LeetCode 64. 最小路径和
LeetCode 64. 最小路径和
题目来源
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/minimum-path-sum/
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
题目描述
给定一个包含非负整数的 m x n 网格,请找出一条从左上角到右下角的路径,使得路径上的数字总和为最小。
说明:每次只能向下或者向右移动一步。
示例 1:
输入:
[
[1,3,1],
[1,5,1],
[4,2,1]
]
输出: 7
解释: 因为路径 1→3→1→1→1 的总和最小。
解法一:递归
首先定义递归方法:
int process(int[][] grid, int row, int col)
其含义为:当前位置在row行,col列,返回到达右下角的最小路径和。
接下来考虑:
- 当前位置在右下角时,最小路径和=右下角的值。
- 当前位置在最后一行时,最小路径和=当前值+右侧最小路径和。
- 当前位置在最后一列时,最小路径和=当前值+下侧最小路径和。
- 当前位置不属于上述情况时,最小路径和=当前值+右侧最小路径和 与 下侧最小路径和 中较小的哪一个。
由此递归方法可以写出:
/**
* 当前位置在row行,col列,返回到达右下角的最小路径
*/
private int process(int[][] grid, int row, int col) {
// 当前位置在右下角,最小路径是当前位置的数字
if (row == grid.length - 1 && col == grid[0].length - 1) {
return grid[row][col];
}
// 当前位置在最后一列,最小路径是当前位置的数字+右边的最小路径
if (row == grid.length - 1) {
return grid[row][col] + process(grid, row, col + 1);
}
// 当前位置在最后一行,最小路径是当前位置的数字+下边的最小路径
if (col == grid[0].length - 1) {
return grid[row][col] + process(grid, row + 1, col);
}
// 其余情况,最小路径是当前位置的数字+右侧或者下侧两者中最小的最小路径
return grid[row][col] + Math.min(process(grid, row, col + 1), process(grid, row + 1, col));
}
解法二:记忆化搜索
首先分析解法一中的递归方法:
int process(int[][] grid, int row, int col)
首先递归会寻找row=0,col=0的结果,
接下来递归函数进行展开,会依次寻找0,1和1,0的结果
……
用图来表示:

可以看到递归方法类似于二叉树的展开过程,
其中存在大量的重复情况,例如图中绿色、红色和橙色标注的部分。
记忆化搜索就是讲已经找到的结果记录下来,来避免重复。
接下来思考递归方法中的参数:
其中grid是永远不变的,row和col的含义是行和列,因此row和col的范围也可以确定,
row的范围是0~grid.length-1
col的范围是0~gird[0].length-1
由此可以通过一个二维数组来记录递归方法的返回值。
修改代码如下:
public int minPathSum(int[][] grid) {
storage = new int[grid.length][grid[0].length];
for (int[] ints : storage) {
Arrays.fill(ints, -1);
}
return process(grid, 0, 0);
}
private int[][] storage;
/**
* 当前位置在row行,col列,返回到达右下角的最小路径
*/
private int process(int[][] grid, int row, int col) {
if (storage[row][col] != -1) {
return storage[row][col];
}
// 当前位置在右下角,最小路径是当前位置的数字
if (row == grid.length - 1 && col == grid[0].length - 1) {
storage[row][col] = grid[row][col];
return storage[row][col];
}
// 当前位置在最后一列,最小路径是当前位置的数字+右边的最小路径
if (row == grid.length - 1) {
storage[row][col] = grid[row][col] + process(grid, row, col + 1);
return storage[row][col];
}
// 当前位置在最后一行,最小路径是当前位置的数字+下边的最小路径
if (col == grid[0].length - 1) {
storage[row][col] = grid[row][col] + process(grid, row + 1, col);
return storage[row][col];
}
// 其余情况,最小路径是当前位置的数字+右侧或者下侧两者中最小的最小路径
storage[row][col] = grid[row][col] + Math.min(process(grid, row, col + 1), process(grid, row + 1, col));
return storage[row][col];
}
解法三:动态规划
示例一中给出的数组:
[
[1,3,1],
[1,5,1],
[4,2,1]
]
通过记忆化搜索我们可以得到一张二维表:
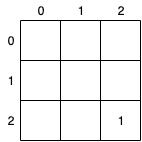
首先考虑一下解法一中的第一种情况:
当前位置在右下角时,最小路径和=右下角的值。
因此矩阵中右下角可以填充上1。
接下来按照解法一的第二种情况和第三种情况依次可以填充最后一行和最后一列。

接下来按照解法一的第四种情况从下往上,从右往左填充:

最终返回(0,0)处的结果即为答案。
private int dp(int[][] grid) {
int[][] dp = new int[grid.length][grid[0].length];
// 最后一个位置
dp[grid.length - 1][grid[0].length - 1] = grid[grid.length - 1][grid[0].length - 1];
// 最后一行
for (int i = grid[0].length - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
dp[grid.length - 1][i] = dp[grid.length - 1][i + 1] + grid[grid.length - 1][i];
}
// 最后一列
for (int i = grid.length - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
dp[i][grid[0].length - 1] = dp[i + 1][grid[0].length - 1] + grid[i][grid[0].length - 1];
}
for (int i = grid.length - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
for (int j = grid[0].length - 2; j >= 0; j--) {
dp[i][j] = Math.min(dp[i][j + 1], dp[i + 1][j]) + grid[i][j];
}
}
return dp[0][0];
}