python不使用框架实现卷积神经网络识别手写数字
网络结构
项目下载地址
不使用框架实现全连接神经网络实现手写数字识别(layer封装好, 可以很好的扩展,修改)
- 第一个卷积层输入:2828、一通道、滤波器55个数为 6个、步长为1、不补零。
- 第一个卷积层输出:24*24、深度为6。
- 第一个池化层输入:2424、6通道、滤波器22,步长为2。
- 第一个池化层输出:12*12,深度为6。
- 第二个卷积层输入:1212,6通道,滤波器55个数为12个,步长为1,不补零。
- 第二个卷积层输出:8*8、深度为12.。
- 第二个池化层输入:88,12通道,滤波器22,步长为2。
- 第二个池化层输出: 44,深度为12,共44*12=192个像素。
- 第一个全连接层:输入为192,输出为10,10个节点,采用softmax激活函数,前面均采用双曲正切函数作为激活函数。
数据集
mnist数据集
t10k-images.idx3-ubyte
t10k-labels.idx1-ubyte
train-images.idx3-ubyte
train-labels.idx1-ubyte
下载
训练结果
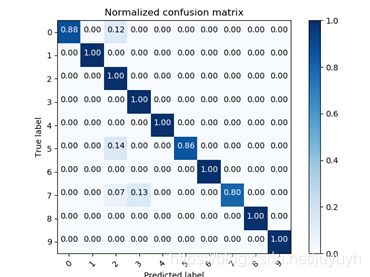
混淆矩阵
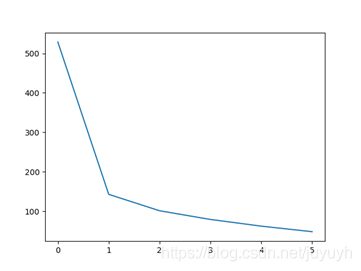
损失曲线
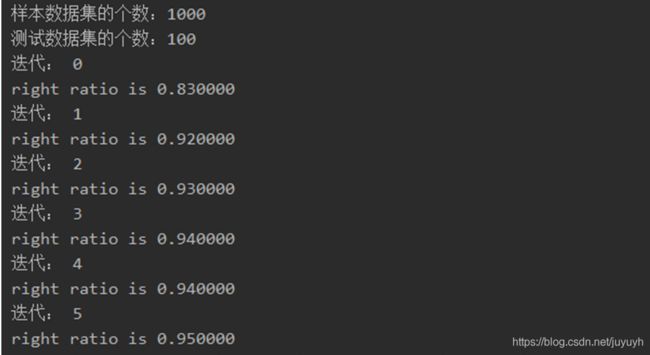
运行结果
# 使用全连接神经网络类,和手写数据加载器,实现验证码识别。
import numpy as np
import Activators # 引入激活器模块
import CNN # 引入卷积神经网络
import MNIST_loader # 引入手写数据加载器
import DNN # 引入全连接神经网络
# 网络模型类
class MNISTNetwork():
# =============================构造网络结构=============================
def __init__(self):
# 初始化构造卷积层:输入宽度、输入高度、通道数、滤波器宽度、滤波器高度、滤波器数目、补零数目、步长、激活器、学习速率
# 输入28*28 一通道,滤波器5*5的6个,步长为1,不补零,所以输出为24*24深度6
self.cl1 = CNN.ConvLayer(28, 28, 1, 5, 5, 6, 0, 1, Activators.TanhActivator(), 0.02)
# 构造降采样层,参数为输入宽度、高度、通道数、滤波器宽度、滤波器高度、步长
self.pl1 = CNN.MaxPoolingLayer(24, 24, 6, 2, 2, 2) # 输入24*24,6通道,滤波器2*2,步长为2,所以输出为12*12,深度保持不变为6
# 初始化构造卷积层:输入宽度、输入高度、通道数、滤波器宽度、滤波器高度、滤波器数目、补零数目、步长、激活器、学习速率
# 输入12*12,6通道,滤波器5*5的12个,步长为1,不补零,所以输出为8*8深度12
self.cl2 = CNN.ConvLayer(12, 12, 6, 5, 5, 12, 0, 1, Activators.TanhActivator(), 0.02)
# 构造降采样层,参数为输入宽度、高度、通道数、滤波器宽度、滤波器高度、步长
self.pl2 = CNN.MaxPoolingLayer(8, 8, 12, 2, 2, 2) # 输入8*8,12通道,滤波器2*2,步长为2,所以输出为4*4,深度保持不变为12。共192个像素
# 全连接层构造函数。input_size: 本层输入向量的维度。output_size: 本层输出向量的维度。activator: 激活函数
self.fl1 = DNN.FullConnectedLayer(192, 10, Activators.SoftmaxActivator(), 0.02) # 输入192个像素,输出为10种分类概率,学习速率为0.05
# 根据输入计算一次输出。因为卷积层要求的数据要求有通道数,所以onepic是一个包含深度,高度,宽度的多维矩阵
def forward(self, onepic): # 池化层不改变深度,只改变宽高 因为池化层的计算是一层一层的提取运算的
# print('图片:',onepic.shape)
self.cl1.forward(onepic) # 返回值6*24*24深度,高度,宽度 即self.cl1.output_array 卷积核为1*5*5 6*24*24
# print('第一层卷积结果:',self.cl1.output_array.shape)
self.pl1.forward(self.cl1.output_array) # 通过最大池化层后,深度不变仍为6 ,卷积核为 2*2 尺寸改变 self.pl1.output_array 6*12*12
# print('第一层采样结果:',self.pl1.output_array.shape)
self.cl2.forward(self.pl1.output_array) # 卷积核为 6*5*5 计算之后尺寸为 self.cl2.output_array 12*8*8
# print('第二层卷积结果:',self.cl2.output_array.shape)
self.pl2.forward(self.cl2.output_array) # 卷积核为 12*2*2 深度不变仍为12 计算之后尺寸为 self.pl2.output_array 12*4*4
# print('第二层采样结果:',self.pl2.output_array.shape)
# 转化为列向量 结果为12*4*4=192 a是个矩阵或者数组,a.flatten()就是把a降到一维,默认是按横的方向降
flinput = self.pl2.output_array.flatten().reshape(-1, 1)
# print(self.pl2.output_array.shape[0])
# print(self.pl2.output_array.shape[1])
# print(self.pl2.output_array.shape[2])
# print(len(flinput))
# print(flinput.shape)
self.fl1.forward(flinput) # flinput尺寸为192*1,全连接层的w是10*192
# print('全连接层结果:',self.fl1.output)#self.fl1.output尺寸为 10*1 因为经过了 W*t+b W为10*192
return self.fl1.output
def backward(self, onepic, labels):
# 计算误差
'''
output = tanh(z)
f'(z) = 1 - tanh(z)^2
delta = (y_pred - y)*f'(z)
'''
# 最后一层采用softmax函数
delta = labels - self.fl1.output
# 反向传播
self.fl1.backward(delta) # 计算了全连接层输入前的误差,以及全连接的w和b的梯度 误差传递公式 error_j=W.T点乘error_k self.fl1.delta=
self.fl1.update() # 更新全连接层的权重w和偏量b
# print('全连接层输入误差:', self.fl1.delta.shape)
sensitivity_array = self.fl1.delta.reshape(
self.pl2.output_array.shape) # 将误差转化为同等形状 self.pl2.output_array 形状为12*4*4
self.pl2.backward(self.cl2.output_array, sensitivity_array) # 计算第二采样层的输入误差。参数为第二采样层的 1、输入,2、输出误差
# print('第二采样层的输入误差:', self.pl2.delta_array.shape)
self.cl2.backward(self.pl1.output_array, self.pl2.delta_array,
Activators.TanhActivator()) # 计算第二卷积层的输入误差。参数为第二卷积层的 1、输入,2、输出误差,3、激活函数
self.cl2.update() # 更新权重w和偏量b 6*12*12 12*8*8
self.pl1.backward(self.cl1.output_array, self.cl2.delta_array) # 计算第一采样层的输入误差。参数为第一采样层的 1、输入,2、输出误差
self.cl1.backward1(onepic, self.pl1.delta_array,
Activators.TanhActivator()) # 计算第一卷积层的输入误差。参数为第一卷积层的 1、输入,2、输出误差,3、激活函数
self.cl1.update() # 更新权重w和偏量b
# print('第一卷积层的输入误差:', self.cl1.delta_array.shape)
# 由于使用了逻辑回归函数,所以只能进行分类识别。识别ont-hot编码的结果
if __name__ == '__main__':
# =============================加载数据集=============================
# 加载训练样本数据集,和one-hot编码后的样本标签数据集。样本数量越大,训练时间越久,也越准确
train_data_set, train_labels = MNIST_loader.get_training_data_set(1000, False)
# print(type(train_data_set))
# 加载测试特征数据集,和one-hot编码后的测试标签数据集。训练时间越久,也越准确
test_data_set, test_labels = MNIST_loader.get_test_data_set(100, False)
train_data_set = np.array(train_data_set).astype(bool).astype(int) # 可以将图片简化为黑白图片
train_labels = np.array(train_labels)
# 可以将图片简化为黑白图片 将数据转化为bool布尔型,True false 进而转化为0、1数据
test_data_set = np.array(test_data_set).astype(bool).astype(int)
test_labels = np.array(test_labels)
print('样本数据集的个数:%d' % len(train_data_set))
print('测试数据集的个数:%d' % len(test_data_set))
# =============================构造网络结构=============================
mynetwork = MNISTNetwork()
losses = []
# =============================迭代训练=============================
for i in range(6): # 迭代训练10次。每个迭代内,对所有训练数据进行训练,更新(训练图像个数/batchsize)次网络参数
print('迭代:', i)
# 使用每一个样本进行训练image.shape[0]#图片垂直尺寸image.shape[1]#图片水平尺寸image.shape[2]#图片通道数
loss = 0
for k in range(train_data_set.shape[0]):
# 正向计算
onepic = train_data_set[k]
onepic = np.array([onepic]) # 卷积神经网络要求的输入必须包含深度、高度、宽度三个维度。
result = mynetwork.forward(onepic) # 前向计算一次
# print(result.flatten())
labels = train_labels[k].reshape(-1, 1) # 获取样本输出,转化为列向量
# print(labels)
mynetwork.backward(onepic, labels)
s_max = result[np.argmax(result)]
loss += -1 * np.log(s_max)
losses.append(loss)
# =============================评估结果=============================
right = 0
for k in range(test_data_set.shape[0]): # 使用每一个样本进行训练
# 正向计算
onepic = test_data_set[k]
onepic = np.array([onepic]) # 卷积神经网络要求的输入必须包含深度、高度、宽度三个维度。
result = mynetwork.forward(onepic) # 前向计算一次
labels = test_labels[k].reshape(-1, 1) # 获取样本输出,转化为列向量
# print(result)
pred_type = result.argmax()
real_type = labels.argmax()
# print(pred_type,real_type)
if pred_type == real_type:
right += 1
print('right ratio is %f' % (right / test_data_set.shape[0])) # 打印输出正确率
# 画损失曲线
from CNN1 import paint_tools
print(losses)
paint_tools.paint_loss_curve(losses)
# 画混淆矩阵
cnf_matrix = np.array([
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
])
for k in range(test_data_set.shape[0]):
# 正向计算
onepic = test_data_set[k]
onepic = np.array([onepic])
result = mynetwork.forward(onepic)
labels = test_labels[k].reshape(-1, 1)
# print(result)
pred_type = result.argmax()
real_type = labels.argmax()
cnf_matrix[real_type][pred_type] += 1
class_names = ['0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9']
paint_tools.plot_confusion_matrix(cnf_matrix, classes=class_names, normalize=True, title='Normalized confusion matrix')
项目下载地址