Python计算机视觉编程 - 第四章 照相机模型与增强现实 -增强现实
1.以平面和标记物进行姿态估计
在第三章中,我们学习了如何从平面间估计单应性矩阵,若图像中包含平面状的标记物体,并且已经对照相机进行了标定,那么我们可以计算出照相机的姿态(旋转和平移)。我们使用照相机拍摄了两幅图像,两张图像都存在平面状的标记物体,先提取两幅图像的SIFT特征,然后使用RANSAC算法稳健估计单应性矩阵。通过单应性矩阵和照相机的标定矩阵,我们可以得出两个视图之间的相对变换。
代码:
from pylab import *
from PIL import Image
from OpenGL.GL import *
#If you have PCV installed, these imports should work
from PCV.geometry import homography, camera
from PCV.localdescriptors import sift
"""
This is the augmented reality and pose estimation cube example from Section 4.3.
"""
def cube_points(c, wid):
""" Creates a list of points for plotting
a cube with plot. (the first 5 points are
the bottom square, some sides repeated). """
p = []
# bottom
p.append([c[0]-wid, c[1]-wid, c[2]-wid])
p.append([c[0]-wid, c[1]+wid, c[2]-wid])
p.append([c[0]+wid, c[1]+wid, c[2]-wid])
p.append([c[0]+wid, c[1]-wid, c[2]-wid])
p.append([c[0]-wid, c[1]-wid, c[2]-wid]) #same as first to close plot
# top
p.append([c[0]-wid, c[1]-wid, c[2]+wid])
p.append([c[0]-wid, c[1]+wid, c[2]+wid])
p.append([c[0]+wid, c[1]+wid, c[2]+wid])
p.append([c[0]+wid, c[1]-wid, c[2]+wid])
p.append([c[0]-wid, c[1]-wid, c[2]+wid]) #same as first to close plot
# vertical sides
p.append([c[0]-wid, c[1]-wid, c[2]+wid])
p.append([c[0]-wid, c[1]+wid, c[2]+wid])
p.append([c[0]-wid, c[1]+wid, c[2]-wid])
p.append([c[0]+wid, c[1]+wid, c[2]-wid])
p.append([c[0]+wid, c[1]+wid, c[2]+wid])
p.append([c[0]+wid, c[1]-wid, c[2]+wid])
p.append([c[0]+wid, c[1]-wid, c[2]-wid])
return array(p).T
def my_calibration(sz):
"""
Calibration function for the camera (iPhone4) used in this example.
"""
row, col = sz
fx = 2555*col/2592
fy = 2586*row/1936
K = diag([fx, fy, 1])
K[0, 2] = 0.5*col
K[1, 2] = 0.5*row
return K
#compute features
sift.process_image('data/test4_f.JPG', 'im0.sift')
l0, d0 = sift.read_features_from_file('im0.sift')
sift.process_image('data/test4_p.JPG', 'im1.sift')
l1, d1 = sift.read_features_from_file('im1.sift')
#match features and estimate homography
matches = sift.match_twosided(d0, d1)
ndx = matches.nonzero()[0]
fp = homography.make_homog(l0[ndx, :2].T)
ndx2 = [int(matches[i]) for i in ndx]
tp = homography.make_homog(l1[ndx2, :2].T)
model = homography.RansacModel()
H, inliers = homography.H_from_ransac(fp, tp, model)
#camera calibration
K = my_calibration((747, 1000))
#3D points at plane z=0 with sides of length 0.2
box = cube_points([0.1, 0.1, 0.1], 0.1)
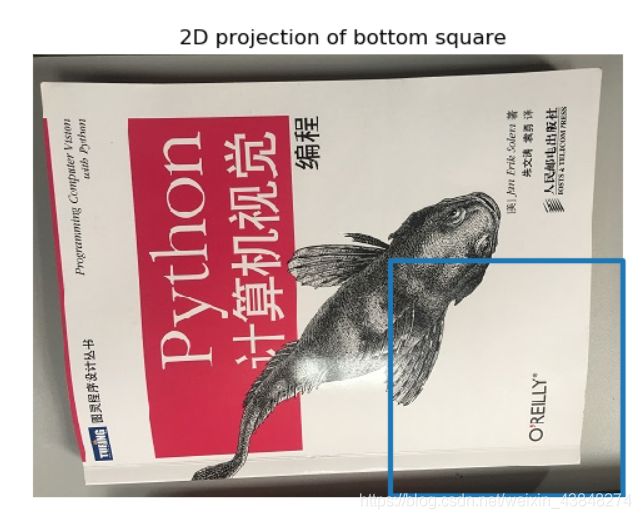
#project bottom square in first image
cam1 = camera.Camera(hstack((K, dot(K, array([[0], [0], [-1]])))))
#first points are the bottom square
box_cam1 = cam1.project(homography.make_homog(box[:, :5]))
#use H to transfer points to the second image
box_trans = homography.normalize(dot(H,box_cam1))
#compute second camera matrix from cam1 and H
cam2 = camera.Camera(dot(H, cam1.P))
A = dot(linalg.inv(K), cam2.P[:, :3])
A = array([A[:, 0], A[:, 1], cross(A[:, 0], A[:, 1])]).T
cam2.P[:, :3] = dot(K, A)
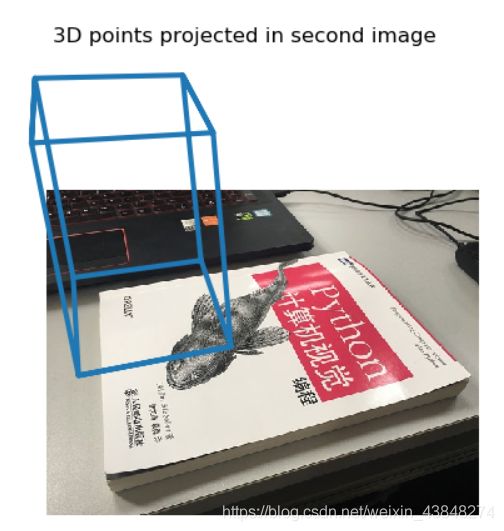
#project with the second camera
box_cam2 = cam2.project(homography.make_homog(box))
#plotting
im0 = array(Image.open('data/test4_f.JPG'))
im1 = array(Image.open('data/test4_p.JPG'))
figure()
imshow(im0)
plot(box_cam1[0, :], box_cam1[1, :], linewidth=3)
title('2D projection of bottom square')
axis('off')
figure()
imshow(im1)
plot(box_trans[0, :], box_trans[1, :], linewidth=3)
title('2D projection transfered with H')
axis('off')
figure()
imshow(im1)
plot(box_cam2[0, :], box_cam2[1, :], linewidth=3)
title('3D points projected in second image')
axis('off')
show()
2增强现实
在进行增强现实(AR)前,我们需要安装pygame和PyOpenGL 两个包。
pygame可直接使用pip install命令安装,但PyOpenGL默认安装32位,我们要手动下载64位下载地址然后在下载位置使用pip install (文件名.whl)进行安装
否则在运行时会出现错误:OpenGL.error.NullFunctionError: Attempt to call an undefined function glutInitDisplayMode…
代码:
import math
import pickle
from pylab import *
from OpenGL.GL import *
from OpenGL.GLU import *
from OpenGL.GLUT import *
import pygame, pygame.image
from pygame.locals import *
from PCV.geometry import homography, camera
from PCV.localdescriptors import sift
def cube_points(c, wid):
""" Creates a list of points for plotting
a cube with plot. (the first 5 points are
the bottom square, some sides repeated). """
p = []
# bottom
p.append([c[0]-wid, c[1]-wid, c[2]-wid])
p.append([c[0]-wid, c[1]+wid, c[2]-wid])
p.append([c[0]+wid, c[1]+wid, c[2]-wid])
p.append([c[0]+wid, c[1]-wid, c[2]-wid])
p.append([c[0]-wid, c[1]-wid, c[2]-wid]) #same as first to close plot
# top
p.append([c[0]-wid, c[1]-wid, c[2]+wid])
p.append([c[0]-wid, c[1]+wid, c[2]+wid])
p.append([c[0]+wid, c[1]+wid, c[2]+wid])
p.append([c[0]+wid, c[1]-wid, c[2]+wid])
p.append([c[0]-wid, c[1]-wid, c[2]+wid]) #same as first to close plot
# vertical sides
p.append([c[0]-wid, c[1]-wid, c[2]+wid])
p.append([c[0]-wid, c[1]+wid, c[2]+wid])
p.append([c[0]-wid, c[1]+wid, c[2]-wid])
p.append([c[0]+wid, c[1]+wid, c[2]-wid])
p.append([c[0]+wid, c[1]+wid, c[2]+wid])
p.append([c[0]+wid, c[1]-wid, c[2]+wid])
p.append([c[0]+wid, c[1]-wid, c[2]-wid])
return array(p).T
def my_calibration(sz):
row, col = sz
fx = 2555*col/2592
fy = 2586*row/1936
K = diag([fx, fy, 1])
K[0, 2] = 0.5*col
K[1, 2] = 0.5*row
return K
def set_projection_from_camera(K):
glMatrixMode(GL_PROJECTION)
glLoadIdentity()
fx = K[0,0]
fy = K[1,1]
fovy = 2*math.atan(0.5*height/fy)*180/math.pi
aspect = (width*fy)/(height*fx)
near = 0.1
far = 100.0
gluPerspective(fovy,aspect,near,far)
glViewport(0,0,width,height)
def set_modelview_from_camera(Rt):
glMatrixMode(GL_MODELVIEW)
glLoadIdentity()
Rx = np.array([[1,0,0],[0,0,-1],[0,1,0]])
R = Rt[:,:3]
U,S,V = np.linalg.svd(R)
R = np.dot(U,V)
R[0,:] = -R[0,:]
t = Rt[:,3]
M = np.eye(4)
M[:3,:3] = np.dot(R,Rx)
M[:3,3] = t
M = M.T
m = M.flatten()
glLoadMatrixf(m)
def draw_background(imname):
bg_image = pygame.image.load(imname).convert()
bg_data = pygame.image.tostring(bg_image,"RGBX",1)
glMatrixMode(GL_MODELVIEW)
glLoadIdentity()
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT)
glEnable(GL_TEXTURE_2D)
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D,glGenTextures(1))
glTexImage2D(GL_TEXTURE_2D,0,GL_RGBA,width,height,0,GL_RGBA,GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE,bg_data)
glTexParameterf(GL_TEXTURE_2D,GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER,GL_NEAREST)
glTexParameterf(GL_TEXTURE_2D,GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER,GL_NEAREST)
glBegin(GL_QUADS)
glTexCoord2f(0.0,0.0); glVertex3f(-1.0,-1.0,-1.0)
glTexCoord2f(1.0,0.0); glVertex3f( 1.0,-1.0,-1.0)
glTexCoord2f(1.0,1.0); glVertex3f( 1.0, 1.0,-1.0)
glTexCoord2f(0.0,1.0); glVertex3f(-1.0, 1.0,-1.0)
glEnd()
glDeleteTextures(1)
def draw_teapot(size):
glEnable(GL_LIGHTING)
glEnable(GL_LIGHT0)
glEnable(GL_DEPTH_TEST)
glClear(GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT)
glMaterialfv(GL_FRONT,GL_AMBIENT,[0,0,0,0])
glMaterialfv(GL_FRONT,GL_DIFFUSE,[0.5,0.0,0.0,0.0])
glMaterialfv(GL_FRONT,GL_SPECULAR,[0.7,0.6,0.6,0.0])
glMaterialf(GL_FRONT,GL_SHININESS,0.25*128.0)
glutSolidTeapot(size)
width,height = 1000,747
def setup():
pygame.init()
pygame.display.set_mode((width,height),OPENGL | DOUBLEBUF)
pygame.display.set_caption("OpenGL AR demo")
# compute features
sift.process_image('book_frontal.JPG', 'im0.sift')
l0, d0 = sift.read_features_from_file('im0.sift')
sift.process_image('book_perspective.JPG', 'im1.sift')
l1, d1 = sift.read_features_from_file('im1.sift')
# match features and estimate homography
matches = sift.match_twosided(d0, d1)
ndx = matches.nonzero()[0]
fp = homography.make_homog(l0[ndx, :2].T)
ndx2 = [int(matches[i]) for i in ndx]
tp = homography.make_homog(l1[ndx2, :2].T)
model = homography.RansacModel()
H, inliers = homography.H_from_ransac(fp, tp, model)
K = my_calibration((747, 1000))
cam1 = camera.Camera(hstack((K, dot(K, array([[0], [0], [-1]])))))
box = cube_points([0, 0, 0.1], 0.1)
box_cam1 = cam1.project(homography.make_homog(box[:, :5]))
box_trans = homography.normalize(dot(H,box_cam1))
cam2 = camera.Camera(dot(H, cam1.P))
A = dot(linalg.inv(K), cam2.P[:, :3])
A = array([A[:, 0], A[:, 1], cross(A[:, 0], A[:, 1])]).T
cam2.P[:, :3] = dot(K, A)
Rt=dot(linalg.inv(K),cam2.P)
setup()
draw_background("book_perspective.bmp")
set_projection_from_camera(K)
set_modelview_from_camera(Rt)
draw_teapot(0.05)
pygame.display.flip()
while True:
for event in pygame.event.get():
if event.type==pygame.QUIT:
sys.exit()
直接运行仍然报错
![]()
这个错误是freeglut和glut共存的缘故,它们俩定义了相同的方法,这个是动态链接库的重叠问题,找到你使用的python路径下\OpenGL\DLLS中的glut64.vcX.dll文件,将其余文件删除就可以了。vcX中的X因不同版本的OpenGL而不同,我的是vc14
我的文件路径如下
D:\Program Files\Python\Python36\Lib\site-packages\OpenGL\DLLS
完成这一切,你就可以将Python计算机视觉编程书上的效果实现了
但当我使用自己拍摄的如1中的图片时,python会停止工作
错误如下,万分抱歉,尚未得到解决
![]()


