【图像处理】NEON编程2 剩余数据处理
原文地址
在这里,我们将处理一种常见的问题:输入的数据不是向量长度的倍数,需要处理数组开头或者结尾的剩余数据时。这种情况下,NEON可以如何处理。
剩余数据
使用NEON通常都是操作长度为4到16位的数据向量。经常地,你将会发现数组并不是那些长度的倍数,你必须单独处理这些剩余的数据。
例如,你想要在每个迭代中用NEON加载、处理及存储8个数据,但是你的数组是21个数据长度。前两次的迭代都能够正常进行,但是第三个迭代中,只有5个数据需要处理时,应该怎么办。
问题解决
有三种方法可以处理这些剩余数据。根据不同的需求、性能及代码大小,每种方法都不尽相同。这些方法如下,速度越快的越靠前。
用更大的数组
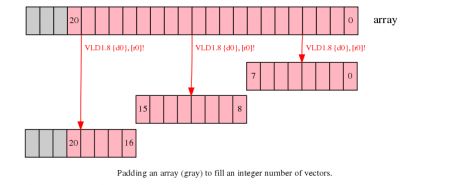
如果你能够改变你将要处理的数组的大小,用填充数据的方式增加数组大小至下一个向量大小的倍数。这可以让你在不影响邻近存储的情况下读取和写入数据。
在下面的例子中,增加数组大小至24个数据,使得第三次迭代可以完成。
需要注意的是
分配更大的数组会消耗更多的内存。如果有很多短数组,这样的分配会带来更多的消耗。
在末尾进行填充的数据需要被初始化,通常将其初始化为不影响计算结果的数据。例如,如果你在对数组进行求和,新的数据必须初始化为0。如果你在查找最小值,新的元素必须设置为最大值。
在一些情况下,初始化不影响填充数据可能不太好实现,如当需要查找数组数据的范围时。
代码
@ r0 = input array pointer
@ r1 = output array pointer
@ r2 = length of data in array
@ We can assume that the array length is greater than zero, is an integer
@ number of vectors, and is greater than or equal to the length of data
@ in the array.
add r2, r2, #7 @ add (vector length-1) to the data length
lsr r2, r2, #3 @ divide the length of the array by the length
@ of a vector, 8, to find the number of
@ vectors of data to be processed
loop:
subs r2, r2, #1 @ decrement the loop counter, and set flags
vld1.8 {d0}, [r0]! @ load eight elements from the array pointed to
@ by r0 into d0, and update r0 to point to the
@ next vector
...
... @ process the input in d0
...
vst1.8 {d0}, [r1]! @ write eight elements to the output array, and
@ update r1 to point to next vector
bne loop @ if r2 is not equal to 0, loop
重叠overlapping
如果操作允许的话,剩余数据可以通过重叠操作进行处理。这将使得一些数据被处理两次。
在上述的例子中,第一次迭代将处理0到7的数据,第二次迭代处理5到12,第三次迭代处理13到20.需要注意5到7的数据被处理了两次。
需要注意的是
重叠操作只有在数据不受访问次数的影响时才能被使用,该操作必须是幂等性的。如,当你需要在数组中查找最大值的时候,可以使用这种策略。当你需要对一个数组进行求和时,重叠的数据会被重复计算。
数据的个数必须至少能够填充一个完整的向量。
代码
@ r0 = input array pointer
@ r1 = output array pointer
@ r2 = length of data in array
@ We can assume that the operation is idempotent, and the array is greater
@ than or equal to one vector long.
ands r3, r2, #7 @ calculate number of elements left over after
@ processing complete vectors using
@ data length & (vector length - 1)
beq loopsetup @ if the result of the ands is zero, the length
@ of the data is an integer number of vectors,
@ so there is no overlap, and processing can begin
@ at the loop
@ handle the first vector separately
vld1.8 {d0}, [r0], r3 @ load the first eight elements from the array,
@ and update the pointer by the number of elements
@ left over
...
... @ process the input in d0
...
vst1.8 {d0}, [r1], r3 @ write eight elements to the output array, and
@ update the pointer
@ now, set up the vector processing loop
loopsetup:
lsr r2, r2, #3 @ divide the length of the array by the length
@ of a vector, 8, to find the number of
@ vectors of data to be processed
@ the loop can now be executed as normal. the
@ first few elements of the first vector will
@ overlap with some of those processed above
loop:
subs r2, r2, #1 @ decrement the loop counter, and set flags
vld1.8 {d0}, [r0]! @ load eight elements from the array, and update
@ the pointer
...
... @ process the input in d0
...
vst1.8 {d0}, [r1]! @ write eight elements to the output array, and
@ update the pointer
bne loop @ if r2 is not equal to 0, loop
单个数据处理
NEON提供了能够在向量中处理单个数据的加载及存储指令。通过这些,你可以加载一个包含一个数据的向量,进行操作,并且写入内存中。
在上述的例子中,前两次的迭代都正常进行,处理0到7,8到15的数据。第三次迭代需要处理5个数据,可以在一个单独的循环中进行处理,每次循环处理一个数据。
需要注意的是
该方法比前面的方法都慢,因为每个数据必须被单独的加载、处理和存储。
处理剩余数据需要两次循环,一次以向量为单位,第二次以单个数据为单位。这将增大代码大小。
NEON单数据加载只改变目标数据的值而不影响其他数据。如果你在向量化的计算中涉及到操作向量的指令,如VPADD,寄存器在加载第一个单数据时必须被初始化。
代码
@ r0 = input array pointer
@ r1 = output array pointer
@ r2 = length of data in array
lsrs r3, r2, #3 @ calculate the number of complete vectors to be
@ processed and set flags
beq singlesetup @ if there are zero complete vectors, branch to
@ the single element handling code
@ process vector loop
vectors:
subs r3, r3, #1 @ decrement the loop counter, and set flags
vld1.8 {d0}, [r0]! @ load eight elements from the array and update
@ the pointer
...
... @ process the input in d0
...
vst1.8 {d0}, [r1]! @ write eight elements to the output array, and
@ update the pointer
bne vectors @ if r3 is not equal to zero, loop
singlesetup:
ands r3, r2, #7 @ calculate the number of single elements to process
beq exit @ if the number of single elements is zero, branch
@ to exit
@ process single element loop
singles:
subs r3, r3, #1 @ decrement the loop counter, and set flags
vld1.8 {d0[0]}, [r0]! @ load single element into d0, and update the
@ pointer
...
... @ process the input in d0[0]
...
vst1.8 {d0[0]}, [r1]! @ write the single element to the output array,
@ and update the pointer
bne singles @ if r3 is not equal to zero, loop
exit:
更深入的思考
起始还是结束
重叠和单数据处理技术能够应用在数组的起始和结束,上面的代码能够根据需要修改。
对齐
加载和存储地址必须对齐到cache,允许更有效的内存存取。
在Cortex-A8这要求至少16字的对齐。如果无法对输入和输出数组进行对齐,你就必须处理数组最开始的部分(需要对齐的部分)及结尾的部分(未完成的向量)。
当对齐数据访问时,记得在加载及存储指令中使用:64 或者:128 或者:256地址限定符来优化性能。你可以对比需要处理加载和存储的时钟周期的个数,使用在 Technical Reference Manual 中的数据。
Here’s the relevant page in the Cortex-A8 TRM.
使用ARM进行修复
在单个数据中,你可以使用ARM指令对每个数据进行操作。然而,用ARM和NEON指令存储到内存的相同区域会降低性能,ARM流水线会被阻塞直到NEON流水线的完成。
一般地,你在代码中可以避免写到相同的内存。