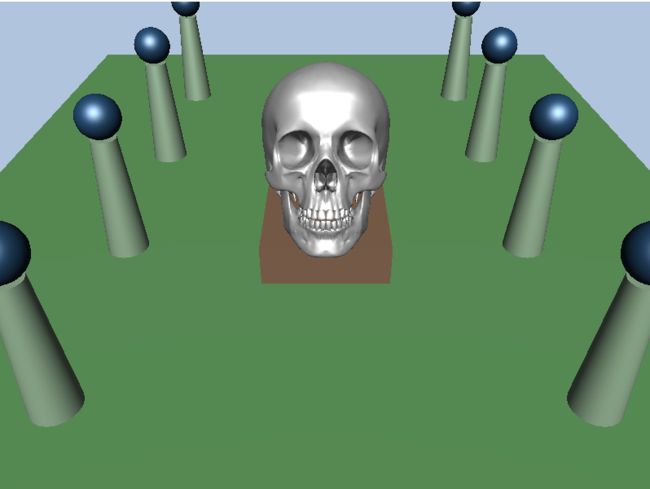
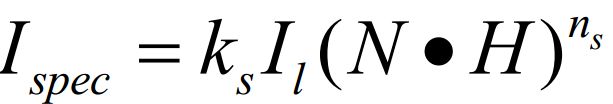三种光照模型的渲染对比
这几天在看《GPU 编程与CG 语言之阳春白雪下里巴人》,看到光照模型那部分,便根据书上的内容作了一下实验
进行对比的三种光照模型分别如下:
Phong模型,对应计算的数学公式如下
Blinn-phong 模型,对应计算的数学公式如下
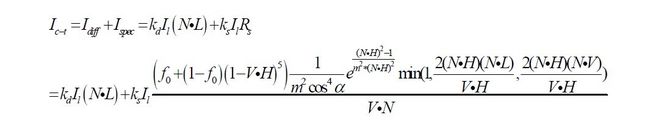
Cook-Torrance 模型,对应计算的数学公式如下
关于上述的数学模型解析叙述可以参考前面的两篇博客 简单的光照模型,三种光照模型的计算
下面是shader实现的光照效果
Phong模型
Blinn-phong 模型
Cook-Torrance 模型
从上面的3张图效果可以知道,而且一般来说Cook-Torrance 模型实现的效果最为真实,贴近现实,接着是Phong模型,然后就是Blinn-phong 模型(贴近艺术性)。当然,Blinn-phong 模型无疑是效率最高的,而Cook-Torrance 模型便是效率最低的。
代码
(基于《Introduction to 3D Game Programming with DirectX 11》的LitSkull Demo修改)
//=============================================================================
// Basic.fx by Frank Luna (C) 2011 All Rights Reserved.
//
// Basic effect that currently supports transformations, lighting, and texturing.
//=============================================================================
#include "LightingHelper.fx"
cbuffer cbPerFrame
{
DirectionalLight gDirLights[3];
float3 gEyePosW;
float gFogStart;
float gFogRange;
float4 gFogColor;
};
cbuffer cbPerObject
{
float4x4 gWorld;
float4x4 gWorldInvTranspose;
float4x4 gWorldViewProj;
float4x4 gTexTransform;
Material gMaterial;
};
// Nonnumeric values cannot be added to a cbuffer.
Texture2D gDiffuseMap;
SamplerState samAnisotropic
{
Filter = ANISOTROPIC;
MaxAnisotropy = 4;
AddressU = WRAP;
AddressV = WRAP;
};
struct VertexIn
{
float3 PosL : POSITION;
float3 NormalL : NORMAL;
};
struct VertexOut
{
float4 PosH : SV_POSITION;
float3 PosW : POSITION;
float3 NormalW : NORMAL;
};
VertexOut VS(VertexIn vin)
{
VertexOut vout;
// Transform to world space space.
vout.PosW = mul(float4(vin.PosL, 1.0f), gWorld).xyz;
vout.NormalW = mul(vin.NormalL, (float3x3)gWorldInvTranspose);
// Transform to homogeneous clip space.
vout.PosH = mul(float4(vin.PosL, 1.0f), gWorldViewProj);
return vout;
}
float4 PS(VertexOut pin, uniform int gLightCount) : SV_Target
{
// Interpolating normal can unnormalize it, so normalize it.
pin.NormalW = normalize(pin.NormalW);
// The toEye vector is used in lighting.
float3 toEye = gEyePosW - pin.PosW;
// Cache the distance to the eye from this surface point.
float distToEye = length(toEye);
// Normalize.
toEye /= distToEye;
//
// Lighting.
//
// Start with a sum of zero.
float4 ambient = float4(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
float4 diffuse = float4(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
float4 spec = float4(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
// Sum the light contribution from each light source.
[unroll]
for(int i = 0; i < gLightCount; ++i)
{
float4 A, D, S;
/*ComputeDirectionalLight(gMaterial, gDirLights[i], pin.NormalW, toEye,
A, D, S);*/
CookTorrance(gMaterial, gDirLights[i], pin.PosW, pin.NormalW, toEye,
A, D, S);
ambient += A;
diffuse += D;
spec += S;
}
float4 litColor = ambient + diffuse + spec;
// Common to take alpha from diffuse material.
litColor.a = gMaterial.Diffuse.a;
return litColor;
}
technique11 Light1
{
pass P0
{
SetVertexShader( CompileShader( vs_5_0, VS() ) );
SetGeometryShader( NULL );
SetPixelShader( CompileShader( ps_5_0, PS(1) ) );
}
}
technique11 Light2
{
pass P0
{
SetVertexShader( CompileShader( vs_5_0, VS() ) );
SetGeometryShader( NULL );
SetPixelShader( CompileShader( ps_5_0, PS(2) ) );
}
}
technique11 Light3
{
pass P0
{
SetVertexShader( CompileShader( vs_5_0, VS() ) );
SetGeometryShader( NULL );
SetPixelShader( CompileShader( ps_5_0, PS(3) ) );
}
}LightingHelper.fx
struct DirectionalLight
{
float4 Ambient; //环境光数值
float4 Diffuse; //散射光数值
float4 Specular; //平面光数值
float3 Direction; //直线方向
float pad;
};
struct PointLight
{
float4 Ambient; //环境光数值
float4 Diffuse; //散射光数值
float4 Specular; //高光数值
float3 Position; //光源位置
float Range; //照射访问
float3 Att; //衰减值
float pad;
};
struct SpotLight
{
float4 Ambient; //环境光数值
float4 Diffuse; //散射光数值
float4 Specular; //高光数值
float3 Position; //光源位置
float Range; //衰减值
float3 Direction; //照射方向
float Spot; //聚光强度系数
float3 Att; //衰减值
float pad;
};
struct Material
{
float4 Ambient; //环境光数值
float4 Diffuse; //散射光数值
float4 Specular; //高光数值
float4 Reflect; //反射数值
};
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// 通过直线光的光照公式计算,环境光、漫反射、平面光的数值
//
// 需要分开输出三者的数值,因为我们后面需要单独修改这些值
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void ComputeDirectionalLight(Material mat, DirectionalLight L,
float3 normal, float3 toEye,//"顶点->眼"向量
out float4 ambient, out float4 diffuse, out float4 spec)
{
//初始化
ambient = float4(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
diffuse = float4(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
spec = float4(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
//光照方向与光源方向相反
float3 lightVec = normalize(-L.Direction);
//处理环境光数值
ambient = mat.Ambient*L.Ambient;
//计算漫反射和镜面反射,给物体表面提供光照
//求漫反射,注意两向量归一化
diffuse = max(dot(lightVec, normal), 0) * mat.Diffuse * L.Diffuse;;
//Phong 光照模型渲染
float3 v = reflect(-lightVec, normal);
float specFactor = pow(max(dot(v, toEye), 0.0f), mat.Specular.w);
//Blinn-phong 光照模型渲染
/*float3 h = normalize(lightVec + toEye);
float specFactor = pow(max(dot(h, normal), 0.0f), mat.Specular.w);*/
spec = specFactor * mat.Specular * L.Specular;
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Cook-Torrance 光照模型渲染
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void CookTorrance(Material mat, DirectionalLight l,
float3 position, float3 normal, float3 toEye,//"顶点->眼"向量
out float4 ambient, out float4 diffuse, out float4 spec)
{
//初始化
ambient = float4(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
diffuse = float4(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
spec = float4(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
float3 P = position.xyz;
float3 N = normal.xyz;
//光照方向与光源方向相反
float3 lightVec = -l.Direction;
float3 L = normalize(lightVec);
//处理环境光数值
ambient = mat.Ambient*l.Ambient;
float nl = max(dot(L, N), 0);
//计算漫反射
diffuse = nl * mat.Diffuse * l.Diffuse;
// Cook-Torrance 光照模型渲染
float3 V = toEye;
float3 H = normalize(L + V);
float nv = dot(N, V);
if (nv > 0 && nl > 0)
{
float nh = dot(N, H);
float m = 0.3;
float temp = (nh*nh - 1) / (m*m*nh*nh);
float roughness = (exp(temp)) / (pow(m, 2)*pow(nh, 4));//粗糙度,根据 beckmann 函数
float vh = dot(V, H);
float a = (2 * nh*nv) / vh;
float b = (2 * nh*nl) / vh;
float geometric = min(a, b);
geometric = min(1, geometric);//几何衰减系数
float f = 0.125;
float fresnelCoe = f + (1 - f)*pow(1 - vh, 5);fresnel 反射系数
float rs = (fresnelCoe*roughness*geometric) / (nv*nl);
spec = rs * nl * mat.Specular * l.Specular;
}
}