机器学习--线性回归练习--Second_Chapter
线性回归带截距项
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif']=['SimHei'] #显示中文标签
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus']=False
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
def y_label_(k,x,b):
y_label_ = k*x +b + np.random.randn(len(x))*0.2
return y_label_
def linear_model(x,k_,b_):
y_hat = k_* x + b_
return y_hat
def loss_model(y_hat,y_label):
loss = 1/(2*len(y_hat))*np.sum((y_hat-y_label)**2)
return loss
if __name__ =="__main__":
x = np.arange(1, 10)
b = 3
y_label = y_label_(1,x,1)
k_ = np.arange(-10,10,1)
b_ = np.arange(-10,10,1)
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))
plt.style.use("ggplot")
i = 1
loss_ = []
k_list = []
b_list = []
for k_,b_ in zip(k_,b_):
y_hat = linear_model(x,k_,b_)
loss = loss_model(y_hat,y_label)
k_list.append(k_)
b_list.append(b_)
loss_.append(loss)
plt.subplot(4,5,i)
plt.scatter(x, y_label)
plt.plot(x, y_hat, linewidth=1, label="k={},b={}".format(k_,b_))
plt.legend(loc=0)
x_min, x_max = x.min()-2, x.max()+2
y_min, y_max = np.min((y_label.min(), y_hat.min())) - 5, \
np.max((y_label.max(), y_hat.max())) + 5
plt.xlim([x_min, x_max])
plt.ylim([y_min, y_max])
plt.locator_params("y", nbins=5)
plt.locator_params("x", nbins=5)
plt.xlabel("x", fontsize=15)
plt.ylabel("y", fontsize=15)
i += 1
plt.show()
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))
ax = Axes3D(fig)
plt.style.use("ggplot")
k1,b1 = np.meshgrid(k_list,b_list)
k1_r = k1.ravel()
b1_r = b1.ravel()
Loss = []
for k1_r,b1_r in zip(k1_r,b1_r):
y_hat = linear_model(x,k1_r,b1_r)
loss_r = loss_model(y_hat,y_label)
Loss.append(loss_r)
Loss = np.array(Loss)
Loss = Loss.reshape(20,20)
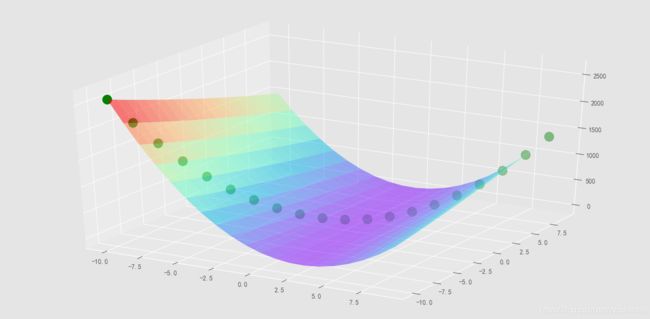
ax.scatter(k_list, b_list, loss_ ,color="g",s=200,label='parametric curve')
ax.plot_surface(k1, b1, Loss, rstride=1, cstride=1, cmap='rainbow',alpha=0.5)
plt.show()
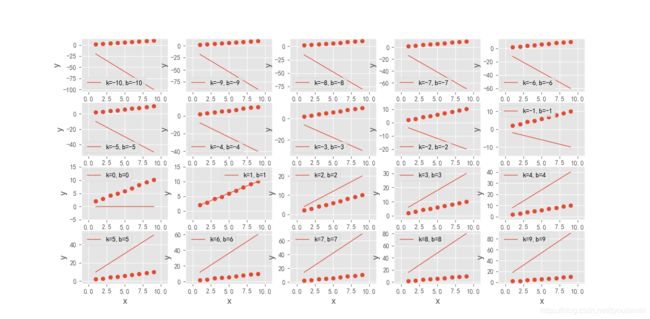
数据分布服从y = x+1
拟合方程为 y = kx + b
k,b取不同值时,拟合y = x+1程度不同
当k=1,b=1时,函数取到最小值时,
拟合情况最好,loss函数在不同的不同k,b下值取到最小