from builtins import range
from builtins import object
import numpy as np
from cs231n.layers import *
from cs231n.layer_utils import *
class TwoLayerNet(object):
"""
A two-layer fully-connected neural network with ReLU nonlinearity and
softmax loss that uses a modular layer design. We assume an input dimension
of D, a hidden dimension of H, and perform classification over C classes.
The architecure should be affine - relu - affine - softmax.
Note that this class does not implement gradient descent; instead, it
will interact with a separate Solver object that is responsible for running
optimization.
The learnable parameters of the model are stored in the dictionary
self.params that maps parameter names to numpy arrays.
"""
def __init__(self, input_dim=3*32*32, hidden_dim=100, num_classes=10,
weight_scale=1e-3, reg=0.0):
"""
Initialize a new network.
Inputs:
- input_dim: An integer giving the size of the input
- hidden_dim: An integer giving the size of the hidden layer
- num_classes: An integer giving the number of classes to classify
- weight_scale: Scalar giving the standard deviation for random
initialization of the weights.
- reg: Scalar giving L2 regularization strength.
"""
self.params = {}
self.reg = reg
############################################################################
# TODO: Initialize the weights and biases of the two-layer net. Weights #
# should be initialized from a Gaussian centered at 0.0 with #
# standard deviation equal to weight_scale, and biases should be #
# initialized to zero. All weights and biases should be stored in the #
# dictionary self.params, with first layer weights #
# and biases using the keys 'W1' and 'b1' and second layer #
# weights and biases using the keys 'W2' and 'b2'. #
############################################################################
W1 = weight_scale * np.random.randn(input_dim,hidden_dim)
b1 = np.zeros(hidden_dim)
W2 = weight_scale * np.random.randn(hidden_dim,num_classes)
b2 = np.zeros(num_classes)
self.params['W1'] = W1
self.params['b1'] = b1
self.params['W2'] = W2
self.params['b2'] = b2
############################################################################
# END OF YOUR CODE #
############################################################################
def loss(self, X, y=None):
"""
Compute loss and gradient for a minibatch of data.
Inputs:
- X: Array of input data of shape (N, d_1, ..., d_k)
- y: Array of labels, of shape (N,). y[i] gives the label for X[i].
Returns:
If y is None, then run a test-time forward pass of the model and return:
- scores: Array of shape (N, C) giving classification scores, where
scores[i, c] is the classification score for X[i] and class c.
If y is not None, then run a training-time forward and backward pass and
return a tuple of:
- loss: Scalar value giving the loss
- grads: Dictionary with the same keys as self.params, mapping parameter
names to gradients of the loss with respect to those parameters.
"""
scores = None
############################################################################
# TODO: Implement the forward pass for the two-layer net, computing the #
# class scores for X and storing them in the scores variable. #
############################################################################
out1, cache1 = affine_forward(X, self.params['W1'], self.params['b1'])
out2, cache2 = relu_forward(out1)
out3, cache3 = affine_forward(out2, self.params['W2'], self.params['b2'])
scores = out3
############################################################################
# END OF YOUR CODE #
############################################################################
# If y is None then we are in test mode so just return scores
if y is None:
return scores
loss, grads = 0, {}
############################################################################
# TODO: Implement the backward pass for the two-layer net. Store the loss #
# in the loss variable and gradients in the grads dictionary. Compute data #
# loss using softmax, and make sure that grads[k] holds the gradients for #
# self.params[k]. Don't forget to add L2 regularization! #
# #
# NOTE: To ensure that your implementation matches ours and you pass the #
# automated tests, make sure that your L2 regularization includes a factor #
# of 0.5 to simplify the expression for the gradient. #
############################################################################
loss, dout = softmax_loss(scores, y)
dx2, dw2, db2 = affine_backward(dout, cache3)
dx1 = relu_backward(dx2, cache2)
dx, dw1, db1 = affine_backward(dx1, cache1)
dw1 = dw1 + self.reg * self.params['W1']
dw2 = dw2 + self.reg * self.params['W2']
grads['W2'] = dw2
grads['b2'] = db2
grads['W1'] = dw1
grads['b1'] = db1
reg_loss = 0.5 * self.reg * (np.sum(self.params['W1']*self.params['W1']) +
np.sum(self.params['W2']*self.params['W2']))
loss = loss + reg_loss
############################################################################
# END OF YOUR CODE #
############################################################################
return loss, grads
class FullyConnectedNet(object):
"""
A fully-connected neural network with an arbitrary number of hidden layers,
ReLU nonlinearities, and a softmax loss function. This will also implement
dropout and batch/layer normalization as options. For a network with L layers,
the architecture will be
{affine - [batch/layer norm] - relu - [dropout]} x (L - 1) - affine - softmax
where batch/layer normalization and dropout are optional, and the {...} block is
repeated L - 1 times.
Similar to the TwoLayerNet above, learnable parameters are stored in the
self.params dictionary and will be learned using the Solver class.
"""
def __init__(self, hidden_dims, input_dim=3*32*32, num_classes=10,
dropout=1, normalization=None, reg=0.0,
weight_scale=1e-2, dtype=np.float32, seed=None):
"""
Initialize a new FullyConnectedNet.
Inputs:
- hidden_dims: A list of integers giving the size of each hidden layer.
- input_dim: An integer giving the size of the input.
- num_classes: An integer giving the number of classes to classify.
- dropout: Scalar between 0 and 1 giving dropout strength. If dropout=1 then
the network should not use dropout at all.
- normalization: What type of normalization the network should use. Valid values
are "batchnorm", "layernorm", or None for no normalization (the default).
- reg: Scalar giving L2 regularization strength.
- weight_scale: Scalar giving the standard deviation for random
initialization of the weights.
- dtype: A numpy datatype object; all computations will be performed using
this datatype. float32 is faster but less accurate, so you should use
float64 for numeric gradient checking.
- seed: If not None, then pass this random seed to the dropout layers. This
will make the dropout layers deteriminstic so we can gradient check the
model.
"""
self.normalization = normalization
self.use_dropout = dropout != 1
self.reg = reg
self.num_layers = 1 + len(hidden_dims)
self.dtype = dtype
self.params = {}
############################################################################
# TODO: Initialize the parameters of the network, storing all values in #
# the self.params dictionary. Store weights and biases for the first layer #
# in W1 and b1; for the second layer use W2 and b2, etc. Weights should be #
# initialized from a normal distribution centered at 0 with standard #
# deviation equal to weight_scale. Biases should be initialized to zero. #
# #
# When using batch normalization, store scale and shift parameters for the #
# first layer in gamma1 and beta1; for the second layer use gamma2 and #
# beta2, etc. Scale parameters should be initialized to ones and shift #
# parameters should be initialized to zeros. #
############################################################################
dims = [input_dim]
dims = dims+hidden_dims
for layer in range(self.num_layers-1):
W = weight_scale * np.random.randn(dims[layer],dims[layer+1])
b = np.zeros(dims[layer+1])
self.params['W%s'% (layer+1)] = W
self.params['b%s'% (layer+1)] = b
############################################################################
# END OF YOUR CODE #
############################################################################
# When using dropout we need to pass a dropout_param dictionary to each
# dropout layer so that the layer knows the dropout probability and the mode
# (train / test). You can pass the same dropout_param to each dropout layer.
self.dropout_param = {}
if self.use_dropout:
self.dropout_param = {'mode': 'train', 'p': dropout}
if seed is not None:
self.dropout_param['seed'] = seed
# With batch normalization we need to keep track of running means and
# variances, so we need to pass a special bn_param object to each batch
# normalization layer. You should pass self.bn_params[0] to the forward pass
# of the first batch normalization layer, self.bn_params[1] to the forward
# pass of the second batch normalization layer, etc.
self.bn_params = []
if self.normalization=='batchnorm':
self.bn_params = [{'mode': 'train'} for i in range(self.num_layers - 1)]
if self.normalization=='layernorm':
self.bn_params = [{} for i in range(self.num_layers - 1)]
# Cast all parameters to the correct datatype
for k, v in self.params.items():
self.params[k] = v.astype(dtype)
def loss(self, X, y=None):
"""
Compute loss and gradient for the fully-connected net.
Input / output: Same as TwoLayerNet above.
"""
X = X.astype(self.dtype)
mode = 'test' if y is None else 'train'
# Set train/test mode for batchnorm params and dropout param since they
# behave differently during training and testing.
if self.use_dropout:
self.dropout_param['mode'] = mode
if self.normalization=='batchnorm':
for bn_param in self.bn_params:
bn_param['mode'] = mode
scores = None
############################################################################
# TODO: Implement the forward pass for the fully-connected net, computing #
# the class scores for X and storing them in the scores variable. #
# #
# When using dropout, you'll need to pass self.dropout_param to each #
# dropout forward pass. #
# #
# When using batch normalization, you'll need to pass self.bn_params[0] to #
# the forward pass for the first batch normalization layer, pass #
# self.bn_params[1] to the forward pass for the second batch normalization #
# layer, etc. #
############################################################################
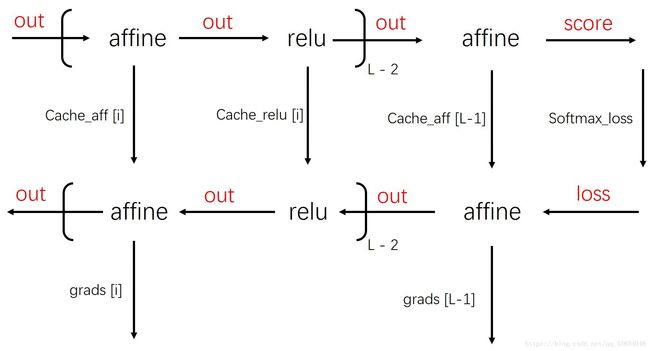
cache_relu = {}
cache_aff = {}
out_list = [X]
for layer in range(self.num_layers-2):
out, cache_aff['%s'% (layer+1)] = affine_forward(out_list.pop(), self.params['W%s'% (layer+1)], self.params['b%s'% (layer+1)])
out_list.append(out)
out, cache_relu['%s'% (layer+1)] = relu_forward(out_list.pop())
out_list.append(out)
scores, cache_aff['%s'%(self.num_layers-1)] = affine_forward(out_list.pop(), self.params['W%s'%(self.num_layers-1)], self.params['b%s'%(self.num_layers-1)])
############################################################################
# END OF YOUR CODE #
############################################################################
# If test mode return early
if mode == 'test':
return scores
loss, grads = 0.0, {}
############################################################################
# TODO: Implement the backward pass for the fully-connected net. Store the #
# loss in the loss variable and gradients in the grads dictionary. Compute #
# data loss using softmax, and make sure that grads[k] holds the gradients #
# for self.params[k]. Don't forget to add L2 regularization! #
# #
# When using batch/layer normalization, you don't need to regularize the scale #
# and shift parameters. #
# #
# NOTE: To ensure that your implementation matches ours and you pass the #
# automated tests, make sure that your L2 regularization includes a factor #
# of 0.5 to simplify the expression for the gradient. #
############################################################################
loss, dout = softmax_loss(scores, y)
dx_list = []
dx_list.append(dout) #safe the dx in list
dx, dw, db = affine_backward(dx_list.pop(),cache_aff['%s'%(self.num_layers-1)])
dx_list.append(dx)
grads['W%s'% (self.num_layers-1)] = dw
grads['b%s'% (self.num_layers-1)] = db
reg_loss = 0.5 * self.reg * np.sum(self.params['W%s'% (self.num_layers-1)]*self.params['W%s'% (self.num_layers-1)])
for layer in range(self.num_layers-2):
dx = relu_backward(dx_list.pop(), cache_relu['%s'%(self.num_layers-2-layer)])
dx_list.append(dx)
dx, dw, db = affine_backward(dx_list.pop(),cache_aff['%s'%(self.num_layers-2-layer)])
dx_list.append(dx)
dw = dw + self.reg * self.params['W%s'% (self.num_layers-2-layer)]
db = db + self.reg * self.params['b%s'% (self.num_layers-2-layer)]
grads['W%s'% (self.num_layers-2-layer)] = dw
grads['b%s'% (self.num_layers-2-layer)] = db
reg_loss = reg_loss + 0.5 * self.reg * np.sum(self.params['W%s'% (self.num_layers-2-layer)]*self.params['W%s'% (self.num_layers-2-layer)])
loss = loss + reg_loss
############################################################################
# END OF YOUR CODE #
############################################################################
return loss, grads
