压实现起来也比较简单)。虽然,最后没有用到字符串的压缩和解压的方式,而是修改客户端(1.http客户端进一步精确查询条件 2.读取返回数据流采用循环读取的方式)来解决此问题,我还是把字符串的压缩和解压做一下简单的记录。
2.关于压缩与解压
压缩算法有多种,我说知道和接触有java I/O自带的zip和gzip两种方式。
本节主要来简单介绍一下在系统交互之间遇到大容量的字符串数据交互时,采用一端压缩,另一端再解压的方式来发送和接收数据。
关于此次的压缩和解压用到的主要就是GZIPOutputStream和GZIPInputStream类,此类的相关介绍在JDK中有详细的介绍,这里就不再累述了。
3.代码如下:
压缩:
/**
* 字符串的压缩
*
* @param str
* 待压缩的字符串
* @return 返回压缩后的字符串
* @throws IOException
*/
public static String compress(String str) throws IOException {
if (null == str || str.length() <= 0) {
return str;
}
// 创建一个新的 byte 数组输出流
ByteArrayOutputStream out = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
// 使用默认缓冲区大小创建新的输出流
GZIPOutputStream gzip = new GZIPOutputStream(out);
// 将 b.length 个字节写入此输出流
gzip.write(str.getBytes());
gzip.close();
// 使用指定的 charsetName,通过解码字节将缓冲区内容转换为字符串
return out.toString("ISO-8859-1");
}解压:
/**
* 字符串的解压
*
* @param str
* 对字符串解压
* @return 返回解压缩后的字符串
* @throws IOException
*/
public static String unCompress(String str) throws IOException {
if (null == str || str.length() <= 0) {
return str;
}
// 创建一个新的 byte 数组输出流
ByteArrayOutputStream out = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
// 创建一个 ByteArrayInputStream,使用 buf 作为其缓冲区数组
ByteArrayInputStream in = new ByteArrayInputStream(str
.getBytes("ISO-8859-1"));
// 使用默认缓冲区大小创建新的输入流
GZIPInputStream gzip = new GZIPInputStream(in);
byte[] buffer = new byte[256];
int n = 0;
while ((n = gzip.read(buffer)) >= 0) {// 将未压缩数据读入字节数组
// 将指定 byte 数组中从偏移量 off 开始的 len 个字节写入此 byte数组输出流
out.write(buffer, 0, n);
}
// 使用指定的 charsetName,通过解码字节将缓冲区内容转换为字符串
return out.toString("GBK");
}完整代码的如下:
ZipStrUtil.java
package gzip;
import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.zip.GZIPInputStream;
import java.util.zip.GZIPOutputStream;
/**
*
*Module: ZipUtil.java
*Description: 对字符串的压缩及解压
*Company:
*Author: pantp
*Date: May 6, 2012
*/
public class ZipStrUtil {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 字符串超过一定的长度
String str = "ABCdef123中文~!@#$%^&*()_+{};/1111111111111111111111111AAAAAAAAAAAJDLFJDLFJDLFJLDFFFFJEIIIIIIIIIIFJJJJJJJJJJJJALLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLLL" +
"LLppppppppppppppppppppppppppppppppppppppppp===========================------------------------------iiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiii";
System.out.println("\n原始的字符串为------->" + str);
float len0=str.length();
System.out.println("原始的字符串长度为------->"+len0);
String ys = compress(str);
System.out.println("\n压缩后的字符串为----->" + ys);
float len1=ys.length();
System.out.println("压缩后的字符串长度为----->" + len1);
String jy = unCompress(ys);
System.out.println("\n解压缩后的字符串为--->" + jy);
System.out.println("解压缩后的字符串长度为--->"+jy.length());
System.out.println("\n压缩比例为"+len1/len0);
//判断
if(str.equals(jy)){
System.out.println("先压缩再解压以后字符串和原来的是一模一样的");
}
}
/**
* 字符串的压缩
*
* @param str
* 待压缩的字符串
* @return 返回压缩后的字符串
* @throws IOException
*/
public static String compress(String str) throws IOException {
if (null == str || str.length() <= 0) {
return str;
}
// 创建一个新的 byte 数组输出流
ByteArrayOutputStream out = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
// 使用默认缓冲区大小创建新的输出流
GZIPOutputStream gzip = new GZIPOutputStream(out);
// 将 b.length 个字节写入此输出流
gzip.write(str.getBytes());
gzip.close();
// 使用指定的 charsetName,通过解码字节将缓冲区内容转换为字符串
return out.toString("ISO-8859-1");
}
/**
* 字符串的解压
*
* @param str
* 对字符串解压
* @return 返回解压缩后的字符串
* @throws IOException
*/
public static String unCompress(String str) throws IOException {
if (null == str || str.length() <= 0) {
return str;
}
// 创建一个新的 byte 数组输出流
ByteArrayOutputStream out = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
// 创建一个 ByteArrayInputStream,使用 buf 作为其缓冲区数组
ByteArrayInputStream in = new ByteArrayInputStream(str
.getBytes("ISO-8859-1"));
// 使用默认缓冲区大小创建新的输入流
GZIPInputStream gzip = new GZIPInputStream(in);
byte[] buffer = new byte[256];
int n = 0;
while ((n = gzip.read(buffer)) >= 0) {// 将未压缩数据读入字节数组
// 将指定 byte 数组中从偏移量 off 开始的 len 个字节写入此 byte数组输出流
out.write(buffer, 0, n);
}
// 使用指定的 charsetName,通过解码字节将缓冲区内容转换为字符串
return out.toString("GBK");
}
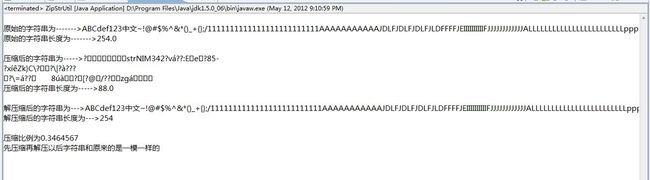
}运行代码中的main方式,测试的效果如下:
说明:
字符串长度很小的时候,测试时你会发现压缩后的长度竟然变长了,字符串必须达到一定长度,压缩比例就可以明显看到很大。
哪位大虾还有什么好的方式处理系统之间大容量数据交互的方式,请指点一二。
我现在的项目中用的是HTTP+JSON的方式。