判断字符串是否为空的org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils类方法isBlank()源码查看
转发请注明出处与作者。个人分析的,正确性欢迎大家一起探讨,有错误还希望指正和批评
首先说结论:isBlank() 会把制表符(tab键 \t,换行符 \n ,回车键等一系列字符格式的unicode编码)等作为空来处理;而我们平时使用的 if(s == null ||"".equals(s)); 不会把特殊字符作为空处理。
判断字符串是否为空,有很多种方法,下面是其中一种:
if(s == null ||"".equals(s));
但这样写看起来是不能从代码本身看到代码本身的业务含义,于是很多追求代码可读性的代码编写者会使用org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils类的isBlank()方法。该方法一看就知道代码是在判断是不是空,但该方法的存在难道只是为了可读性吗?这个方法仅仅是封装了下判断逻辑吗,还是还有其他的优势?为了搞懂这个问题,我查找了下源代码。
/**
* Checks if a CharSequence is whitespace, empty ("") or null.
*
*
* StringUtils.isBlank(null) = true
* StringUtils.isBlank("") = true
* StringUtils.isBlank(" ") = true
* StringUtils.isBlank("bob") = false
* StringUtils.isBlank(" bob ") = false
*
*
* @param cs the CharSequence to check, may be null
* @return {@code true} if the CharSequence is null, empty or whitespace
* @since 2.0
* @since 3.0 Changed signature from isBlank(String) to isBlank(CharSequence)
*/
public static boolean isBlank(CharSequence cs) {
int strLen;
if (cs == null || (strLen = cs.length()) == 0) {
return true;
}
for (int i = 0; i < strLen; i++) {
if (Character.isWhitespace(cs.charAt(i)) == false) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}该方法的形参,是CharSequence类型,我们判断的是字符串,却用了这个类型接收。我们先看下该类型是类还是接口。
通过api查找,jdk7在线文档,可以看到,CharSequence是java.long包下的接口。那么按照向上转型的原理,我们可以猜测,字符串实现了该接口。查看api 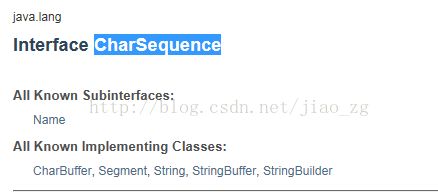
确实是String实现了该接口。
读到这里,就可以判断,isBlank()方法不仅是通过简单的封装了 if(s == null ||"".equals(s));这个逻辑实现可读性而存在的。
那么这样做的原因还有什么?我继续看了下源码实现:
int strLen;
if (cs == null || (strLen = cs.length()) == 0) {
return true;
}这一步,先判断CharSequence对象是不是null,如果是null,那么肯定是空,就不需要判断长度,直接返回true,表示字符串是空;如果不是null,那么就判断长度,如果长度是0,那么也返回true,表示字符串是空。
判断字符串是否是null这种情况两种实现方式都有判断。那么这两种实现方式是否是完全等价的?
"".equals(s)这个判断,跟后面一系列的判断是否本质上是一样的呢?
我继续查看了下String的equals()方法。
/**
* Compares this string to the specified object. The result is {@code
* true} if and only if the argument is not {@code null} and is a {@code
* String} object that represents the same sequence of characters as this
* object.
*
* @param anObject
* The object to compare this {@code String} against
*
* @return {@code true} if the given object represents a {@code String}
* equivalent to this string, {@code false} otherwise
*
* @see #compareTo(String)
* @see #equalsIgnoreCase(String)
*/
public boolean equals(Object anObject) {
if (this == anObject) {
return true;
}
if (anObject instanceof String) {
String anotherString = (String) anObject;
int n = value.length;
if (n == anotherString.value.length) {
char v1[] = value;
char v2[] = anotherString.value;
int i = 0;
while (n-- != 0) {
if (v1[i] != v2[i])
return false;
i++;
}
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
equals方法的判断,是先判断是不是同一个引用,如果引用相同,那么直接返回true。( 这里可以看到,对于String类型变量,同一个引用地址,指向的是同一个对象。这个容易理解,不可能指向的同一块内存地址了,还不是同一个对象。但反过来,相同的对象,不一定存放在同一块内存地址中)。接着判断传递过来的对象是不是String类型,即便是StringBuffer或者StringBuilder也不行,因为StringBuffer和String都实现了 CharSequence,但两者并不存在继承关系。如果不是,直接返回false。只有是string类型的对象,才会进行比较。然后比较两个字符串的长度,如果不同,返回false,表示不是同一个字符串。如果长度相同,再转换为字符,挨个比较字符。
看一下这段代码
while (n-- != 0) {
if (v1[i] != v2[i])
return false;
i++;
}之前知道,判断为空,"".equals(str) 这种比str.equals("")效率要高。这里可以看到,如果判断为空的情况,"".equals(str)不会进入循环,而后者会进入循环判断一下。如果字符串的各个字符都相同,就认为是相同的字符串。
上面对equals的判断,我们可以看到,对于"".equals(str)判断,就是根据类型和长度进行判断是否是空的。
那么再继续看isBlank()方法后续的实现:
for (int i = 0; i < strLen; i++) {
if (Character.isWhitespace(cs.charAt(i)) == false) {
return false;
}
}首先判断长度,如果长度是0,直接返回是空;如果长度不为0,那么依次判断字符是否是表示空格的字符,继续查看
isWhitespace()方法:
/**
* Determines if the specified character (Unicode code point) is
* white space according to Java. A character is a Java
* whitespace character if and only if it satisfies one of the
* following criteria:
*
* - It is a Unicode space character ({@link #SPACE_SEPARATOR},
* {@link #LINE_SEPARATOR}, or {@link #PARAGRAPH_SEPARATOR})
* but is not also a non-breaking space ({@code '\u005Cu00A0'},
* {@code '\u005Cu2007'}, {@code '\u005Cu202F'}).
*
- It is {@code '\u005Ct'}, U+0009 HORIZONTAL TABULATION.
*
- It is {@code '\u005Cn'}, U+000A LINE FEED.
*
- It is {@code '\u005Cu000B'}, U+000B VERTICAL TABULATION.
*
- It is {@code '\u005Cf'}, U+000C FORM FEED.
*
- It is {@code '\u005Cr'}, U+000D CARRIAGE RETURN.
*
- It is {@code '\u005Cu001C'}, U+001C FILE SEPARATOR.
*
- It is {@code '\u005Cu001D'}, U+001D GROUP SEPARATOR.
*
- It is {@code '\u005Cu001E'}, U+001E RECORD SEPARATOR.
*
- It is {@code '\u005Cu001F'}, U+001F UNIT SEPARATOR.
*
*
*
* @param codePoint the character (Unicode code point) to be tested.
* @return {@code true} if the character is a Java whitespace
* character; {@code false} otherwise.
* @see Character#isSpaceChar(int)
* @since 1.5
*/
public static boolean isWhitespace(int codePoint) {
return CharacterData.of(codePoint).isWhitespace(codePoint);
}
注释全是unicode编码, 看不懂,继续查看,
// Character <= 0xff (basic latin) is handled by internal fast-path
// to avoid initializing large tables.
// Note: performance of this "fast-path" code may be sub-optimal
// in negative cases for some accessors due to complicated ranges.
// Should revisit after optimization of table initialization.
static final CharacterData of(int ch) {
if (ch >>> 8 == 0) { // fast-path
return CharacterDataLatin1.instance;
} else {
switch(ch >>> 16) { //plane 00-16
case(0):
return CharacterData00.instance;
case(1):
return CharacterData01.instance;
case(2):
return CharacterData02.instance;
case(14):
return CharacterData0E.instance;
case(15): // Private Use
case(16): // Private Use
return CharacterDataPrivateUse.instance;
default:
return CharacterDataUndefined.instance;
}
}
}往下再继续看,就是字符编码的处理了,看不懂了。回头看下api文档,
- It is a Unicode space character (
SPACE_SEPARATOR,LINE_SEPARATOR, orPARAGRAPH_SEPARATOR) but is not also a non-breaking space ('\u00A0','\u2007','\u202F'). - It is
'\t', U+0009 HORIZONTAL TABULATION. - It is
'\n', U+000A LINE FEED. - It is
'\u000B', U+000B VERTICAL TABULATION. - It is
'\f', U+000C FORM FEED. - It is
'\r', U+000D CARRIAGE RETURN. - It is
'\u001C', U+001C FILE SEPARATOR. - It is
'\u001D', U+001D GROUP SEPARATOR. - It is
'\u001E', U+001E RECORD SEPARATOR. - It is
'\u001F', U+001F UNIT SEPARATOR.
public class BlankTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
char c = '\n';
String str = String.valueOf(c);
System.out.println(str.length());
String ss = "a"+str+"dd";
System.out.println(ss);
}
}1
a
ddpublic class BlankTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("换行符是否是空字符:"+newLineCharIsOrNotBlank());
}
public static boolean newLineCharIsOrNotBlank(){
return "".equals('\n');
}
} public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("s==null||\"\".equals('\\n')换行符是否是空字符:"+newLineCharIsOrNotBlank(String.valueOf('\n')));
System.out.println("isBlank()判断换行符是否是空字符:"+StringUtils.isBlank(String.valueOf('\n')));
}
public static boolean newLineCharIsOrNotBlank(String s){
return s==null||"".equals('\n');
}结果:
isBlank()判断换行符是否是空字符:true