kairosDB
kairosDB持续更新中…
最近工作需要开始接触kairosDB,其github网址为:[http://kairosdb.github.io/][6],在此我会在这记录一些操作与分享经验。
经过近大半个月的学习,基本的功能已经掌握,这几天会将这篇东西完成。
下面是我的环境说明
- 使用VMware上安装的Ubuntu操作系统
- **
- 因为才刚刚开始,所以内容会有些凌乱,随着研究深入会逐渐修改
- **
- KairosDB 可以使用cassandra、H2(开发环境中)作为后端存储。默认情况下,KairosDB运行在H2数据库下,开发环境不需要cassandra。
- **
- 在开始学习kairosDB之前如果对kairosDB没有一个大概认知的话,可以参考:[http://liubin.org/blog/2016/02/18/tsdb-intro/ ],了解一些关于TSDB的知识。
- **
- 这里是我的实验代码,有需要的可以参考:【https://github.com/congshenV/work/tree/master/kairosDB】
kairosDB概要
KairosDB是一个快速可靠的分布式时间序列数据库,主要用Cassandra来做底层存储,也可以使用H2。KairosDB是在OpenTSDB基础上重写的。 KairosDB主页: https://code.google.com/p/kairosdb/
- 其主要的功能如下:
1、可以获取基础设施和服务的实时状态信息,展示集群的各种软硬件错误,性能变化以及性能瓶颈。
2、可以衡量系统的SLA(服务类型、服务质量等),理解复杂系统间的相互作用,展示资源消耗情况。集群的整体作业情况,可以用以辅助预算和集群资源协调。
3、可以展示集群的主要性能瓶颈,经常出现的错误,从而可以着力重点解决重要问题。
- 组成
- Collectors——数据采集
数据可以通过多种协议写入KairosDB,比如Telnet的按行写入,HTTP API,Graphite以及批处理导入。此外,还可以使用或者自己编写插件。 - Storage——存储
KairosDB 采用了 Cassandra 作为数据存储方式,Cassandra 也是一个比较流行的NoSQL数据库,很多开源软件基于此数据库。 - REST API
KairosDB提供了REST API,以完成对metric名称,tag等的查询,当然,也少不了存储和查询数据点(data points)。 - WEB UI
KairosDB也提供了基于Web API的查询接口。 - Aggregators——聚合
作为数据分析系统,分组和聚合则是必不可少的功能。 KairosDB的聚合(也就是down samples)功能,支持的标准函数有min、max、sum、count、mean、histogram、gaps等,而且都非常实用。 - Tools——工具
KairosDB提供了进行数据导入导出的命令行工具。在kairosDB服务器上可进行命令行的导入导出操作,数据存储的内部指标可以监视服务器的性能 - Client library
KairosDB客户端是一个Java库,使用HttpClient类,可以简单地进行发送指标和查询KairosDB服务器。 - Plugins——插件
KairosDB也提供多种基于Guice的插件机制来进行扩展(数据点侦听器,数据存储器,协议处理程序等)。
- Collectors——数据采集
- 其他说明
KairosDB是从OpenTSDB fork过来的,因此最初它是支持HBase的,不过现在HBase已经不能完全支持KairosDB所需的特性,将来会取消对HBase的支持,不过如果只是做简单地实验,可以继续实验HBase。
安装
kairosDB运行需要安装java运行环境。java的安装可以比较简单,可以参考:
[http://blog.csdn.net/rchm8519/article/details/48721913 ]
在[https://github.com/kairosdb/kairosdb/releases ]中下载kairosDB最新版本的压缩包,然后tar -zxvf 到你想要放的地方,我放到了/usr/kairosdb/中。
到这里,安装就算完成了,接下来就是如何去使用这个kairosDB了。
使用kairosDB还需要配置存储方式,这是最重要的配置,默认是使用H2,如果是用H2那就不需要进行修改了。
-数据存储方式 kairosDB有几种后端数据存储方式。默认设置了内存H2数据库(java开发的关系型数据库)来存储,一般来说比较慢,可以通过修改conf/kairosdb.properties文件中的kairosdb.service.datastore属性来更改存储方式。
使用H2:kairosdb.service.datastore=org.kairosdb.datastore.h2.H2Module
使用Cassandra:kairosdb.service.datastore=org.kairosdb.datastore.cassandra.CassandraModule
默认情况下使用H2作为存储方式,进入bin/目录下,运行
./kairosdb.sh run #使用run是在前台显示服务执行过程,使用start是在后台执行,使用stop是关闭服务。可以通过可视界面查询一些kairosDB的数据,通过访问
http://localhost:8080/ #localhost改为kairosDB的服务器IP,如果是本地,就用localhost
看到有一篇讲kairosDB的安装的文章,也很清晰:
[http://blog.csdn.net/lzqs201314/article/details/51326623 ]
-文件句柄 当客户端数量较多,而句柄数量不足,可增加文件句柄数量
推送数据
这里使用了默认的H2数据库进行实例操作。
kairosDB可以使用telnet协议的4242端口或http的8080端口来推送数据(端口可以在kairosdb.properties文件中更改)。
#使用telnet写入数据,格式如下
#put <metric name> <time stamp> <value> <tag> <tag>... \n
echo "put test.cpu.1 1453109876000 0.32 host=test-1" |nc -w 30 127.0.0.1 4242
通过查询语句可以查到这条信息已经写入
#查询指标名称
curl http://localhost:8080/api/v1/metricnames | jq .这里对上面几个参数作一些简单地介绍,metric name就是指标名称,time stamp就是13位时间戳,value就是要监控的指标的值,tag就是标签,在查看数据时方便进行将数据区分。
nc指令就是向指定端口中传输数据,-w 30表示超时时间为30秒。
#使用http写入数据,在命令行下格式如下
curl -v -H "Content-type: application/json" -X POST http://localhost:8080/api/v1/datapoints -d '
> [{
> "name":"asd.redis.cpu.1",
> "timestamp":1453109876000,
> "type":"double",
> "value":0.32,
> "tags":{"host":"redus-test"}
> }]
> '
#示例中的例子:
curl -v -H "Content-type: application/json" -X POST http://localhost:8080/api/v1/datapoints -d'
[{
"name": "archive.file.tracked",
"timestamp": 1349109376,
"type": "long",
"value": 123,
"tags":{"host":"test"}
},
{
"name": "archive.file.search",
"timestamp": 999,
"type": "double",
"value": 32.1,
"tags":{"host":"test"}
}]
'
这里也对上面的参数进行简单介绍,name、timestamp、value、tags和telnet协议的意思一样。type确定数据的类型,这里默认有三种:long、double、string。
这里再详细介绍一下指标所包含的各个参数:
- Metric:一个可测量的单位的标称。metric不包括一个数值或一个时间,其仅仅是一个标签,包含数值和时间的叫datapoints,metric是用逗号连接的不允许有空格,例如:
kairosdb.datastore.xxx
kairosdb.jvm.xxx - Tags:一个metric应该描述什么东西被测量,通常的做法是用Tags来描述具有相同维度的metric。Tags由tagk和tagv组成,前者表示一个分组,后者表示一个特定的项。例如:
host=test - Timestamp:一个绝对时间,用来描述一个数值或者一个给定的metric是在什么时候定义的。
- Value:一个Value表示一个metric的实际数值。
在安装好kairosDB之后,kairosDB自带监控一些metric,下面就介绍下原有的指标内容:
- kairosdb.datastore.cassandra.key_query_time —— 从Cassandra查询行键的时间(以毫秒为单位)。
- kairosdb.datastore.query_collisions ——同时运行的相同查询请求的数量。(或者一个在另一个完成之前开始。)
- kairosdb.datastore.query_row_count —— The number of rows a query
retrieved data from.查询从中检索数据的行数。
- kairosdb.datastore.query_sample_size —— The number of data points a
query retrieves from Cassandra (before aggregation).查询从Cassandra(聚合前)检索的数据点的数量。
- kairosdb.datastore.query_time - The number of milliseconds to
retreive the data out of Cassandra for a query (not including key
lookup).从查询的Cassandra中检索数据的毫秒数(不包括键查找)。
- kairosdb.datastore.write_size - The number of data points written to
the data store during the last write.在上次写入期间写入数据存储的数据点数。
- kairosdb.http.ingest_count - The number of data points ingested via
HTTP since the last report.自上次报告以来通过HTTP提取的数据点数。
- kairosdb.http.ingest_time - The amount of time to ingest the number
of metrics from kairosdb.http.ingest_count. So ingest_count /
ingest_time is an average of how fast a single metric is inserted.从kairosdb.http.ingest_count获取度量标准的时间量。因此,ingest_count / ingest_time是单个指标插入速度的平均值。
- kairosdb.http.query_time - The amount of time a query takes from
processing the request to formating the response. Does not include
time to send data to client.查询从处理请求到形成响应所需的时间。不包括向客户端发送数据的时间。
- kairosdb.http.request_time - The total amount of time an HTTP request
takes from recieving data to sending response.HTTP请求从接收数据到发送响应所花费的总时间。
- kairosdb.jvm.free_memory - The amount of free memory available in the
JVM.JVM中可用的可用内存量。
- kairosdb.jvm.total_memory - The amount of total memory in the JVM.JVM中的总内存量。
- kairosdb.jvm.max_memory - The maximum amount of memory the JVM will
attempt to use.JVM将尝试使用的最大内存量。
- kairosdb.jvm.thread_count - The total number of threads running in
the JVM. JVM中运行的线程总数。
- kairosdb.metric_counters - Counts the number of data points received
since the last report. Tags are used to separate one metric from
another.计算自上次报告以来接收的数据点数。标签用于将一个指标与另一个指标分开。
- kairosdb.protocol.http_request_count - The number of HTTP requests
for each method. This includes a method tag that indicates the method
that was called. For example, method=query if a query was done.每个方法的HTTP请求数。这包括一个方法标记,指示被调用的方法。例如,如果查询已完成,method = query。
- kairosdb.protocol.telnet_request_count - The number of telnet
requests for each method. This includes a method tag that indicates
the method that called. For example, method=put if the put method was
called.每个方法的telnet请求数。这包括一个方法标签,指示被调用的方法。例如,如果put方法被调用,method = put。
Graphite协议,KairosDB现在支持Graphite纯文本和pickle协议。可以整合KairosDB现有的应用程序和推送到Graphite的数据。
自定义metric推送
上面介绍了推送数据的方法,这里我将做出一个自定义的metric实例。
自带的metric里面没有cpu的数据,这里做出一个cpu的metric。
#使用telnet写入数据,具体内容如下:
#!/bin/bash
set -e
metric_name="newdata.loadavg"
time_out=30
ip=127.0.0.1
port=4242
while true
do
cat /proc/loadavg |awk -v now=$(($(date +%s%N)/1000000)) -v host='yyc' \
'{print "put newdata.loadavg.1m " now " " $1 " host=" host;
print "put newdata.loadavg.5m " now " " $2 " host=" host;
print "put newdata.loadavg.15m " now " " $3 " host=" host }' | nc -w $time_out $ip $port
sleep 1
done
通过查询语句或者在web上可以访问写入的数据:
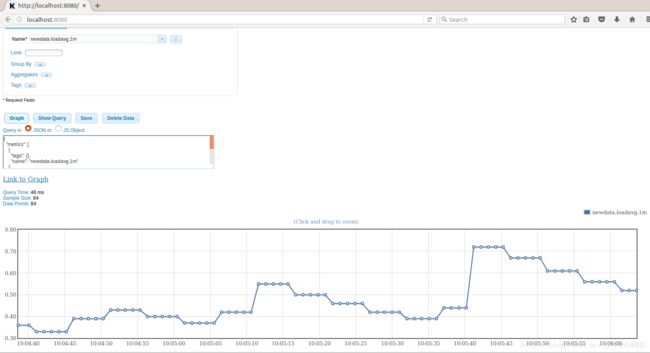
另外一个例子是cpu状态的
``` shell
#使用telnet写入数据:
#!/bin/bash
set -e
metric_name="newdata.stat"
time_out=30
ip=127.0.0.1
port=4242
while true
do
cat /proc/stat | grep cpu0 |awk -v now=$(($(date +%s%N)/1000000)) -v host='yyc' \
'{print "put newdata.stat " now " " ($2+$3+$4)/($2+$3+$4+$5) " host=" host }' | nc -w $time_out $ip $port
sleep 1
done
如果需要其他的系统数据,根据上面的脚本进行修改即可。
当然,如果需要长期进行监控,上面的脚本还需要进行修改,不再使用无限循环进行监控,改成使用crontab服务进行监控。
这里有一些python操作redis的实例:
https://github.com/paladini/kairosdb-examples-python
并且,也有python、php、java、node.js等语言的客户端封装,可以通过:【点击这里查看】找到相应的客户端进行安装使用。
此外,我也使用了python进行了开发,将redis 的一些数据进行监控。实例稍后再进行更新。。。
