参考资料:
https://morvanzhou.github.io/
非常感谢莫烦老师的教程
http://mnemstudio.org/path-finding-q-learning-tutorial.htm
http://www.cnblogs.com/dragonir/p/6224313.html
这篇文章也是用非常简单的说明将 Q-Learning 的过程给讲解清楚了
http://www.cnblogs.com/jinxulin/tag/%E5%A2%9E%E5%BC%BA%E5%AD%A6%E4%B9%A0/
还有感谢这位园友,将增强学习的原理讲解的非常清晰
深度增强学习(DRL)漫谈 - 从DQN到AlphaGo
这篇文章详细描写了 DQN 的演变过程,建议先看看
目录:
Deep Q-Network 学习笔记(一)—— Q-Learning
Deep Q-Network 学习笔记(二)—— Q-Learning与神经网络结合使用
这里将使用 tensorflow 框架重写上一篇的示例。
一、思路
Q-Learning与神经网络结合使用就是 Deep Q-Network,简称 DQN。在现实中,状态的数量极多,并且需要人工去设计特征,而且一旦特征设计不好,则得不到想要的结果。
神经网络正是能处理解决这个问题,取代原来 Q 表的功能。
当神经网络与Q-Learning结合使用的时候,又会碰到几个问题:
1.loss 要怎么计算?
增强学习是试错学习(Trail-and-error),由于没有直接的指导信息,智能体要以不断与环境进行交互,通过试错的方式来获得最佳策略。
Q-Learning正是其中的一种,所以Q值表中表示的是当前已学习到的经验。而根据公式计算出的 Q 值是智能体通过与环境交互及自身的经验总结得到的一个分数(即:目标 Q 值)。
最后使用目标 Q 值(target_q)去更新原来旧的 Q 值(q)。
而目标 Q 值与旧的 Q 值的对应关系,正好是监督学习神经网络中结果值与输出值的对应关系。
所以,loss = (target_q - q)^2
即:整个训练过程其实就是 Q 值(q)向目标 Q 值(target_q)逼近的过程。
2.训练样本哪来?
在 DQN 中有 Experience Replay 的概念,就是经验回放。
就是先让智能体去探索环境,将经验(记忆)池累积到一定程度,在随机抽取出一批样本进行训练。
为什么要随机抽取?因为智能体去探索环境时采集到的样本是一个时间序列,样本之间具有连续性,如果每次得到样本就更新Q值,受样本分布影响,会对收敛造成影响。
从现在开始,一定要理清楚算法的所有思路,比如什么时候该做什么,怎么随机选择动作,神经网络的参数是否调试完成等等,各种问题调试都没结果的,就因为这个卡在这里大半个星期才搞定。
二、模拟流程
1.随机初始化一个状态 s,初始化记忆池,设置观察值。
2.循环遍历(是永久遍历还是只遍历一定次数这个自己设置):
(1)根据策略选择一个行为(a)。
(2)执行该行动(a),得到奖励(r)、执行该行为后的状态 s`和游戏是否结束 done。
(3)保存 s, a, r, s`, done 到记忆池里。
(4)判断记忆池里的数据是否足够(即:记忆池里的数据数量是否超过设置的观察值),如果不够,则转到(5)步。
① 在记忆池里随机抽取出一部分数据做为训练样本。
② 将所有训练样本的 s`做为神经网络的输入值,进行批量处理,得到 s`状态下每个行为的 q 值的表。
③ 根据公式计算出 q 值表对应的 target_q 值表。
公式:Q(s, a) = r + Gamma * Max[Q(s`, all actions)]
④ 使用 q 与 target_q 训练神经网络。
(5)判断游戏是否结束。
① 游戏结束,给 s 随机设置一个状态。
① 未结束,则当前状态 s 更新为 s`。
三、代码实现
首先,创建一个类来实现 DQN。
import tensorflow as tf import numpy as np from collections import deque import random class DeepQNetwork: r = np.array([[-1, -1, -1, -1, 0, -1], [-1, -1, -1, 0, -1, 100.0], [-1, -1, -1, 0, -1, -1], [-1, 0, 0, -1, 0, -1], [0, -1, -1, 1, -1, 100], [-1, 0, -1, -1, 0, 100], ]) # 执行步数。 step_index = 0 # 状态数。 state_num = 6 # 动作数。 action_num = 6 # 训练之前观察多少步。 OBSERVE = 1000. # 选取的小批量训练样本数。 BATCH = 20 # epsilon 的最小值,当 epsilon 小于该值时,将不在随机选择行为。 FINAL_EPSILON = 0.0001 # epsilon 的初始值,epsilon 逐渐减小。 INITIAL_EPSILON = 0.1 # epsilon 衰减的总步数。 EXPLORE = 3000000. # 探索模式计数。 epsilon = 0 # 训练步数统计。 learn_step_counter = 0 # 学习率。 learning_rate = 0.001 # γ经验折损率。 gamma = 0.9 # 记忆上限。 memory_size = 5000 # 当前记忆数。 memory_counter = 0 # 保存观察到的执行过的行动的存储器,即:曾经经历过的记忆。 replay_memory_store = deque() # 生成一个状态矩阵(6 X 6),每一行代表一个状态。 state_list = None # 生成一个动作矩阵。 action_list = None # q_eval 网络。 q_eval_input = None action_input = None q_target = None q_eval = None predict = None loss = None train_op = None cost_his = None reward_action = None # tensorflow 会话。 session = None def __init__(self, learning_rate=0.001, gamma=0.9, memory_size=5000): self.learning_rate = learning_rate self.gamma = gamma self.memory_size = memory_size # 初始化成一个 6 X 6 的状态矩阵。 self.state_list = np.identity(self.state_num) # 初始化成一个 6 X 6 的动作矩阵。 self.action_list = np.identity(self.action_num) # 创建神经网络。 self.create_network() # 初始化 tensorflow 会话。 self.session = tf.InteractiveSession() # 初始化 tensorflow 参数。 self.session.run(tf.initialize_all_variables()) # 记录所有 loss 变化。 self.cost_his = [] def create_network(self): """ 创建神经网络。 :return: """ pass def select_action(self, state_index): """ 根据策略选择动作。 :param state_index: 当前状态。 :return: """ pass def save_store(self, current_state_index, current_action_index, current_reward, next_state_index, done): """ 保存记忆。 :param current_state_index: 当前状态 index。 :param current_action_index: 动作 index。 :param current_reward: 奖励。 :param next_state_index: 下一个状态 index。 :param done: 是否结束。 :return: """ pass def step(self, state, action): """ 执行动作。 :param state: 当前状态。 :param action: 执行的动作。 :return: """ pass def experience_replay(self): """ 记忆回放。 :return: """ pass def train(self): """ 训练。 :return: """ pass def pay(self): """ 运行并测试。 :return: """ pass if __name__ == "__main__": q_network = DeepQNetwork() q_network.pay()
1.将状态与动作初始化成以下矩阵,以方便处理。
图 3.1
四、创建神经网络
然后,创建一个神经网络,并使用该神经网络来替换掉 Q 值表(上一篇中的 Q 矩阵)
神经网络的输入是 Agent 当前的状态,输出是 Agent 当前状态可以执行的动作的 Q 值表。
由于总共有 6 个状态和 6 种动作,所以,这里将创建一个简单 3 层的神经网络,输入层的参数是 6 个和输出层输出 6 个值,运行并调试好参数,确认能正常运行。
测试代码:
import tensorflow as tf import numpy as np input_num = 6 output_num = 6 x_data = np.linspace(-1, 1, 300).reshape((-1, input_num)) # 转为列向量 noise = np.random.normal(0, 0.05, x_data.shape) y_data = np.square(x_data) + 0.5 + noise xs = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, input_num]) # 样本数未知,特征数为 6,占位符最后要以字典形式在运行中填入 ys = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, output_num]) neuro_layer_1 = 3 w1 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([input_num, neuro_layer_1])) b1 = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1, neuro_layer_1]) + 0.1) l1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(xs, w1) + b1) neuro_layer_2 = output_num w2 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([neuro_layer_1, neuro_layer_2])) b2 = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1, neuro_layer_2]) + 0.1) l2 = tf.matmul(l1, w2) + b2 # reduction_indices=[0] 表示将列数据累加到一起。 # reduction_indices=[1] 表示将行数据累加到一起。 loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.reduce_sum(tf.square((ys - l2)), reduction_indices=[1])) # 选择梯度下降法 train = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.001).minimize(loss) # train = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(1e-1).minimize(loss) init = tf.initialize_all_variables() sess = tf.Session() sess.run(init) for i in range(100000): sess.run(train, feed_dict={xs: x_data, ys: y_data}) if i % 1000 == 0: print(sess.run(loss, feed_dict={xs: x_data, ys: y_data}))
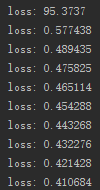
执行后 loss 一直持续减少,确认该神经网络正常运行就行了,注意调好学习率和神经网络的层数及神经元个数。
确认正常后,开始实现 DeepQNetwork 类中的 def create_network(self) 函数:
def create_network(self): """ 创建神经网络。 :return: """ self.q_eval_input = tf.placeholder(shape=[None, self.state_num], dtype=tf.float32) self.action_input = tf.placeholder(shape=[None, self.action_num], dtype=tf.float32) self.q_target = tf.placeholder(shape=[None], dtype=tf.float32) neuro_layer_1 = 3 w1 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([self.state_num, neuro_layer_1])) b1 = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1, neuro_layer_1]) + 0.1) l1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(self.q_eval_input, w1) + b1) w2 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([neuro_layer_1, self.action_num])) b2 = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1, self.action_num]) + 0.1) self.q_eval = tf.matmul(l1, w2) + b2 # 取出当前动作的得分。 self.reward_action = tf.reduce_sum(tf.multiply(self.q_eval, self.action_input), reduction_indices=1) self.loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square((self.q_target - self.reward_action))) self.train_op = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(self.learning_rate).minimize(self.loss) self.predict = tf.argmax(self.q_eval, 1)
这里说明一下 loss 的计算,由于状态是根据图 3.1 的矩阵的方式显示的,比如,当前状态如果是在 1 号房间,
则输入参数(q_eval_input)的值是:[[0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0]]
由于 Agent 执行了动作 3,也就是移动到了 3 号房间,
所以 Agent 的动作参数(action_input)的值是:[[0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0]]
因为神经网络的输出结果(q_eval)是 Agent 当前状态下可执行的动作的价值,由于每个状态都有 6 个动作,而状态数也是 6 个,所以
神经网络的输出结果(q_eval)与输入参数是一样的,所以输出的格式也一样,
假设输出结果(q_eval)是:[[0.81, 0.5, 0.24, 0.513, 0.9, 0.71]]
tf.multiply(self.q_eval, self.action_input)
就是矩阵的点积,也就是每个元素分别相乘。
这里表示的就是获得 Agent 执行了 action_input 的价值(Q 值)。
也就是 q = q_eval * action_input = [[0, 0, 0, 0.513, 0, 0]]
所以:
self.reward_action = tf.reduce_sum(tf.multiply(self.q_eval, self.action_input), reduction_indices=1)
也就相当于:q = SUM(q_eval * action_input) = SUM([[0, 0, 0, 0.513, 0, 0, 0]]) = 0.513
即:Agent 在 1 号房间执行移动到 3 号房间动作时,神经网络给出的价值(q 值)是 0.513 分
而 q_target 在前面也提过,是 Agent 经过环境体验后,根据公式计算出来的目标 q 值,假设该值是 1.03 分
所以:
self.loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square((self.q_target - self.reward_action)))
就相当于:
loss = ((1.03 - 0.513)^2) / 1 = 0.267289
然后,learning_rate 也就是学习率,经过调试,这里是设置成 0.001 比较好。
五、搜索动作策略
这里是 DQN 需要注意的地方之一,这里的方法将直接影响到 DQN 是否可以收敛,或者是否是陷入局部最小值等情况。
现在在这里选择了最直接的方法,使用随机的方式来选择行动。
使用随机的方式来选择行动,可以让 Agent 能得到更多的探索机会,这样在训练时才能有效的跳出陷入局部最小值的情况,当训练时,可以减少探索机会。
流程如下:
1.初始化 epsilon 变量,并设置它的最小值(FINAL_EPSILON)与最大值(INITIAL_EPSILON),并将 epsilon 的初始值设置成 INITIAL_EPSILON。
2.随机生成一个数 n。
3.判断 n 是否小于 epsilon,如果 n 小于 epsilon 则转到 4,否则转到 5。
4.使用随机策略(增加探索机会),转到 6。
随机选择一个在 Agent 当前状态下可以执行的动作。
5.使用神经网络直接计算出结果(实际应用时也是应用这方法),转到6。
神经网络会输出在当前状态下所有动作的 Q 值,选择其中最有价值(Q 值最大)的动作返回。
6.判断是否开始训练,如果是,则逐步减少 epsilon 来减少探索机会,否则跳过。
开始实现 DeepQNetwork 类中的 def select_action(self, state_index) 函数:
def select_action(self, state_index): """ 根据策略选择动作。 :param state_index: 当前状态。 :return: """ current_state = self.state_list[state_index:state_index + 1] if np.random.uniform() < self.epsilon: current_action_index = np.random.randint(0, self.action_num) else: actions_value = self.session.run(self.q_eval, feed_dict={self.q_eval_input: current_state}) action = np.argmax(actions_value) current_action_index = action # 开始训练后,在 epsilon 小于一定的值之前,将逐步减小 epsilon。 if self.step_index > self.OBSERVE and self.epsilon > self.FINAL_EPSILON: self.epsilon -= (self.INITIAL_EPSILON - self.FINAL_EPSILON) / self.EXPLORE return current_action_index
六、保存记忆
这里使用了一个先进先出的队列,设置好队列的 size,直接将“当前状态”、“执行动作”、“奖励分数”、“下一个状态”和“游戏是否结束”保存进去就行了。
开始实现 DeepQNetwork 类中的 def save_store(self, current_state_index, current_action_index, current_reward, next_state_index, done) 函数:
def save_store(self, current_state_index, current_action_index, current_reward, next_state_index, done): """ 保存记忆。 :param current_state_index: 当前状态 index。 :param current_action_index: 动作 index。 :param current_reward: 奖励。 :param next_state_index: 下一个状态 index。 :param done: 是否结束。 :return: """ current_state = self.state_list[current_state_index:current_state_index + 1] current_action = self.action_list[current_action_index:current_action_index + 1] next_state = self.state_list[next_state_index:next_state_index + 1] # 记忆动作(当前状态, 当前执行的动作, 当前动作的得分,下一个状态)。 self.replay_memory_store.append(( current_state, current_action, current_reward, next_state, done)) # 如果超过记忆的容量,则将最久远的记忆移除。 if len(self.replay_memory_store) > self.memory_size: self.replay_memory_store.popleft() self.memory_counter += 1
七、执行动作
这里就是取得游戏是否结束状态,动作奖励和下一个状态并返回就可以了。
开始实现 DeepQNetwork 类中的 def step(self, state, action) 函数:
def step(self, state, action): """ 执行动作。 :param state: 当前状态。 :param action: 执行的动作。 :return: """ reward = self.r[state][action] next_state = action done = False if action == 5: done = True return next_state, reward, done
八、记忆回放
这是 DQN 的重点之一,在记忆池里随机抽取出一小批的数据当做训练样本,并计算出目标 Q 值来训练神经网络。
流程如下:
1. 初始化时先设置抽取的样本数。
2. 从记忆池里随机抽取出一批样本。
3. 由于每条样本中,都保存有当时的数据(当前状态,动作,奖励分数,下一个状态,是否结束),所以,为了计算出这些样本数据的目标 Q 值,就必须先取出样本中“下一个状态(next_state)”(注意:这里取到的是所有这批样本的“下一个状态”的列表!)。
4. 将 next_state (这是批数据!!)当做参数传入神经网络,得到 Agent 在 next_state 状态时所有可执行的动作的 Q 值表(q_next),q_next 表示这批样本中所有的 next_state 状态的 Q 值表的集合。
5. 现在,已经拿到了
Agent 当时的状态(state),
当时的动作(action),
当时的状态(state)下执行动作(action)得到的奖励R(state, action),
当时的状态(state)下执行动作(action)后的状态(next_state)下所有可执行的动作的 Q 值表(q_next)。
现在就可以使用上面提到的公式来计算出目标 Q 值Q(state, action)。
Q(state, action) = R(state, action) + Gamma * Max{q_next}
6. 根据游戏状态判断,当前选择的动作是否是违规(不可执行)的动作,如果是,则不做经验计算,直接扣除分数,否则使用上面的公式来计算出Q(state, action)。违规的动作,在搜索动作的时候,是不应该能选择出来的,即:能走到这一步的都必须是有效动作!
7. 将计算得到的所有样本的 Q(state, action) 保存到集合中(q_target)。
8. 将这批样本的当前状态的集合,动作的集合与 q_target 传入神经网络并进行训练。
特别注意第 6 条的内容,如果这里处理不好,一样会得不到结果的,具体原因可以看上一篇 。
开始实现 DeepQNetwork 类中的 def experience_replay(self)函数:
def experience_replay(self): """ 记忆回放。 :return: """ # 随机选择一小批记忆样本。 batch = self.BATCH if self.memory_counter > self.BATCH else self.memory_counter minibatch = random.sample(self.replay_memory_store, batch) batch_state = None batch_action = None batch_reward = None batch_next_state = None batch_done = None for index in range(len(minibatch)): if batch_state is None: batch_state = minibatch[index][0] elif batch_state is not None: batch_state = np.vstack((batch_state, minibatch[index][0])) if batch_action is None: batch_action = minibatch[index][1] elif batch_action is not None: batch_action = np.vstack((batch_action, minibatch[index][1])) if batch_reward is None: batch_reward = minibatch[index][2] elif batch_reward is not None: batch_reward = np.vstack((batch_reward, minibatch[index][2])) if batch_next_state is None: batch_next_state = minibatch[index][3] elif batch_next_state is not None: batch_next_state = np.vstack((batch_next_state, minibatch[index][3])) if batch_done is None: batch_done = minibatch[index][4] elif batch_done is not None: batch_done = np.vstack((batch_done, minibatch[index][4])) # q_next:下一个状态的 Q 值。 q_next = self.session.run([self.q_eval], feed_dict={self.q_eval_input: batch_next_state}) q_target = [] for i in range(len(minibatch)): # 当前即时得分。 current_reward = batch_reward[i][0] # # 游戏是否结束。 # current_done = batch_done[i][0] # 更新 Q 值。 q_value = current_reward + self.gamma * np.max(q_next[0][i]) # 当得分小于 -1 时,表示走了不可走的位置。 if current_reward <= -1: q_target.append(current_reward) else: q_target.append(q_value) _, cost, reward = self.session.run([self.train_op, self.loss, self.reward_action], feed_dict={self.q_eval_input: batch_state, self.action_input: batch_action, self.q_target: q_target}) self.cost_his.append(cost) # if self.step_index % 1000 == 0: # print("loss:", cost) self.learn_step_counter += 1
九、训练
这部分在前面都分析过了,看看就行了。
实现 DeepQNetwork 类中的 def train(self)函数:
def train(self): """ 训练。 :return: """ # 初始化当前状态。 current_state = np.random.randint(0, self.action_num - 1) self.epsilon = self.INITIAL_EPSILON while True: # 选择动作。 action = self.select_action(current_state) # 执行动作,得到:下一个状态,执行动作的得分,是否结束。 next_state, reward, done = self.step(current_state, action) # 保存记忆。 self.save_store(current_state, action, reward, next_state, done) # 先观察一段时间累积足够的记忆在进行训练。 if self.step_index > self.OBSERVE: self.experience_replay() if self.step_index > 10000: break if done: current_state = np.random.randint(0, self.action_num - 1) else: current_state = next_state self.step_index += 1
十、执行并测试训练结果
实现 DeepQNetwork 类中的 def pay(self)函数:
def pay(self): """ 运行并测试。 :return: """ self.train() # 显示 R 矩阵。 print(self.r) for index in range(5): start_room = index print("#############################", "Agent 在", start_room, "开始行动", "#############################") current_state = start_room step = 0 target_state = 5 while current_state != target_state: out_result = self.session.run(self.q_eval, feed_dict={ self.q_eval_input: self.state_list[current_state:current_state + 1]}) next_state = np.argmax(out_result[0]) print("Agent 由", current_state, "号房间移动到了", next_state, "号房间") current_state = next_state step += 1 print("Agent 在", start_room, "号房间开始移动了", step, "步到达了目标房间 5") print("#############################", "Agent 在", 5, "结束行动", "#############################")
十一、完整源码
import tensorflow as tf import numpy as np from collections import deque import random class DeepQNetwork: r = np.array([[-1, -1, -1, -1, 0, -1], [-1, -1, -1, 0, -1, 100.0], [-1, -1, -1, 0, -1, -1], [-1, 0, 0, -1, 0, -1], [0, -1, -1, 1, -1, 100], [-1, 0, -1, -1, 0, 100], ]) # 执行步数。 step_index = 0 # 状态数。 state_num = 6 # 动作数。 action_num = 6 # 训练之前观察多少步。 OBSERVE = 1000. # 选取的小批量训练样本数。 BATCH = 20 # epsilon 的最小值,当 epsilon 小于该值时,将不在随机选择行为。 FINAL_EPSILON = 0.0001 # epsilon 的初始值,epsilon 逐渐减小。 INITIAL_EPSILON = 0.1 # epsilon 衰减的总步数。 EXPLORE = 3000000. # 探索模式计数。 epsilon = 0 # 训练步数统计。 learn_step_counter = 0 # 学习率。 learning_rate = 0.001 # γ经验折损率。 gamma = 0.9 # 记忆上限。 memory_size = 5000 # 当前记忆数。 memory_counter = 0 # 保存观察到的执行过的行动的存储器,即:曾经经历过的记忆。 replay_memory_store = deque() # 生成一个状态矩阵(6 X 6),每一行代表一个状态。 state_list = None # 生成一个动作矩阵。 action_list = None # q_eval 网络。 q_eval_input = None action_input = None q_target = None q_eval = None predict = None loss = None train_op = None cost_his = None reward_action = None # tensorflow 会话。 session = None def __init__(self, learning_rate=0.001, gamma=0.9, memory_size=5000): self.learning_rate = learning_rate self.gamma = gamma self.memory_size = memory_size # 初始化成一个 6 X 6 的状态矩阵。 self.state_list = np.identity(self.state_num) # 初始化成一个 6 X 6 的动作矩阵。 self.action_list = np.identity(self.action_num) # 创建神经网络。 self.create_network() # 初始化 tensorflow 会话。 self.session = tf.InteractiveSession() # 初始化 tensorflow 参数。 self.session.run(tf.initialize_all_variables()) # 记录所有 loss 变化。 self.cost_his = [] def create_network(self): """ 创建神经网络。 :return: """ self.q_eval_input = tf.placeholder(shape=[None, self.state_num], dtype=tf.float32) self.action_input = tf.placeholder(shape=[None, self.action_num], dtype=tf.float32) self.q_target = tf.placeholder(shape=[None], dtype=tf.float32) neuro_layer_1 = 3 w1 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([self.state_num, neuro_layer_1])) b1 = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1, neuro_layer_1]) + 0.1) l1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(self.q_eval_input, w1) + b1) w2 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([neuro_layer_1, self.action_num])) b2 = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1, self.action_num]) + 0.1) self.q_eval = tf.matmul(l1, w2) + b2 # 取出当前动作的得分。 self.reward_action = tf.reduce_sum(tf.multiply(self.q_eval, self.action_input), reduction_indices=1) self.loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square((self.q_target - self.reward_action))) self.train_op = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(self.learning_rate).minimize(self.loss) self.predict = tf.argmax(self.q_eval, 1) def select_action(self, state_index): """ 根据策略选择动作。 :param state_index: 当前状态。 :return: """ current_state = self.state_list[state_index:state_index + 1] if np.random.uniform() < self.epsilon: current_action_index = np.random.randint(0, self.action_num) else: actions_value = self.session.run(self.q_eval, feed_dict={self.q_eval_input: current_state}) action = np.argmax(actions_value) current_action_index = action # 开始训练后,在 epsilon 小于一定的值之前,将逐步减小 epsilon。 if self.step_index > self.OBSERVE and self.epsilon > self.FINAL_EPSILON: self.epsilon -= (self.INITIAL_EPSILON - self.FINAL_EPSILON) / self.EXPLORE return current_action_index def save_store(self, current_state_index, current_action_index, current_reward, next_state_index, done): """ 保存记忆。 :param current_state_index: 当前状态 index。 :param current_action_index: 动作 index。 :param current_reward: 奖励。 :param next_state_index: 下一个状态 index。 :param done: 是否结束。 :return: """ current_state = self.state_list[current_state_index:current_state_index + 1] current_action = self.action_list[current_action_index:current_action_index + 1] next_state = self.state_list[next_state_index:next_state_index + 1] # 记忆动作(当前状态, 当前执行的动作, 当前动作的得分,下一个状态)。 self.replay_memory_store.append(( current_state, current_action, current_reward, next_state, done)) # 如果超过记忆的容量,则将最久远的记忆移除。 if len(self.replay_memory_store) > self.memory_size: self.replay_memory_store.popleft() self.memory_counter += 1 def step(self, state, action): """ 执行动作。 :param state: 当前状态。 :param action: 执行的动作。 :return: """ reward = self.r[state][action] next_state = action done = False if action == 5: done = True return next_state, reward, done def experience_replay(self): """ 记忆回放。 :return: """ # 随机选择一小批记忆样本。 batch = self.BATCH if self.memory_counter > self.BATCH else self.memory_counter minibatch = random.sample(self.replay_memory_store, batch) batch_state = None batch_action = None batch_reward = None batch_next_state = None batch_done = None for index in range(len(minibatch)): if batch_state is None: batch_state = minibatch[index][0] elif batch_state is not None: batch_state = np.vstack((batch_state, minibatch[index][0])) if batch_action is None: batch_action = minibatch[index][1] elif batch_action is not None: batch_action = np.vstack((batch_action, minibatch[index][1])) if batch_reward is None: batch_reward = minibatch[index][2] elif batch_reward is not None: batch_reward = np.vstack((batch_reward, minibatch[index][2])) if batch_next_state is None: batch_next_state = minibatch[index][3] elif batch_next_state is not None: batch_next_state = np.vstack((batch_next_state, minibatch[index][3])) if batch_done is None: batch_done = minibatch[index][4] elif batch_done is not None: batch_done = np.vstack((batch_done, minibatch[index][4])) # q_next:下一个状态的 Q 值。 q_next = self.session.run([self.q_eval], feed_dict={self.q_eval_input: batch_next_state}) q_target = [] for i in range(len(minibatch)): # 当前即时得分。 current_reward = batch_reward[i][0] # # 游戏是否结束。 # current_done = batch_done[i][0] # 更新 Q 值。 q_value = current_reward + self.gamma * np.max(q_next[0][i]) # 当得分小于 -1 时,表示走了不可走的位置。 if current_reward <= -1: q_target.append(current_reward) else: q_target.append(q_value) _, cost, reward = self.session.run([self.train_op, self.loss, self.reward_action], feed_dict={self.q_eval_input: batch_state, self.action_input: batch_action, self.q_target: q_target}) self.cost_his.append(cost) # if self.step_index % 1000 == 0: # print("loss:", cost) self.learn_step_counter += 1 def train(self): """ 训练。 :return: """ # 初始化当前状态。 current_state = np.random.randint(0, self.action_num - 1) self.epsilon = self.INITIAL_EPSILON while True: # 选择动作。 action = self.select_action(current_state) # 执行动作,得到:下一个状态,执行动作的得分,是否结束。 next_state, reward, done = self.step(current_state, action) # 保存记忆。 self.save_store(current_state, action, reward, next_state, done) # 先观察一段时间累积足够的记忆在进行训练。 if self.step_index > self.OBSERVE: self.experience_replay() if self.step_index > 10000: break if done: current_state = np.random.randint(0, self.action_num - 1) else: current_state = next_state self.step_index += 1 def pay(self): """ 运行并测试。 :return: """ self.train() # 显示 R 矩阵。 print(self.r) for index in range(5): start_room = index print("#############################", "Agent 在", start_room, "开始行动", "#############################") current_state = start_room step = 0 target_state = 5 while current_state != target_state: out_result = self.session.run(self.q_eval, feed_dict={ self.q_eval_input: self.state_list[current_state:current_state + 1]}) next_state = np.argmax(out_result[0]) print("Agent 由", current_state, "号房间移动到了", next_state, "号房间") current_state = next_state step += 1 print("Agent 在", start_room, "号房间开始移动了", step, "步到达了目标房间 5") print("#############################", "Agent 在", 5, "结束行动", "#############################") if __name__ == "__main__": q_network = DeepQNetwork() q_network.pay()